Tested Applications
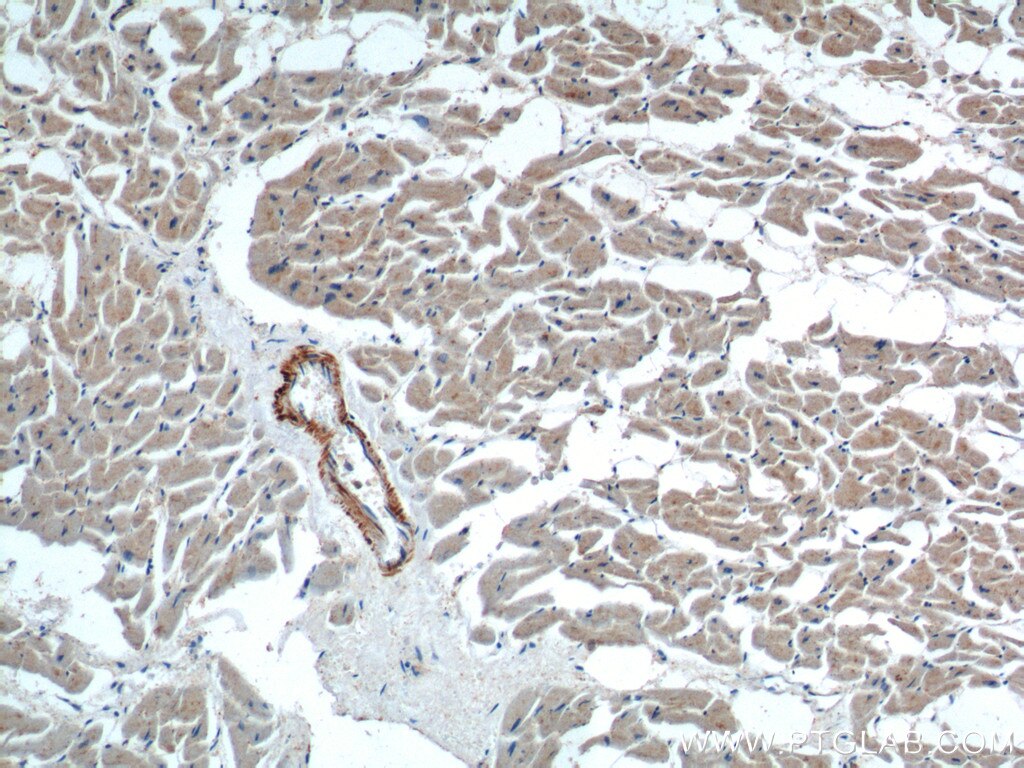
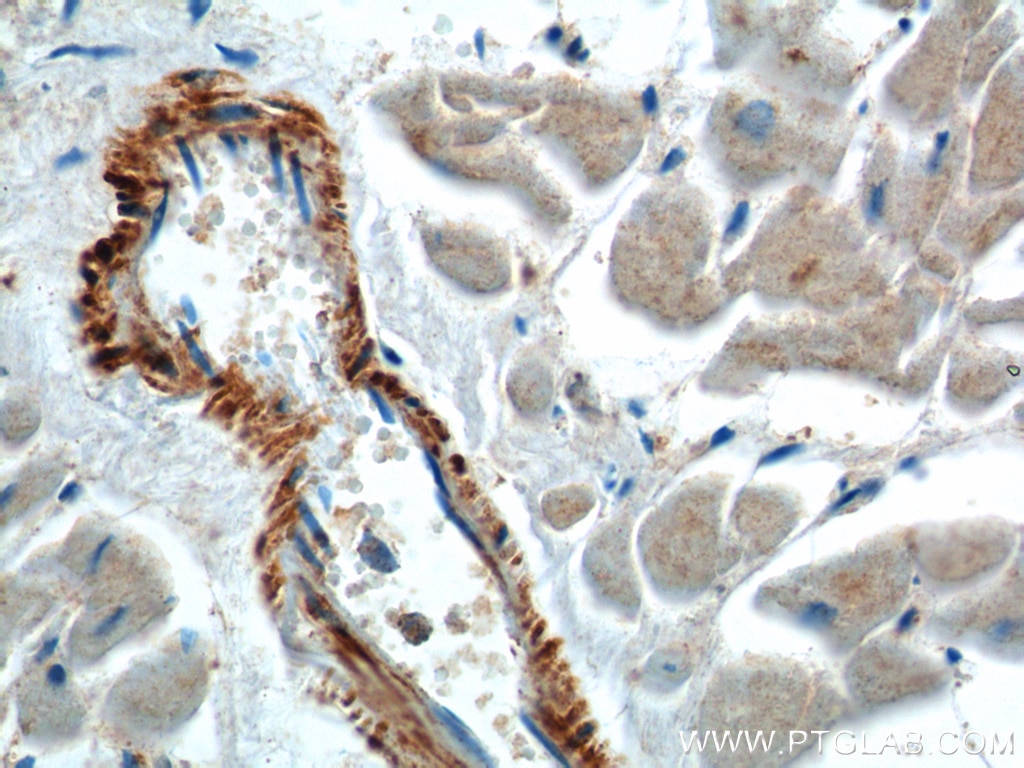
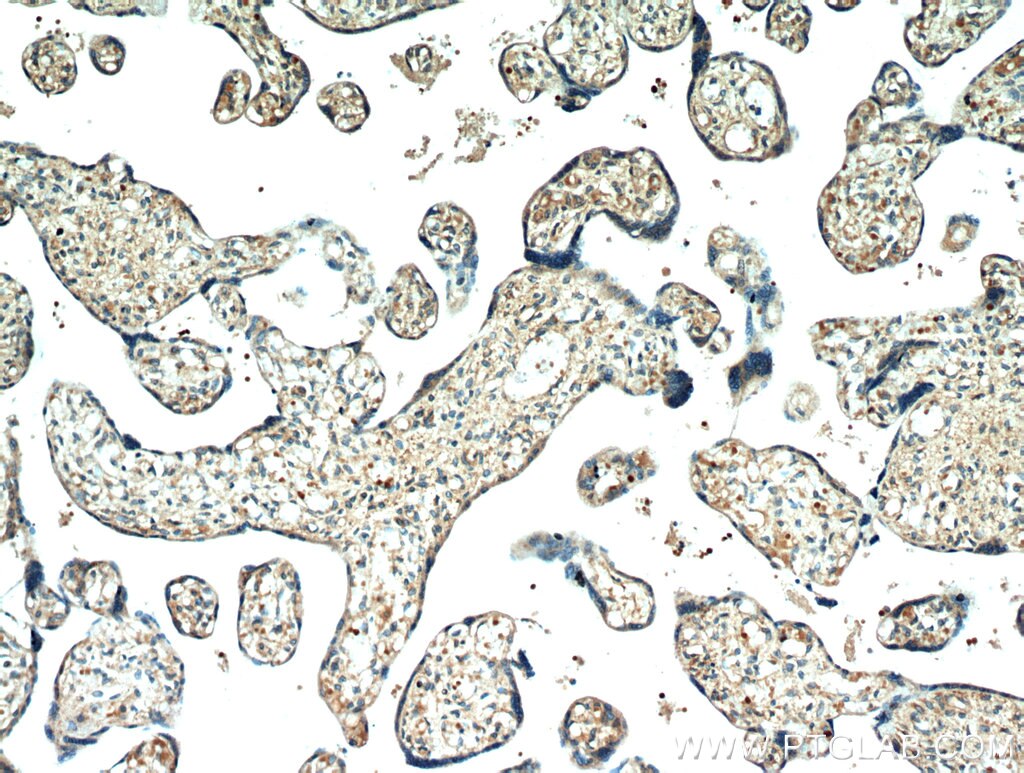
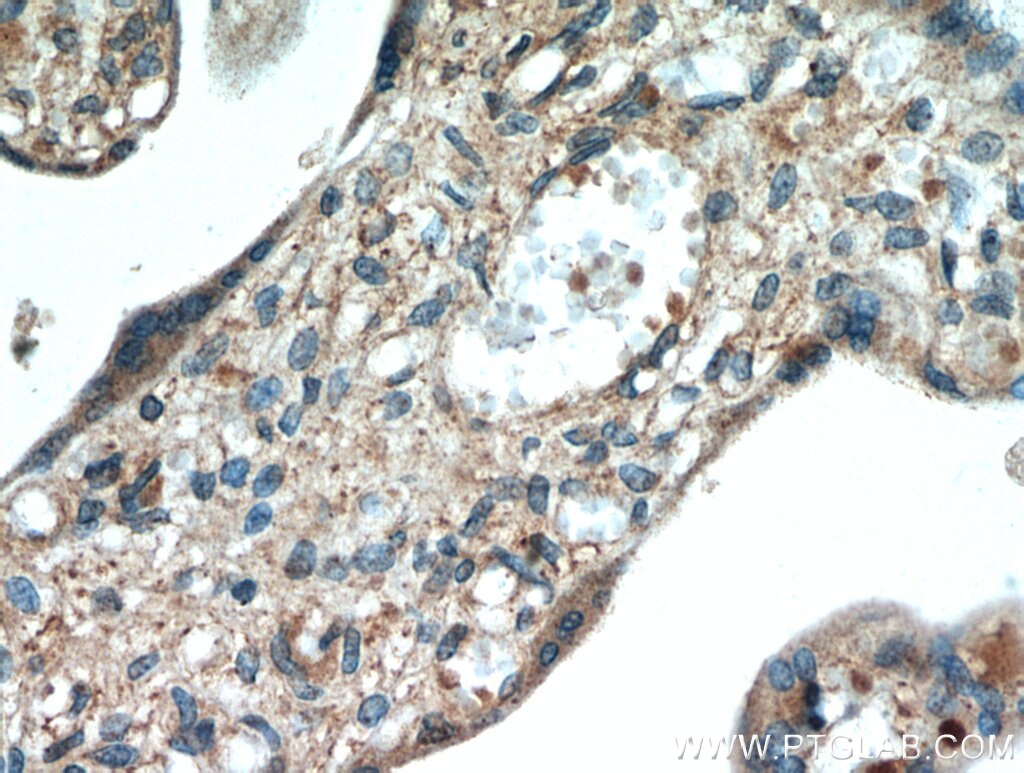
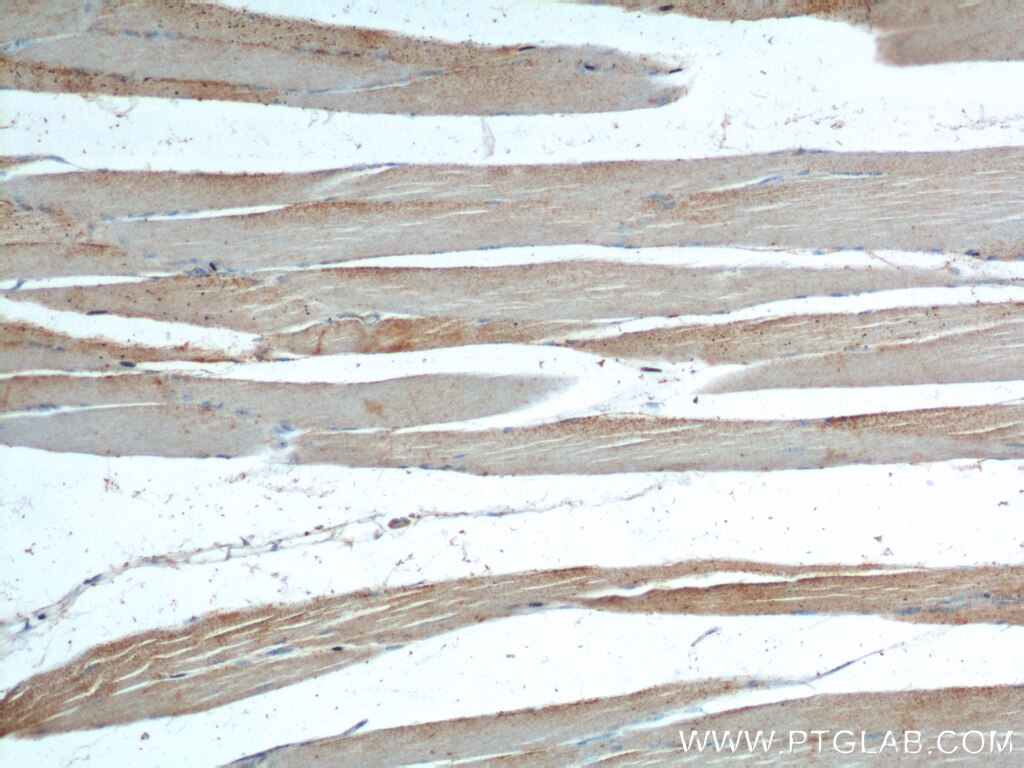
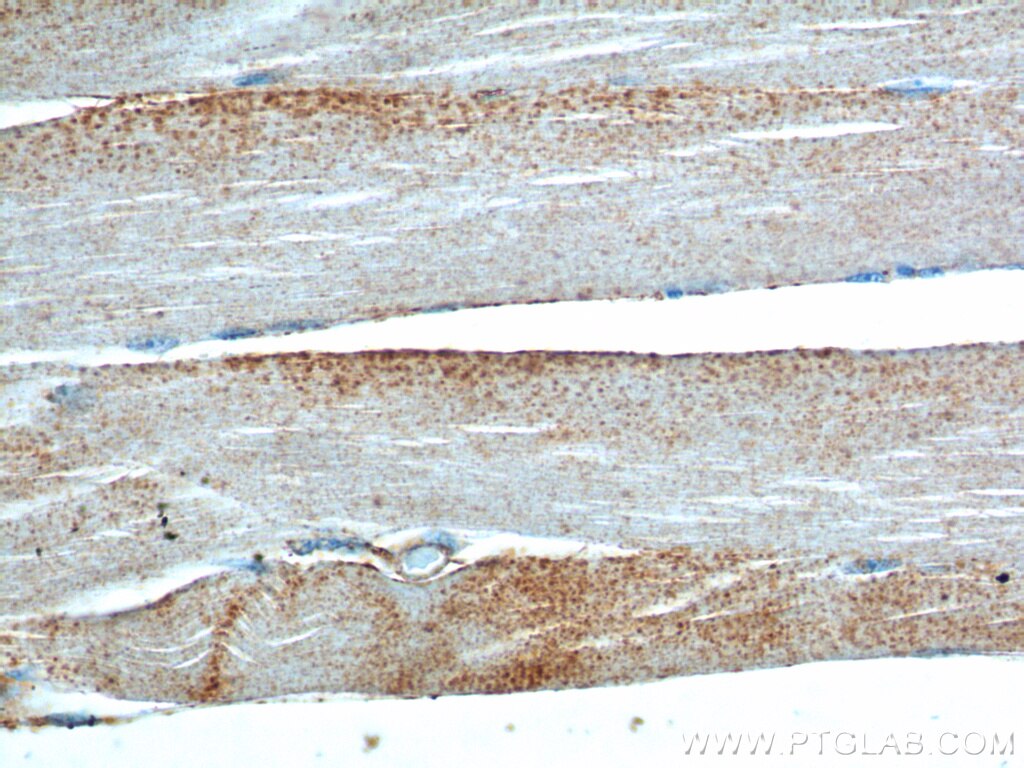
| Positive IHC detected in | human heart tissue, human placenta tissue, human skeletal muscle tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
20807-1-AP targets Neuron navigator 1 in IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag14747 Product name: Recombinant human NAV1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1359-1530 aa of BC007523 Sequence: LKVAPGPSSGSTPGQVPGSSALSSPRRSLGLALTHSFGPSLADTDLSPMDGISTCGPKEEVTLRVVVRMPPQHIIKGDLKQQEFFLGCSKVSGKVDWKMLDEAVFQVFKDYISKMDPASTLGLSTESIHGYSISHVKRVLDAEPPEMPPCRRGVNNISVSLKGLKEKCVDSL Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | neuron navigator 1 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 1877 aa, 202 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC007523 |
| Gene Symbol | NAV1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 89796 |
| RRID | AB_10732685 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q8NEY1 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Neuron navigator 1 (NAV1) gene encodes a large protein belongs to the Nav/unc-53 family and 7 isoforms of NAV1 are produced by alternative splicing. NAV1 is localized in cytoplasm and expressed at high levels in heart, skeletal muscle and placenta, and especially in neuronal growth cones. Besides its nucleotide binding activity, NAV1 interacts with tubulin and associates with a subset of microtubule plus end, therefore playing a role in neuronal migration.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for Neuron navigator 1 antibody 20807-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |