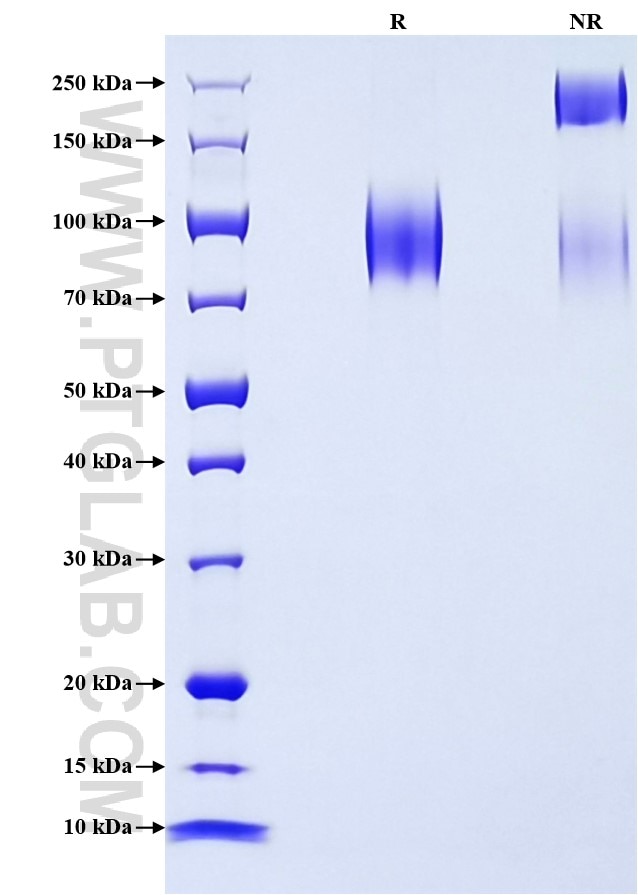
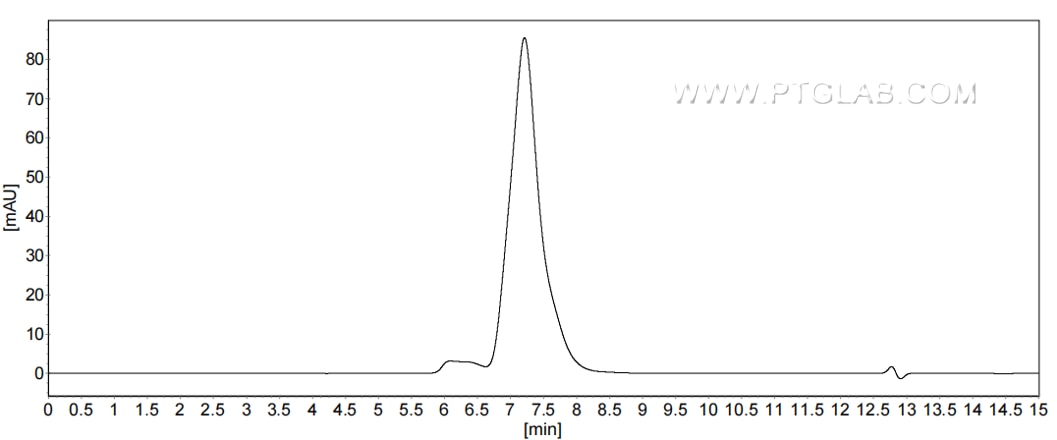
Recombinant Human CD107a/LAMP1 protein (rFc Tag) (HPLC verified)
Species
Human
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
>90 %, SEC-HPLC
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg2611
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE >90 %, SEC-HPLC |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human CD107a protein Ala26-Ser381 (Accession# P11279-1) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 3916 |
| Accession | P11279-1 |
| PredictedSize | 64.5 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 75-120 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
LAMP1 (CD107a) is a heavily glycosylated membrane protein enriched in the lysosomal membrane. LAMP1 is extensively glycosylated with asparagine-linked oligosaccharides which protect it from intracellular proteolysis. Although LAMP1 is expressed largely in the endosome-lysosomal membrane of cells, it is also found on the plasma membrane. Elevated LAMP1 expression at the cell surface has also been detected during platelet and granulocytic cell activation, as well as in some tumor cells. LAMP1 functions to provide selectins with carbohydrate ligands. This protein has also been shown to be a marker of degranulation on lymphocytes such as CD8+ and NK cells and may also play a role in tumor cell differentiation and metastasis.
References:
1. Kundra R. et al. (1999) J Biol Chem. Oct 22;274(43):31039-31046. 2. Parkinson-Lawrence. E. J. et al. (2005) Cell Immunol. 236(1-2):161-166. 3. Wang Q. et al. (2017) Oncol Lett. 14(4):4729-4735. 4. Aktas E. et al. (2009) Cell Immunol. 254(2):149-154.