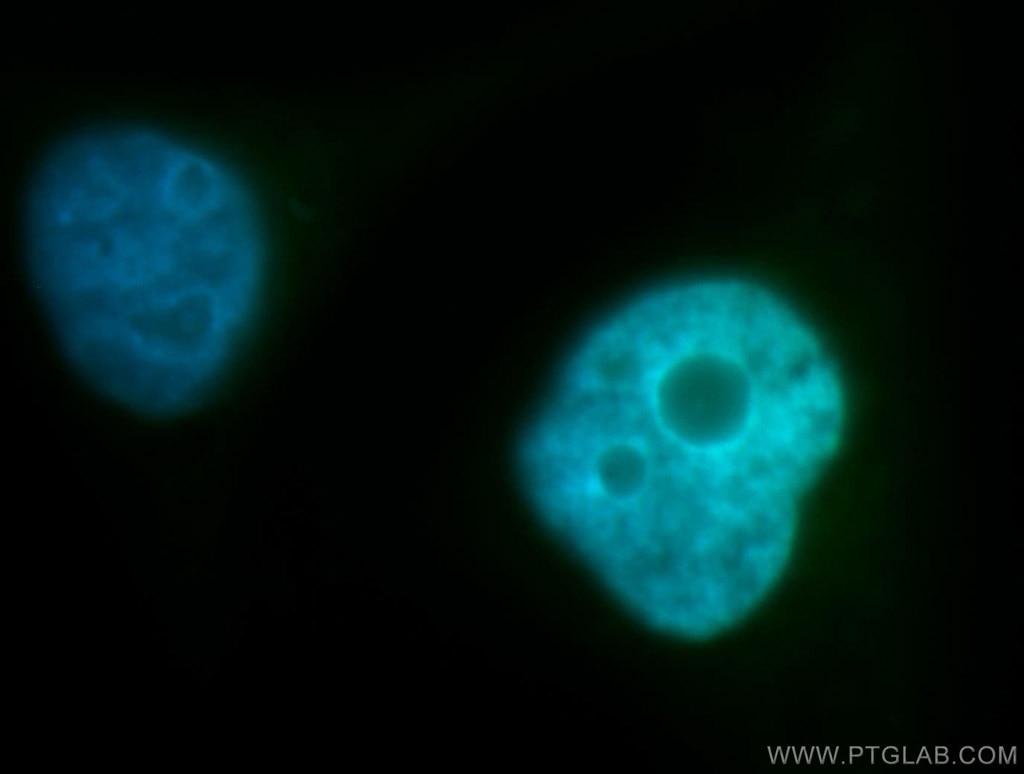
Tested Applications
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HepG2 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
10123-2-AP targets BUB3 in IF, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag0167 Product name: Recombinant human BUB3 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 124-253 aa of BC005138 Sequence: DPRTPCNAGTFSQPEKVYTLSVSGDRLIVGTAGRRVLVWDLRNMGYVQQRRESSLKYQTRCIRAFPNKQGYVLSSIEGRVAVEYLDPSPEVQKKKYAFKCHRLKENNIEQIYPVNAISFHNIHNTFATGG Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 3 homolog (yeast) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 37 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC005138 |
| Gene Symbol | BUB3 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 9184 |
| RRID | AB_2066209 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O43684 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
BUB3 is a conserved component of the mitotic spindle assembly complex and is an essential compent of spindle-assembly checkpoint (SAC) signaling that operates during early embryogenesis. BUB3 null embryos treated with a spindle-depolymerising agent fail to arrest in metaphase and show an increase in mitotic disarray. In mitosis, the SAC prevents anaphase onset until all chromosomes have been attached to the spindle microtubules and aligned correctly at the equatorial metaphase plate. BUB3 is involved in promoting the establishment of correct kinetochore-microtubule (K-MT) attachments in mammalian oocyte meiosis.