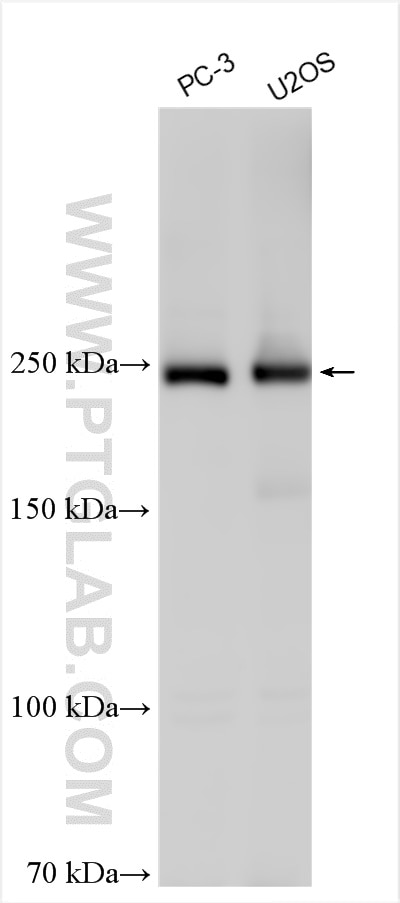
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | PC-3 cells, U2OS cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
31658-1-AP targets dysferlin in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | dysferlin fusion protein Ag35810 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | dysferlin, limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2B (autosomal recessive) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 237 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 240 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_001130455 |
| Gene Symbol | DYSF |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8291 |
| RRID | AB_3670065 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity Purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O75923 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Dysferlin, also known as FER1L1, belongs to the ferlin family and is a member of a putative muscle-specific repair complex. It has many isoforms and is a large membrane protein that is most abundant in striated muscle. It plays a role in sarcolemmal repair and is a key calcium ion sensor involved in Ca(2+)-triggered synaptic vesicle-plasma membrane fusion.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for dysferlin antibody 31658-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |