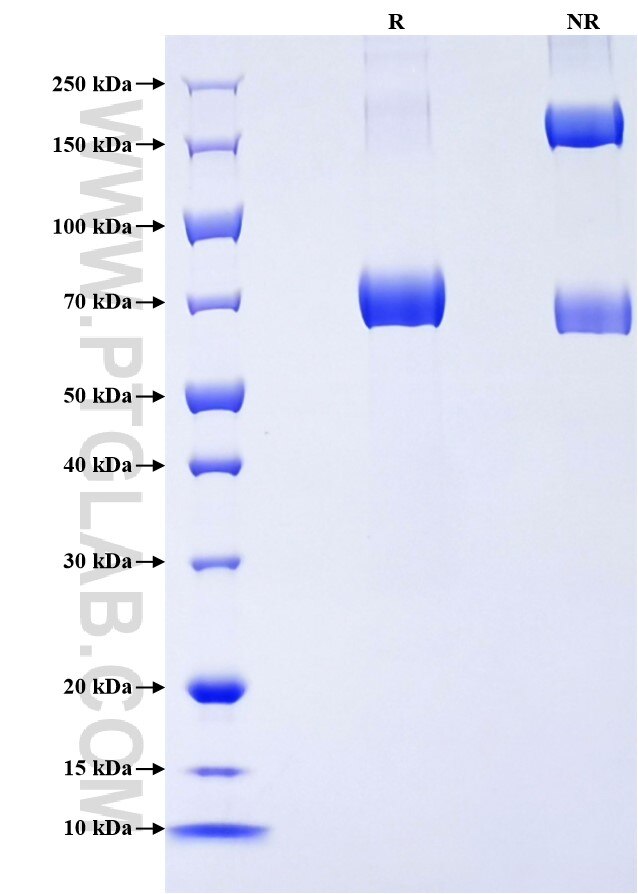
Recombinant Human Lumican protein (rFc Tag)
Species
Human
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg2923
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human Lumican protein Gln19-Asn338 (Accession# P51884) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 4060 |
| Accession | P51884 |
| PredictedSize | 62.7 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 65-80 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Lumican (LUM), a member of the small leucine-rich proteoglycan (SLRP) family, is one of the major extracellular components in interstitial collagenous matrices of the corneal stroma, aorta, skin, skeletal muscle, lung, kidney, bone, cartilage, and intervertebral discs. SLRPs constitute an important fraction of noncollagenous extracellular matrix proteins and have important effects on cell behavior. Lumican regulates collagenous matrix assembly as a keratan sulfate proteoglycan in the cornea and may exist as a glycoprotein in the connective tissues of other organs. Posttranslational modifications lumican goes through can increase its apparent molecular weight to 50-90 kDa. Studies show that lumican participates in the maintenance of tissue homeostasis and modulates cellular functions including cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation.
References:
1. Nikitovic D. et al. (2008) IUBMB Life. 60(12):818-23. 2. Liu CY. et al. (2012) Methods Mol Biol. 836:285-90. 3. Dolhnikoff M. et al. (1998) Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 19(4):582-7. 4. Yang CH. et al. (2012) Vet J. 193(2):374-80.