Recombinant Mouse Coagulation factor II/F2 protein (His Tag)
Species
Mouse
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
His Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg0943
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Mouse Coagulation factor II protein Gln25-Gly618 (Accession# P19221) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 14061 |
| Accession | P19221 |
| PredictedSize | 69.0 kDa |
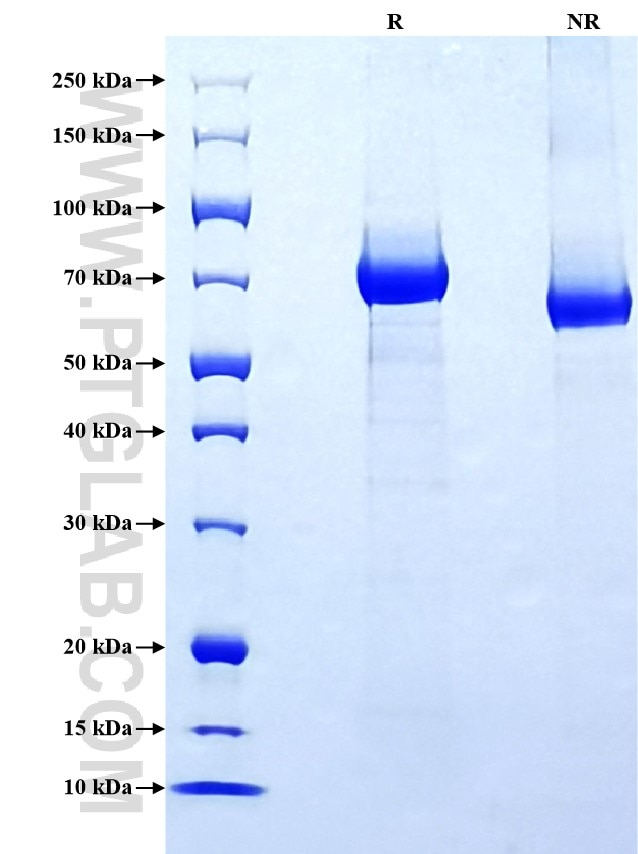
| SDS-PAGE | 65-80 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Normal blood coagulation is a complex process, involving a cascade of activation of different plasma proteins, ultimately resulting in the formation of a clot, called fibrin. Coagulation Factor II (F2), also known as prothrombin or factor II, is one of the components of this chain of plasma proteins involved in blood coagulation. Prothrombin is the precursor of thrombin, which is essential in the processes of hemostasis and thrombosis. Prothrombin circulates in the bloodstream in an inactive form until an injury occurs. In response to that, prothrombin is converted to its active form, thrombin. Thrombin next converts a protein called fibrinogen into fibrin. Thrombin is also important for cell growth and division, tissue repair, and new blood vessel formation - angiogenesis.
References:
1. Akhavan S, et al. (2000). Thromb Haemost. 84(6):989-97. 2. Danckwardt S, et al.(2006). Acta Haematol.115(3-4):192-7. 3.Jayandharan G, et al.(2005). Journal of thrombosis and hemostasis. 3(7):1446-53. 4.McGlennen RC, et al. (2002). Arch Pathol Lab Med.126(11):1319-25.