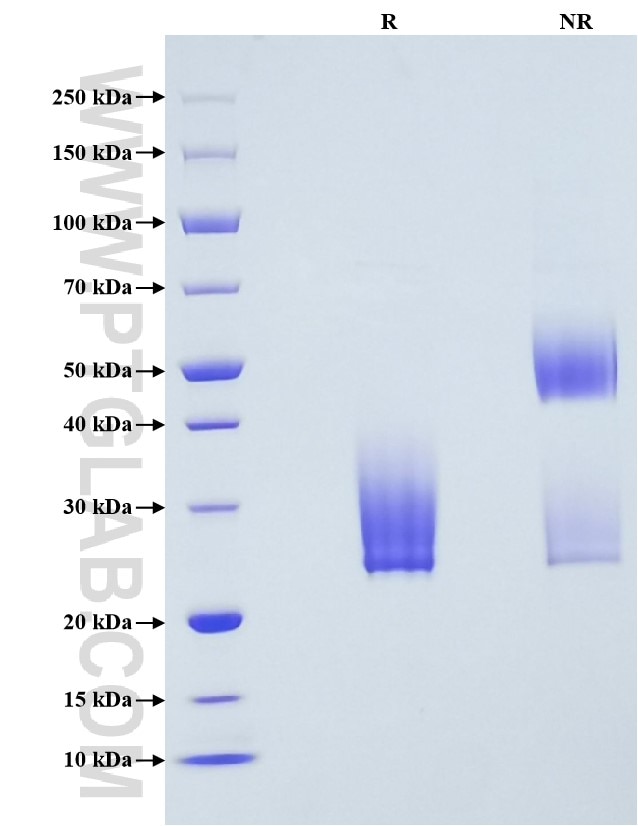
Recombinant Mouse SCF protein (His Tag)
Species
Mouse
Purity
>95 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
His Tag
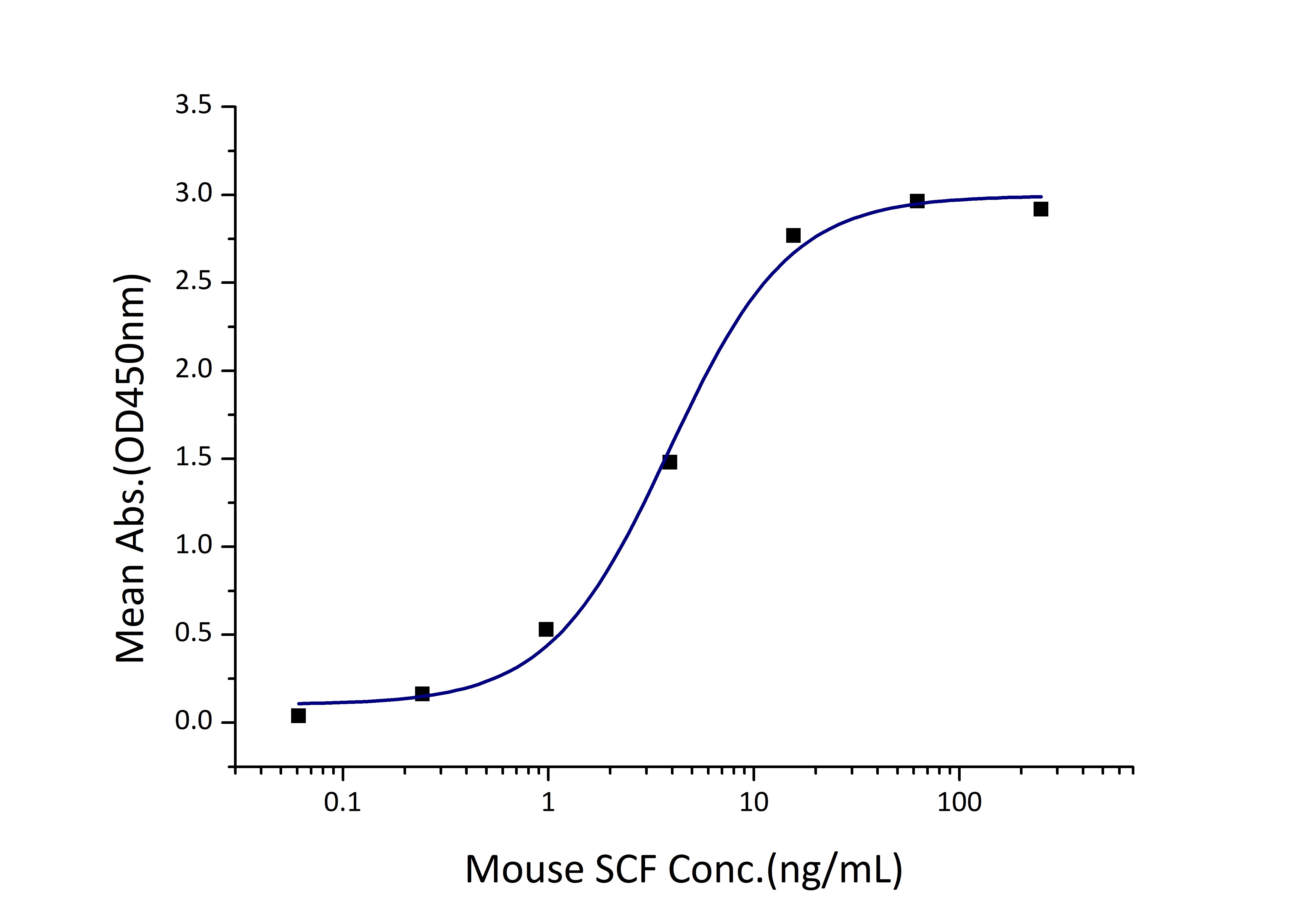
Activity
EC50: 2-8 ng/mL
Cat no : Eg0402
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >95 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Immobilized Mouse CD117 (His tag) at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Mouse SCF (His tag) with a linear range of 2-8 ng/mL. |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Mouse SCF protein Lys26-Ala189 (Accession# P20826-1) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 17311 |
| Accession | P20826-1 |
| PredictedSize | 22.3 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 25-35 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
SCF(Stem cell factor) also known as mast cell growth factorang kit ligand, is a hematopoietic growth factor. It plays an role in hematopoiesis (formation of blood cells), spermatogenesis, and melanogenesis. SCF is expressed in where hematopoiesis takes place, such as the fetal liver and bone marrow. SCF binding to c-kit ligand(CD117)causes the receptor to homodimerize and auto-phosphorylate at tyrosine residues. SCF and c-kit ligand are up-regulated in human malignancies including gastrointestinal stromal tumor, breast cancer, hematopoietic cell, myeloid leukaemia, and glioma. The SCF/c-kit pathway also plays a rolein the regulation of cell survival and proliferation, stem cell maintenance, mast cell development, migration.SCF and c-kit were confirmed as key role in hematopoietic function in adult mice.
References:
1.M Ogawa. et al.(1991)J Exp Med. 174(1): 63-71. 2.Gu Y. et al.(2011) PLoS One. 6(10): e25984. 3.Pedersen M. et al.(2008) Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 377(1): 98-103. 4.Talaiezadeh A. et al. (2012) Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 16(4): 306-9. 5.Bai CG. et al. (2012) World J Gastroenterol.18(23): 2929-37. 6.Lennartsson J. et al. (2012) Physiol Rev. 92(4): 1619-49. 7. Liang J. et al.(2013) Int J Biol Sci. 9(5): 435-43.