Recombinant Mouse CCL3 protein (rFc Tag)
Species
Mouse
Purity
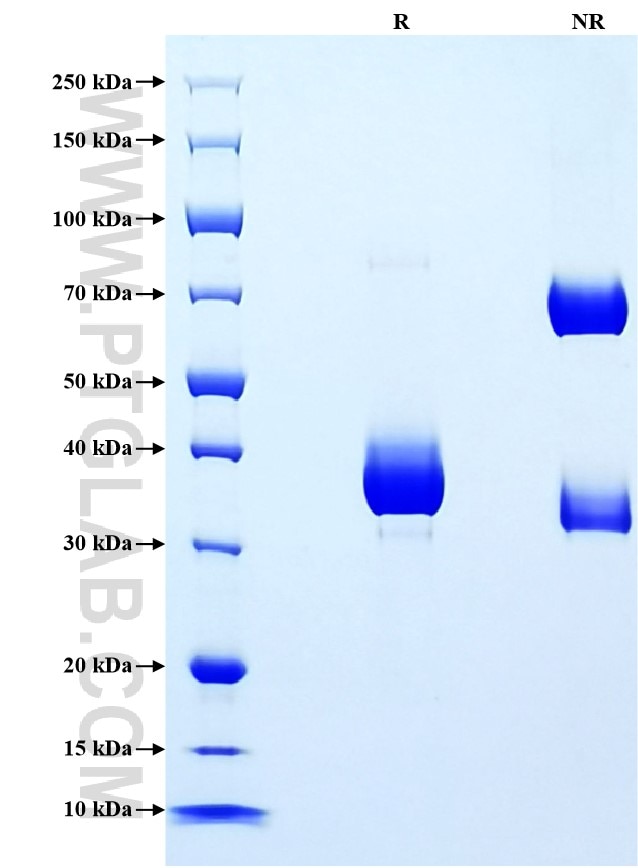
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg2170
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Mouse CCL3 protein Ala24-Ala92 (Accession# P10855) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the N-terminus. |
| GeneID | 20302 |
| Accession | P10855 |
| PredictedSize | 35.1 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 33-40 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3 (CCL3), also known as MIP-1 alpha, belongs to the family of chemokines. CCL3 has been found in the central nervous system and its cognate receptors, CCR1 and CCR5, have been reported to be expressed by astrocytes, microglia and neurons. CCL3 and its receptors, CCR1 and CCR5, also contribute to the development of bone disease in multiple myeloma by supporting tumor growth and regulating osteoclast differentiation. CCL3 is also associated with the regulation of cell growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis of different tumors such as melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, and colorectal cancer. Moreover, CCL3 enhances cell migration and metastasis by up-regulating matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP)-2 expression in chondrosarcoma cells.
References:
1. Menten P. et al. (2002). Cytokine & growth factor reviews. 13:455-481. 2. Vallet S. et al. (2011). Leukemia. 25: 1174-1181. 3. Nakasone Y. et al. (2012). Am J Pathol. 180: 365-374. 4. Wu Y. et al. (2008). J Immunol. 181: 6384-6393. 5. Zhu X. B. et al. (2012). Neurobiol. 38: 602-616.