Tested Applications
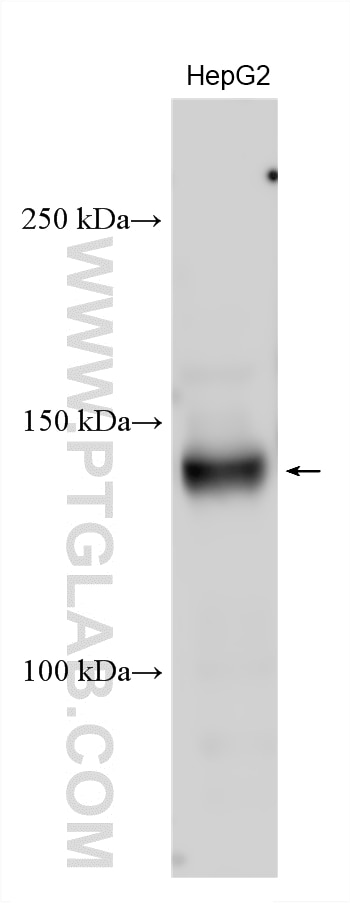
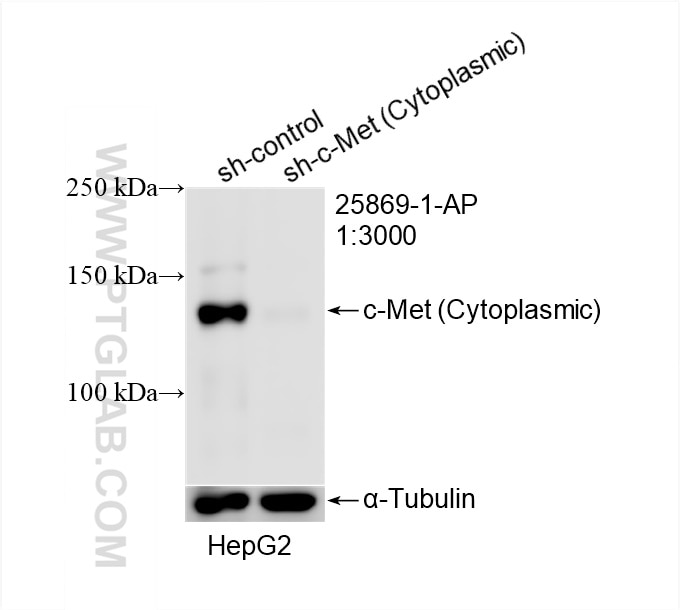
| Positive WB detected in | HepG2 cells, MDCK cells |
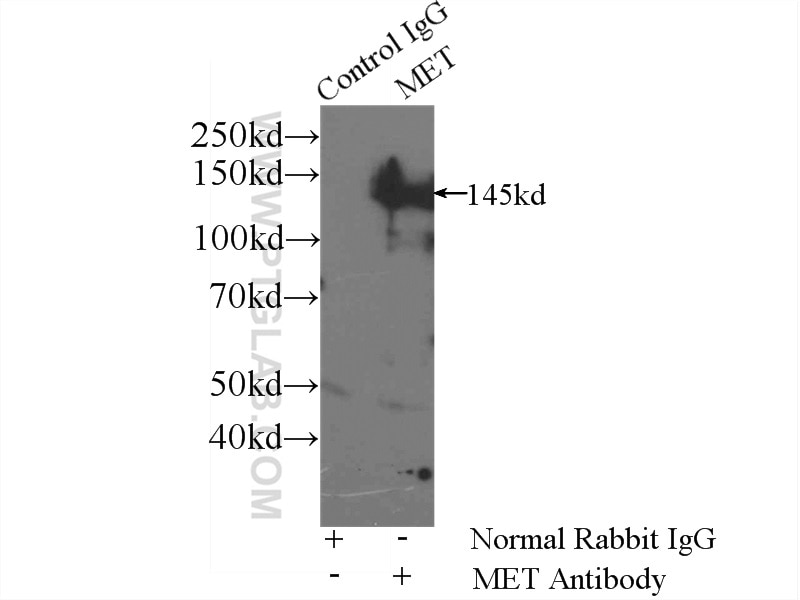
| Positive IP detected in | HeLa cells |
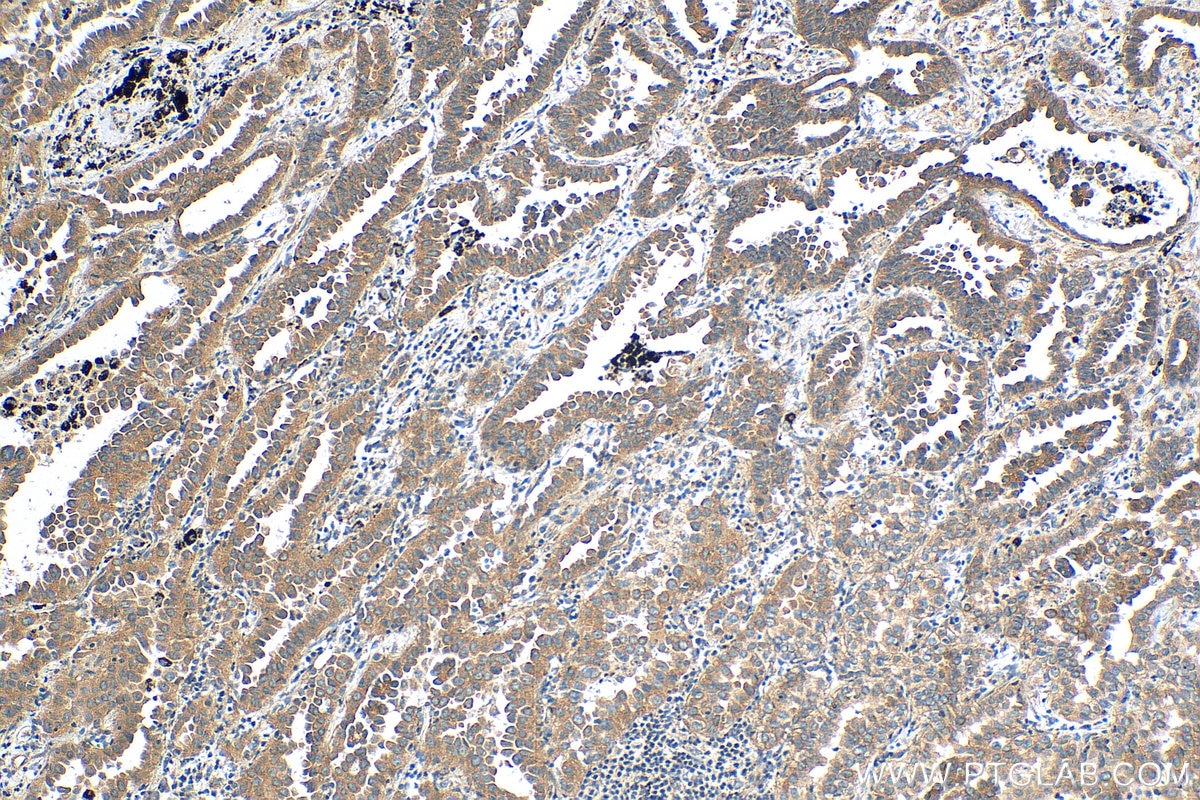
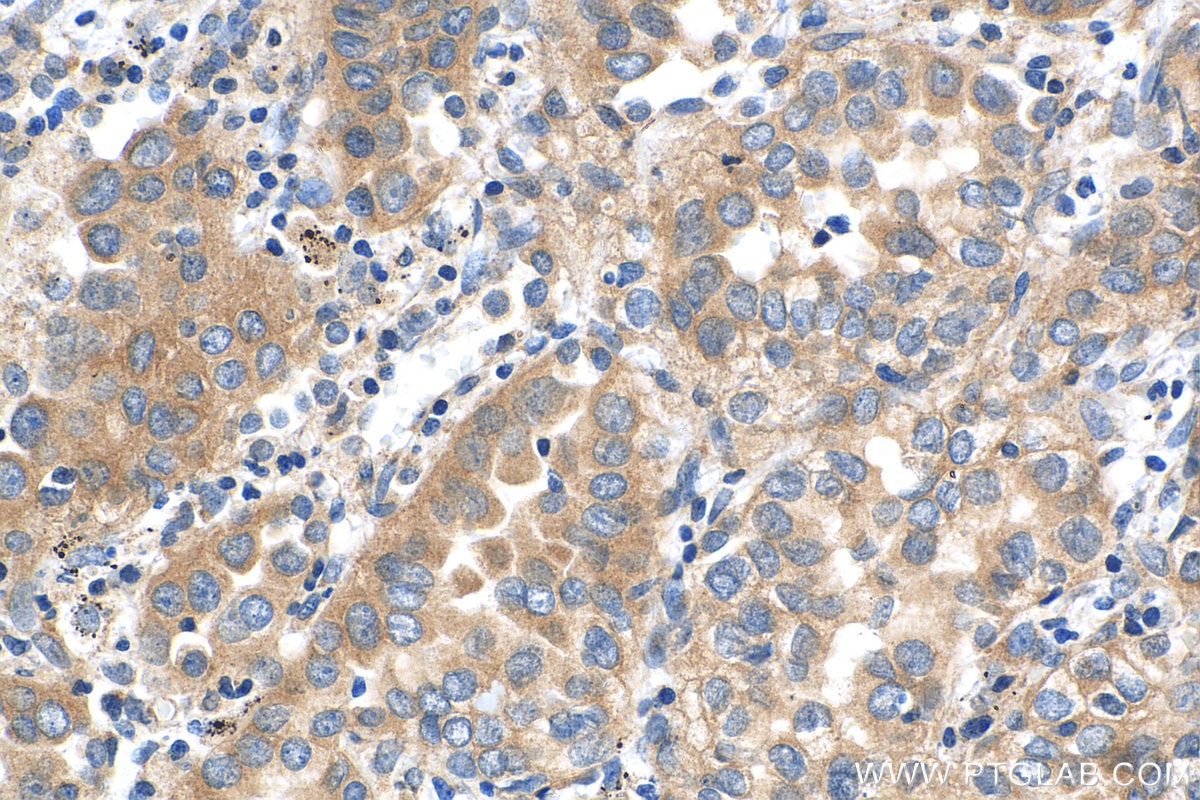
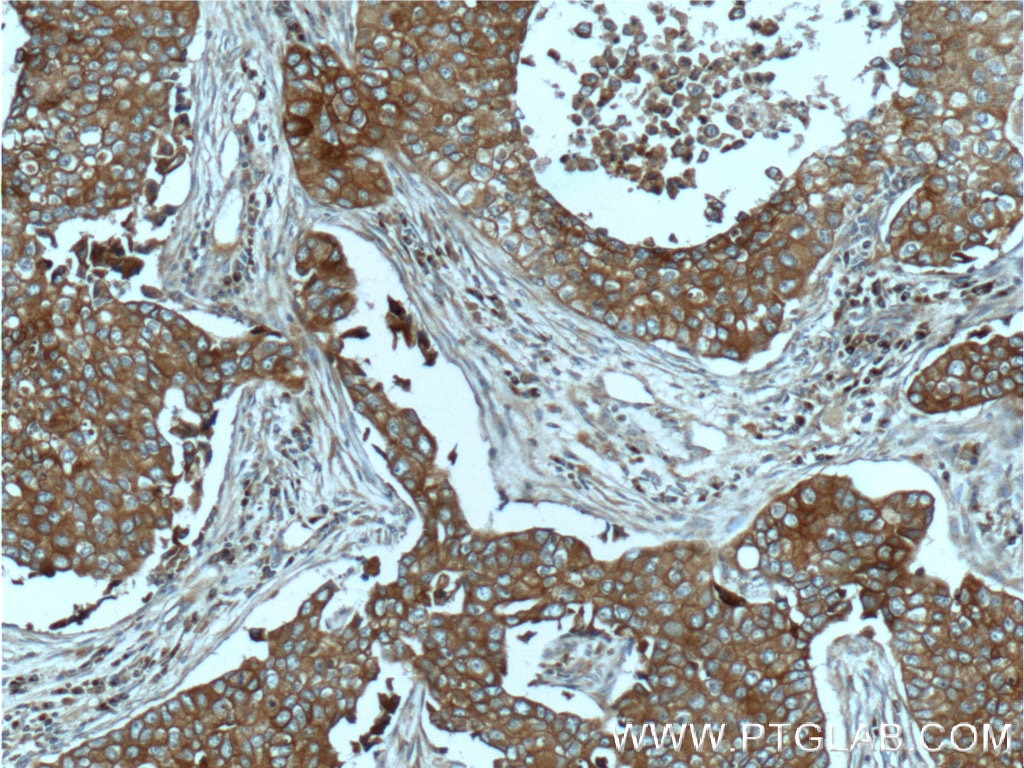
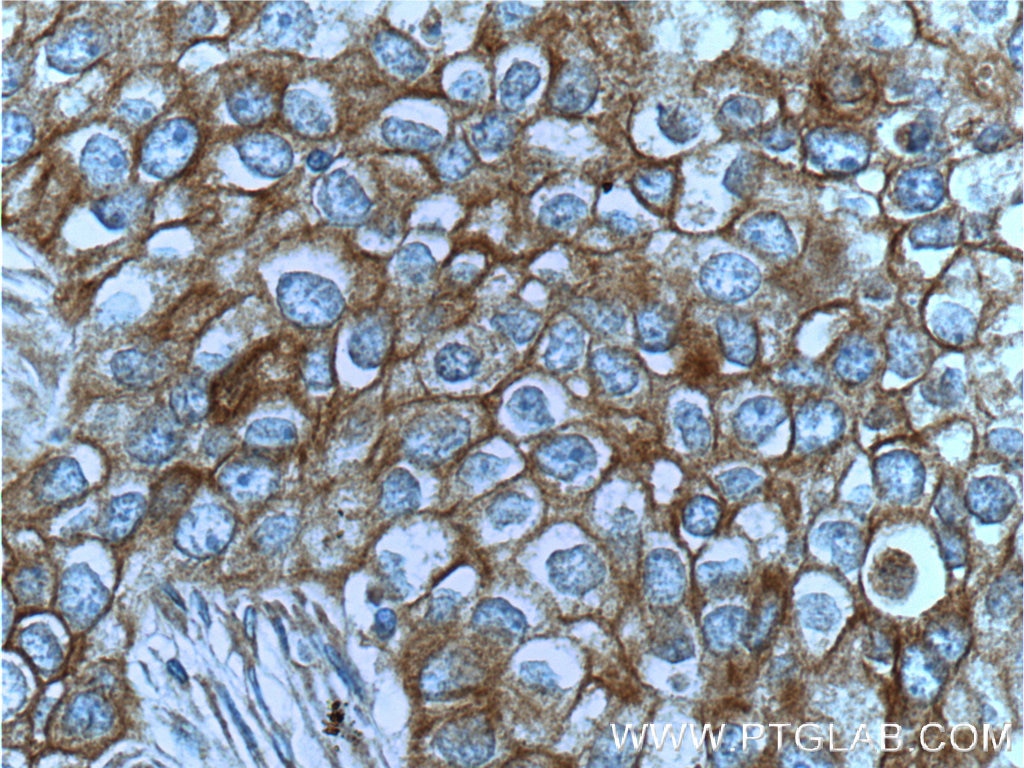
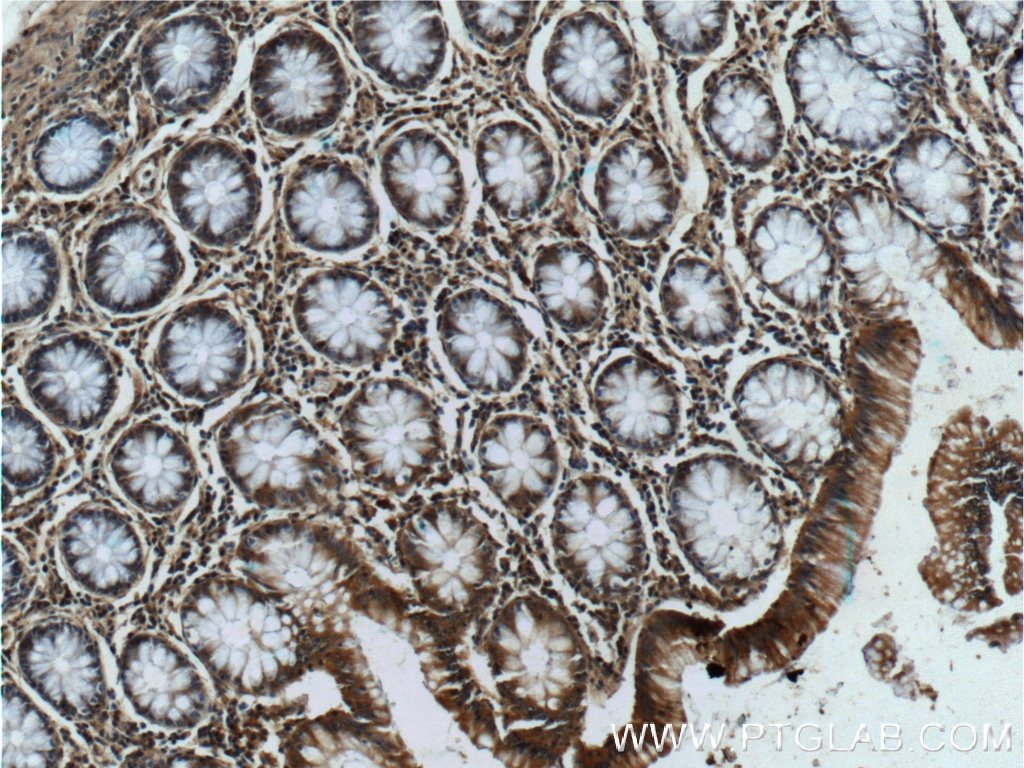
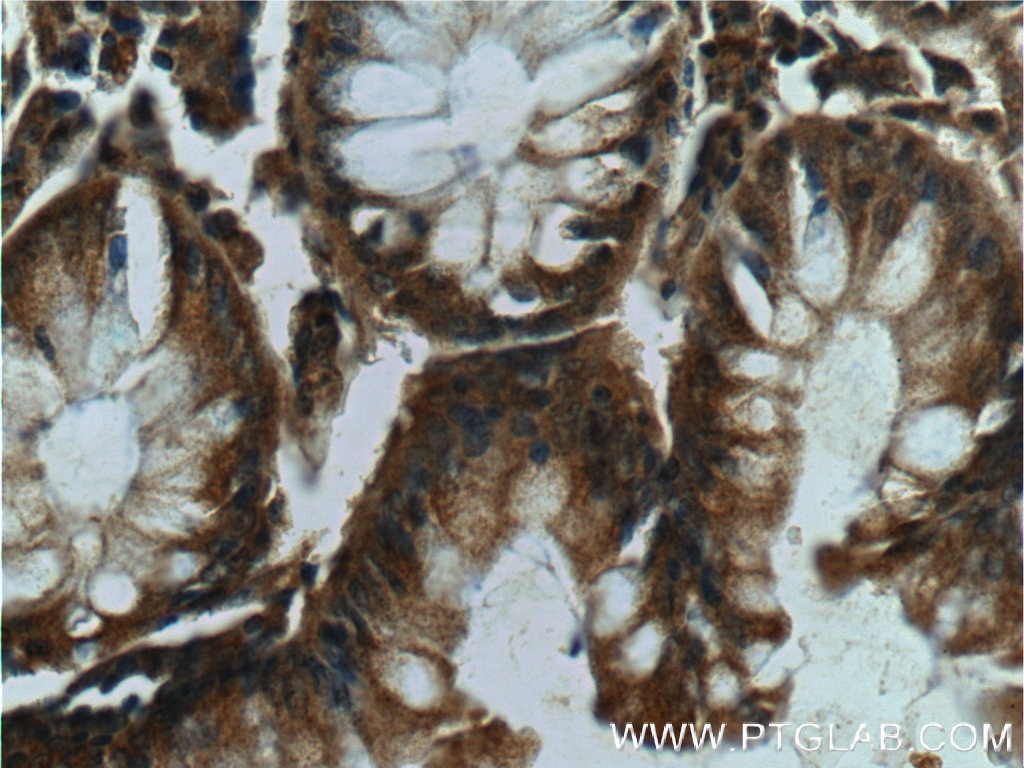
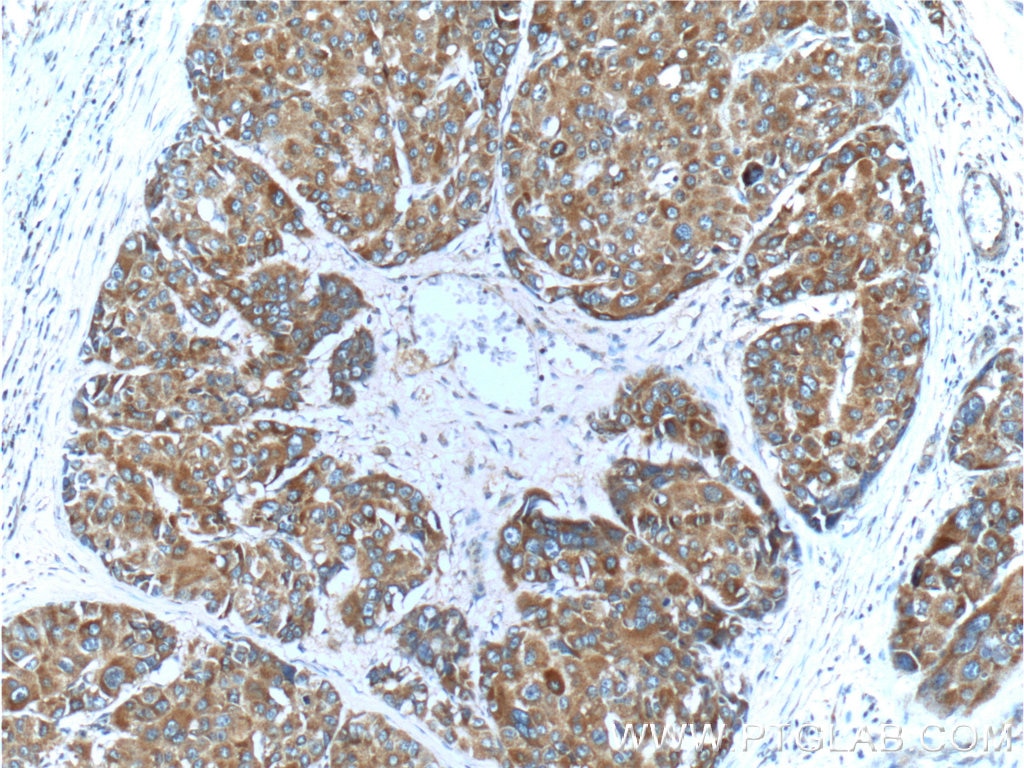
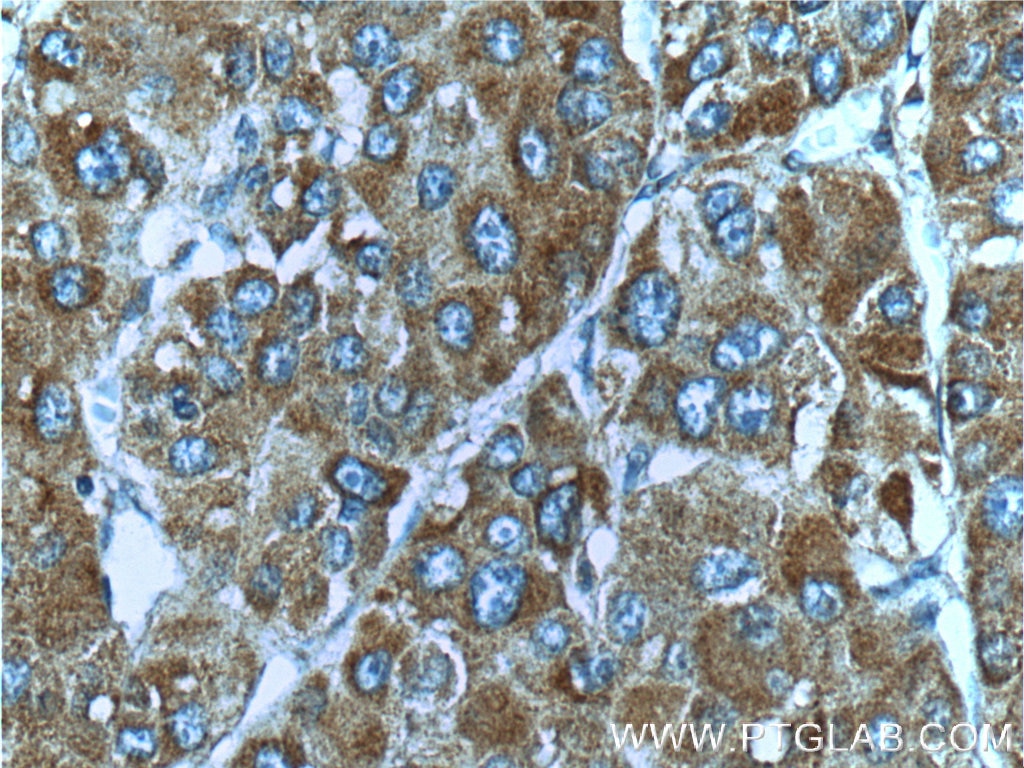
| Positive IHC detected in | human lung cancer tissue, human breast cancer tissue, human colon tissue, human liver cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
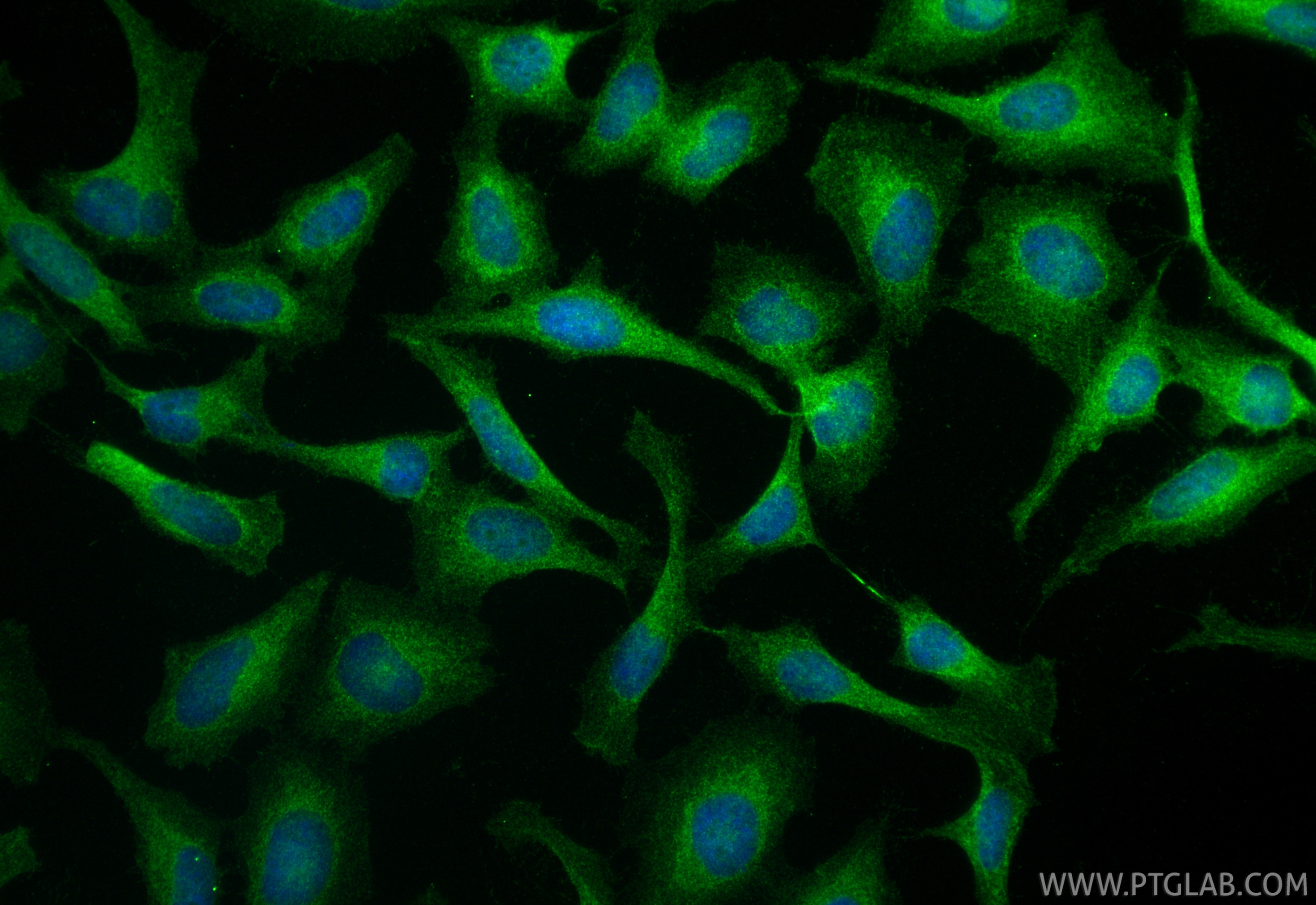
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HeLa cells |
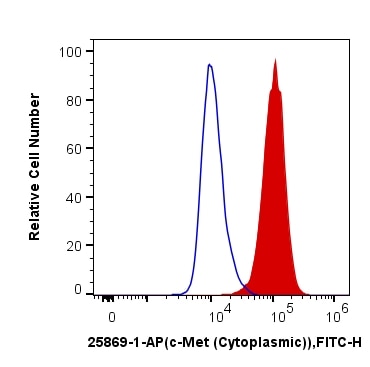
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | HeLa cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:12000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 9 publications below |
| WB | See 48 publications below |
| IHC | See 16 publications below |
| IP | See 2 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
| RIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
25869-1-AP targets c-Met (Cytoplasmic) in WB, IHC, FC (Intra), IP, CoIP, RIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, canine samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, canine |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag23140 Product name: Recombinant human MET protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 965-1085 aa of BC130420 Sequence: GSELVRYDARVHTPHLDRLVSARSVSPTTEMVSNESVDYRATFPEDQFPNSSQNGSCRQVQYPLTDMSPILTSGDSDISSPLLQNTVHIDLSALNPELVQAVQHVVIGPSSLIVHFNEVIG Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | met proto-oncogene (hepatocyte growth factor receptor) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 1390 aa, 155 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 145 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC130420 |
| Gene Symbol | MET |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4233 |
| RRID | AB_2880276 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P08581 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
c-Met (also named MET or HGFR) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that transduces signals from the extracellular matrix into the cytoplasm by binding to the HGF ligand. c-Met regulates many physiological processes including proliferation, scattering, morphogenesis, and survival. The primary single-chain precursor protein is post-translationally cleaved to produce the alpha and beta subunits, which are disulfide-linked to form the mature receptor. Overexpression and/or mutation of c-Met has been reported in various human malignancies, including lung cancer, breast cancer, head and neck cancer, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, bladder cancer, uterine cervix carcinoma, esophageal carcinoma, c-Met could serve as an important therapeutic target (PMID: 26036285). The c-met receptor is a 190-kD glycoprotein consisting of a 145-kD membrane-spanning beta chain and a 50-kD alpha chain (PMID: 7806559). In Western blot, this antibody produces bands of unknown identity at 55 and 100 kDa.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for c-Met (Cytoplasmic) antibody 25869-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for c-Met (Cytoplasmic) antibody 25869-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for c-Met (Cytoplasmic) antibody 25869-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for c-Met (Cytoplasmic) antibody 25869-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for c-Met (Cytoplasmic) antibody 25869-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Metab LIFR regulates cholesterol-driven bidirectional hepatocyte-neutrophil cross-talk to promote liver regeneration | ||
Acta Pharmacol Sin GPR97 deficiency ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis in mouse hypertensive nephropathy | ||
Clin Transl Med Ursodesoxycholic acid alleviates liver fibrosis via proregeneration by activation of the ID1-WNT2/HGF signaling pathway. | ||
Mol Ther Nucleic Acids miRNA in food simultaneously controls animal viral disease and human tumorigenesis. | ||
Mol Ther Nucleic Acids Shrimp miR-34 from Shrimp Stress Response to Virus Infection Suppresses Tumorigenesis of Breast Cancer. |
Reviews
The reviews below have been submitted by verified Proteintech customers who received an incentive for providing their feedback.
FH Marius (Verified Customer) (09-30-2025) | Clear signal at 145 kDa. As depicted in datasheet second signal at around 100 kDa.
|