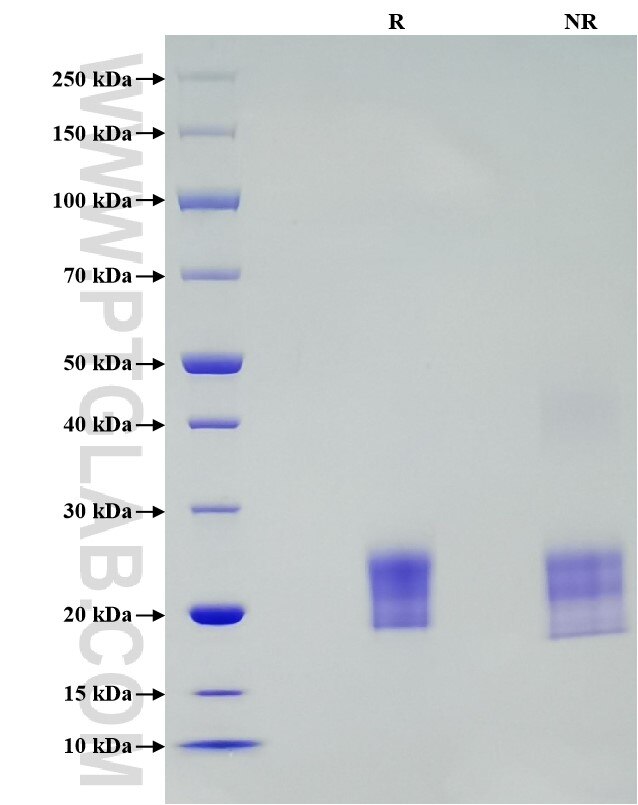
Recombinant Rat IL-2 protein (His Tag)
Species
Rat
Purity
>95 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
His Tag
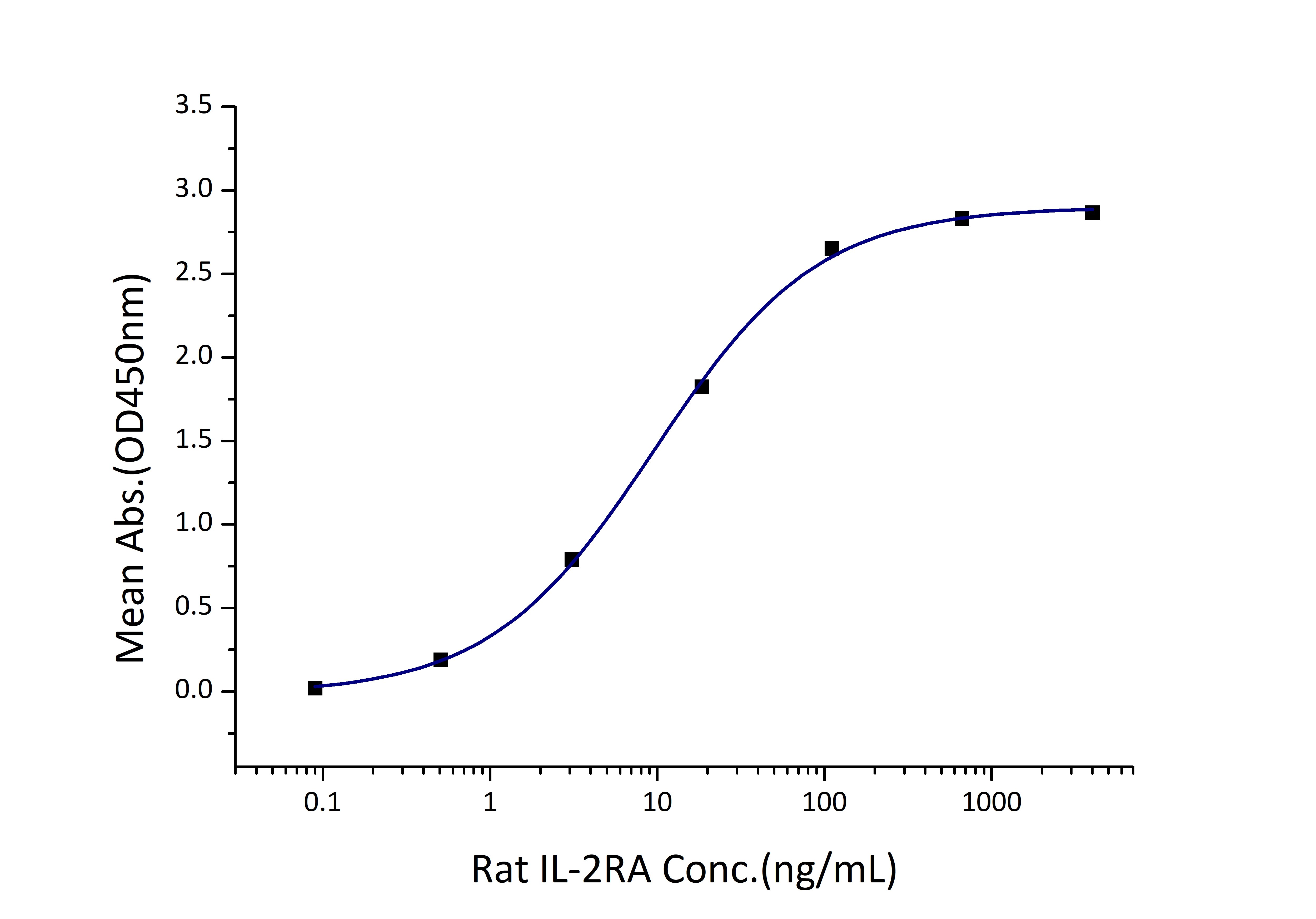
Activity
EC50: 5-19 ng/mL
Cat no : Eg0260
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >95 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Immobilized Rat IL-2 (His tag) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Rat IL-2RA (rFc tag) with a linear range of 5-19 ng/mL. |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Rat IL-2 protein Met+Ala21-Gln155 (Accession# P17108) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 116562 |
| Accession | P17108 |
| PredictedSize | 17.3 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 19-26 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
IL-2 (Interleukin-2) is an interleukin, a type of cytokine signaling molecule in the immune system. It regulates white blood cells (leukocytes, often lymphocytes) that are responsible for immunity. The major sources of IL-2 are activated CD4+ T cells and activated CD8+ T cells. IL-2 mediates its effects by binding to IL-2 receptors which are expressed by lymphocytes. IL-2 signal can be transduced by 3 different signaling pathways: JAK/STAT, PI3K/Akt/mTOR and MAPK/ERK pathway. IL-2 plays a role in regulating the adaptive immune system by controlling the survival and proliferation of regulatory T-cells, which are required for the maintenance of immune tolerance. It also promotes proliferation of activated B cells and subsequently immunoglobulin production.
References:
1.M C Mingari. et al. (1984). Nature. 312(5995): 641-3. 2.Thomas R Malek. et al. (2010). Immunity. 33(2): 153-65. 3.Wei Liao. et al. (2011). Curr Opin Immunol. 23(5): 598-604. 4.Natalia Arenas Ramirez. et al. (2015). Trends Immunol. 36(12): 763-777.