Product Information
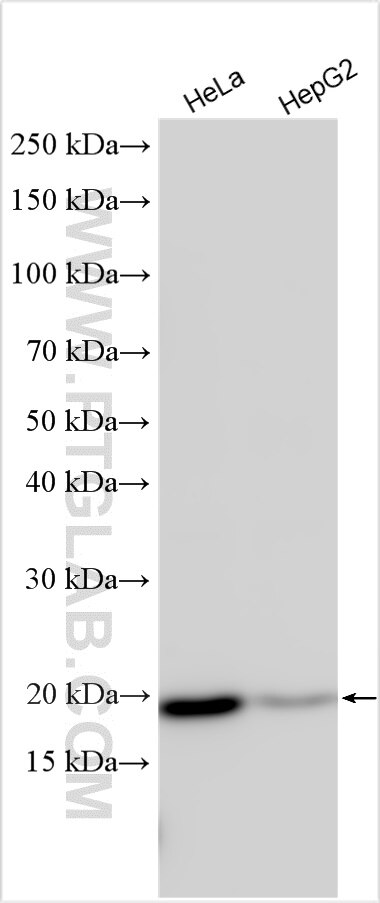
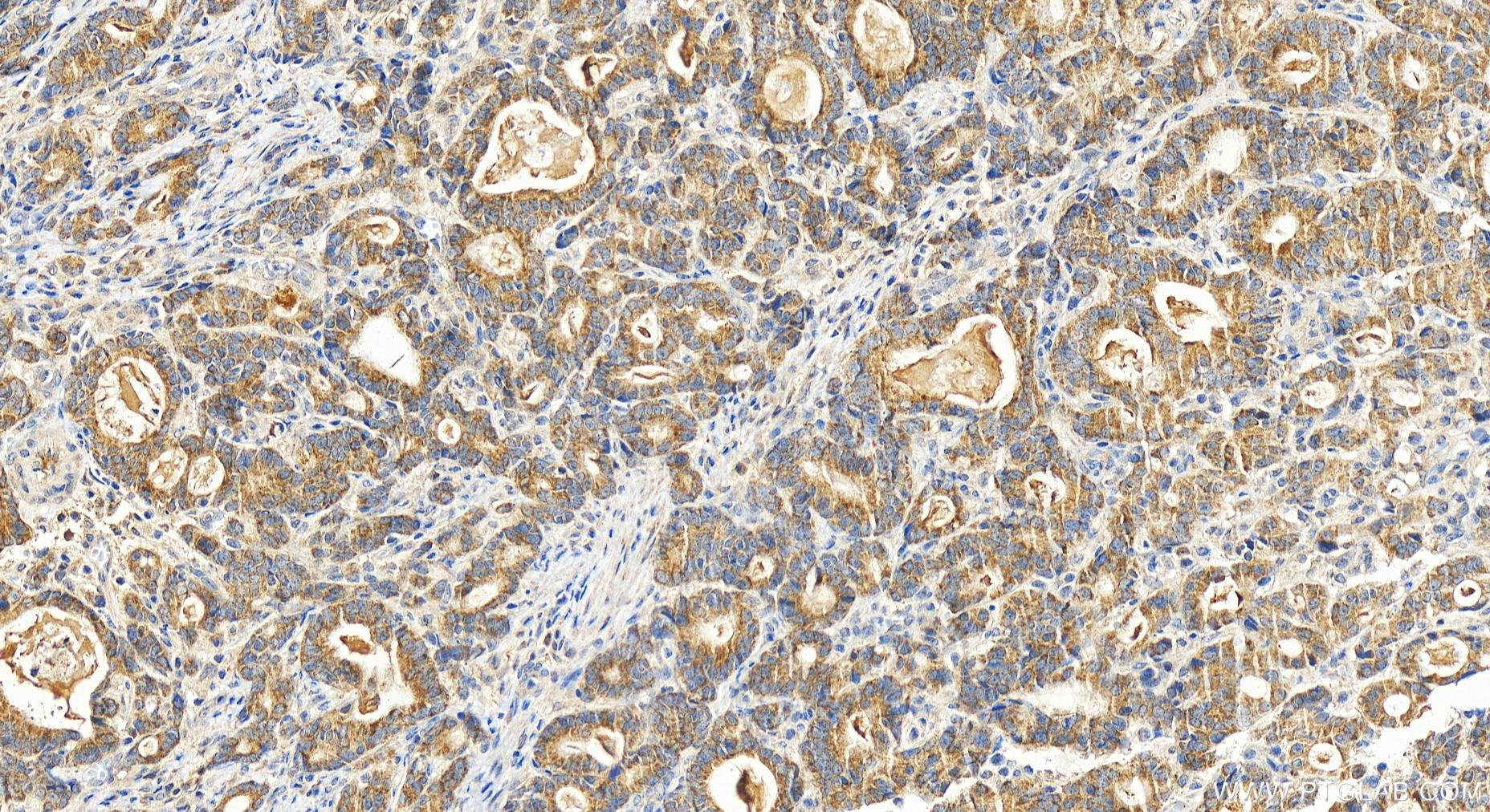
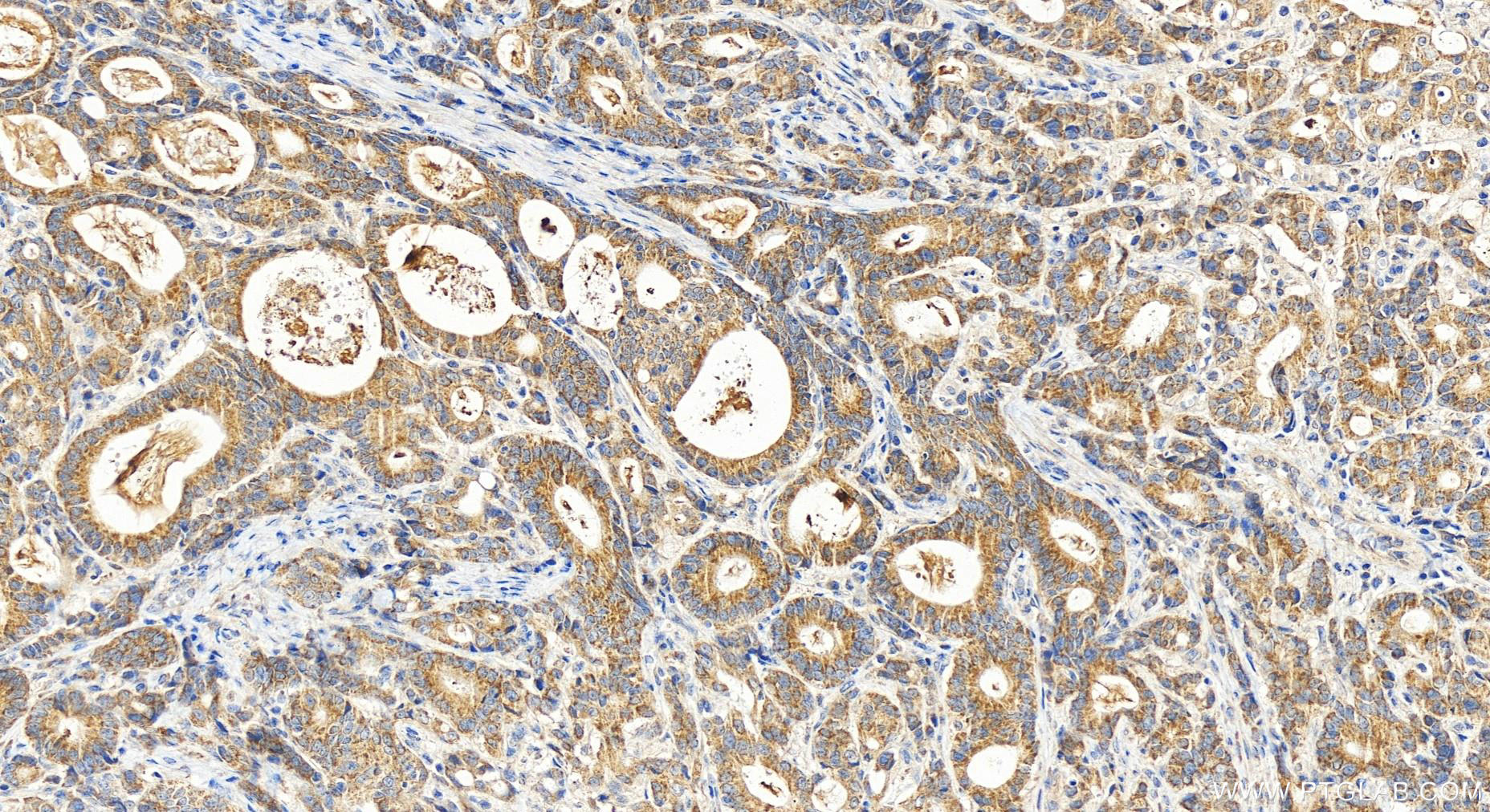
19832-1-PBS targets FUNDC2 in WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | FUNDC2 fusion protein Ag13800 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | FUN14 domain containing 2 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 189 aa, 21 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 21 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC000255 |
| Gene Symbol | FUNDC2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 65991 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9BWH2 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
FUNDC2, or FUN14 domain-containing protein 2, is a mitochondrial outer membrane protein that plays a significant role in various cellular processes, including the regulation of cell survival, apoptosis, and metabolism. It has been implicated in the progression of several types of cancer, particularly in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and liver cancer. In the context of cancer, FUNDC2 has been shown to promote tumorigenesis. It is associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and is involved in mitochondrial fragmentation by inhibiting MFN1-mediated mitochondrial fusion, which can lead to changes in cellular metabolism and energy levels. FUNDC2 also plays a role in platelet function and survival. It binds directly to phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3), which is a key lipid second messenger in cell signaling, and this interaction is crucial for the recruitment of PIP3 to mitochondria. FUNDC2 deficiency has been shown to decrease platelet aggregation and impair hemostasis in mice, highlighting its importance in platelet function.