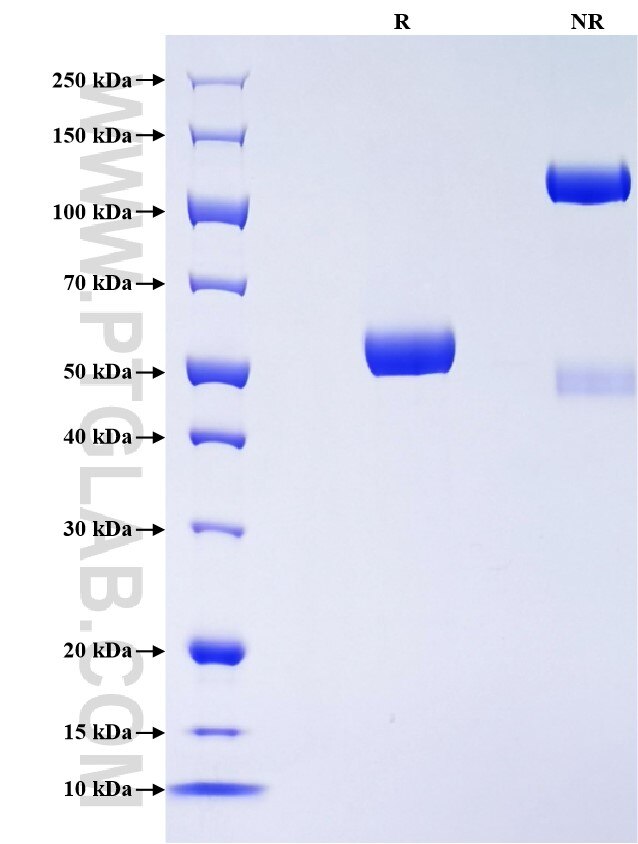
Recombinant Rat TIMP-1 protein (rFc Tag)
Species
Rat
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg3212
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Rat TIMP-1 protein Cys24-Ala217 (Accession# P30120) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 116510 |
| Accession | P30120 |
| PredictedSize | 47.8 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 50-60 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteases 1 (TIMP1) is named for its well established function of inhibiting the proteolytic activity of matrix metalloproteases (MMPs). The balance between the activities of MMPs and TIMPs is essential for extracellular matrix maintenance, remodeling, and turnover in physiological events. TIMP1 inhibits extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation mediated by MMPs. TIMP1 plays a crucial role in remodeling the ECM associated with ovulation, luteinization, and degeneration. TIMP1 has several MMP-independent functions such as promotion of cell proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis. As a soluble protein secreted into the extracellular environment, TIMP1 is found in most tissues and body fluids. TIMP1 expression can be induced in several cell types, mainly due to external stimuli, such as growth factors (β-FGF, PDGF, EGF), phorbol esters, serum, and cytokines (IL-6 and IL-1).
References:
1.Justo BL and Jasiulionis MG. (2021) Int J Mol Sci. 22(17):9319. 2.Schoeps B. et al. (2021) Cancer Res. 81(13):3568-3579. 3.Tan Y. et al. (2021) Biochem Pharmacol. 189:114085. 4.Hong L. et al. (2022) Arch Anim Breed. 65(1):105-111.