Recombinant Mouse ICOS/CD278 protein (rFc Tag)
Species
Mouse
Purity
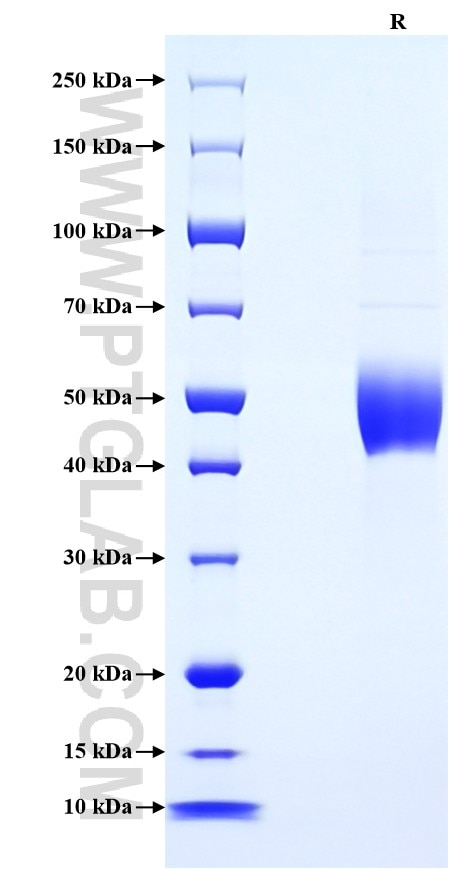
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg3198
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Mouse ICOS protein Glu21-Leu144 (Accession# Q9WVS0) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 54167 |
| Accession | Q9WVS0 |
| PredictedSize | 40.5 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 42-55 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Inducible T-cell costimulator (ICOS) is an activation-dependent, T cell-specific cell surface molecule related to CD28 and CTLA-4. ICOS enhances all basic T-cell responses to a foreign antigen, namely proliferation, secretion of lymphokines, up-regulation of molecules that mediate cell-cell interaction, and effective help for antibody secretion by B-cells. ICOS has to be de novo induced on the T-cell surface, does not upregulate the production of interleukin-2, but superinduces the synthesis of interleukin-10, a B-cell-differentiation factor. ICOS activated T-cells, Highly expressed on tonsillar T-cells, are closely associated with B-cells in the apical light zone of germinal centers, the site of terminal B-cell maturation. It is expressed at lower levels in thymus, lung, lymph node, and peripheral blood leukocytes. It is also expressed in the medulla of the fetal and newborn thymus.
References:
1. Beier KC, et al. (2000). Eur J Immunol. 30(12):3707-17 2. Hutloff A, et al. (1999). Nature. 397(6716):263-266 3. Tezuka K, et al. (2000). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 276(1):335-345