Recombinant Mouse Transferrin R/CD71 protein (rFc Tag)
Species
Mouse
Purity
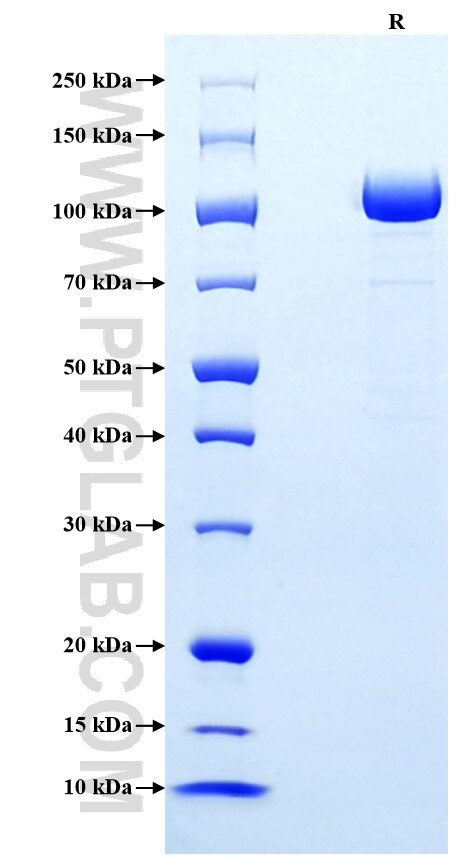
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg3385
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Mouse Transferrin R protein Cys89-Phe763 (Accession# Q62351) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the N-terminus. |
| GeneID | 22042 |
| Accession | Q62351 |
| PredictedSize | 103.1 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 95-125 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
The transferrin receptor is a membrane glycoprotein whose only clearly defined function is to mediate cellular uptake of iron from a plasma glycoprotein, transferrin. Iron uptake from transferrin involves the binding of transferrin to the transferrin receptor, internalization of transferrin within an endocytic vesicle by receptor-mediated endocytosis and the release of iron from the protein by a decrease in endosomal pH. With the exception of highly differentiated cells, transferrin receptors are probably expressed on all cells but their levels vary greatly. Transferrin receptors are highly expressed on immature erythroid cells, placental tissue, and rapidly dividing cells, both normal and malignant.
References:
1. Chiappelli F. et al. (2024) Bioinformation. 20(3):208-211. 2. D'Aprile S. et al. (2023) J Transl Med. 21(1):780. 3. Liu X. et al. (2023) Asian J Pharm SCI. 18(4):100826. 4. Grzywa T. et al. (2022) BLOOD. 140(Supple 1):8166-8167.