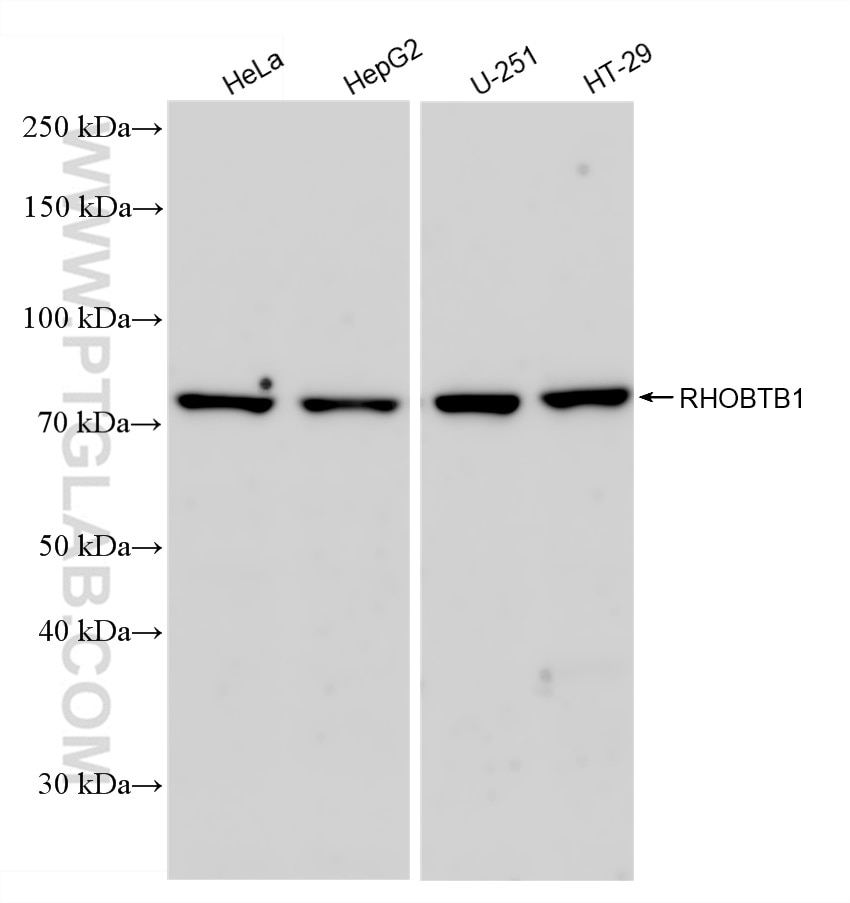
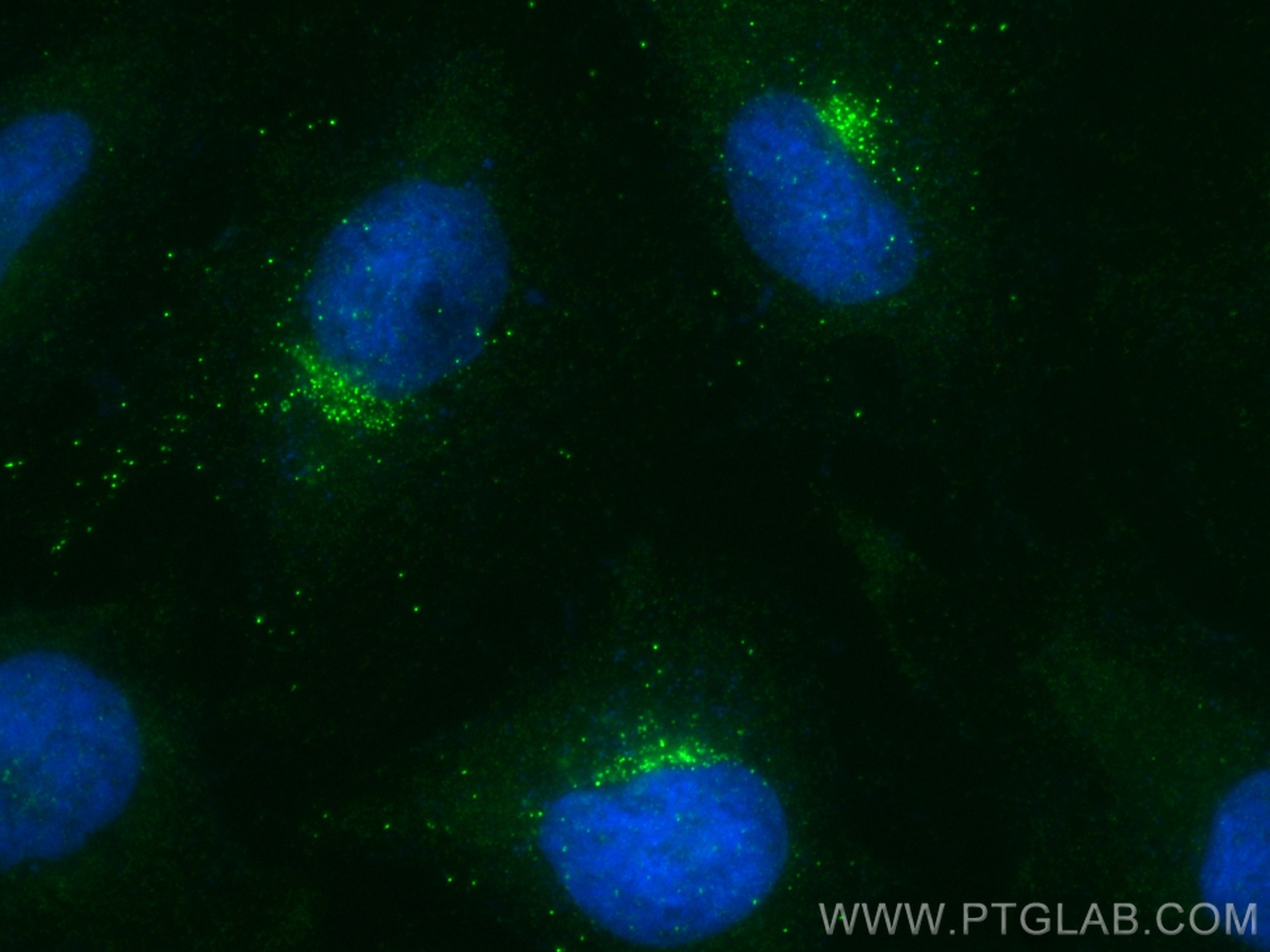
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | HeLa cells, HepG2 cells, U-251 cells, HT-29 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
83342-1-RR targets RHOBTB1 in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | RHOBTB1 fusion protein Ag3365 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | Rho-related BTB domain containing 1 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 696 aa, 79 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 79 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC032848 |
| Gene Symbol | RHOBTB1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 9886 |
| RRID | AB_3671003 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O94844 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Rho-related BTB domain containing protein 1 (RhoBTB1) is also named as KIAA0740. RhoBTB1 is an atypical Rho GTPase with two BTB domains in addition to its Rho domain. RhoBTB1 is a substrate for ROCK1, and mutation of putative phosphorylation sites reduces its association with Cullin3, a scaffold for ubiquitin ligases (PMID: 31431478). RHOBTB1 is a novel PPARγ gene target in vascular smooth muscle cells that mediates the protective effect of PPARγ by serving as a substrate adaptor between the Cullin-3 RING ubiquitin ligase and phosphodiesterase 5, thus restraining its activity through ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation (PMID: 31789920).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for RHOBTB1 antibody 83342-1-RR | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |