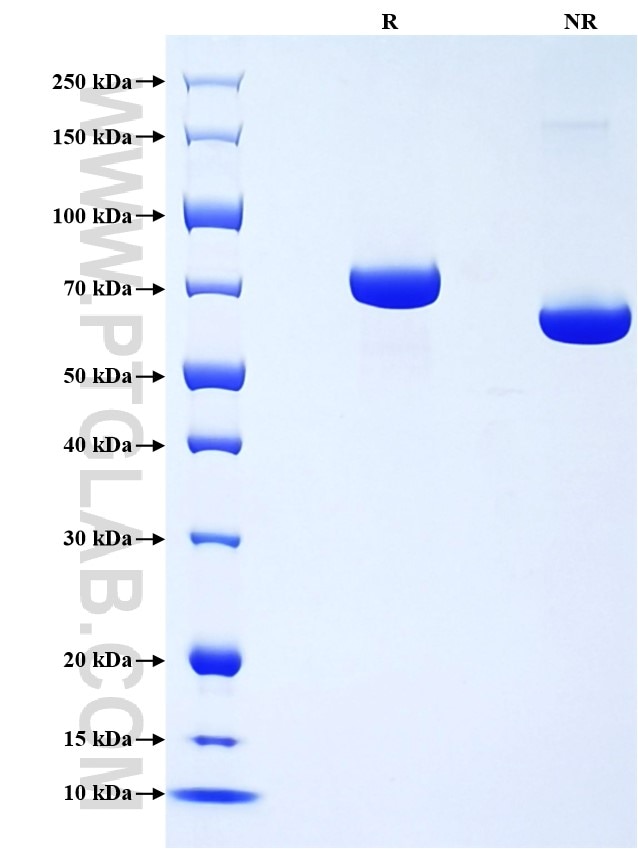
Recombinant Mouse Transferrin protein (His Tag)
Species
Mouse
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
His Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg1066
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Mouse Transferrin protein Val20-His697 (Accession# Q921I1) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 22041 |
| Accession | Q921I1 |
| PredictedSize | 76.0 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 65-80 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Transferrin, also known as Trf, is a crucial iron-binding transport protein. It plays a vital role in iron homeostasis by binding and transporting iron throughout the body, particularly from the sites of absorption to the sites of storage and utilization. Transferrin is primarily synthesized by the liver. It can bind two ferric iron (Fe3+) ions, each associated with a bicarbonate anion, which helps maintain iron in a soluble form and minimizes its redox activity. Transferrin also interacts with clotting factors and plays a central role in coagulation balance. It has been shown to potentiate the enzymatic activity of thrombin and FXIIa and inhibit antithrombin (AT) independently of iron. Elevated levels of transferrin have been associated with atherosclerosis, and it has been found in increased amounts in the plasma of mice fed a high-fat diet, which correlates with atherosclerotic plaque development.
References:
1. Julia T Bu. et al. (2015). Biometals. 28(3):473-480. 2. Xiaopeng Tang. et al.(2020). Cell Res. 30(2):119-132. 3. Konstantinos Gkouvatsos. et al. (2012). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1820(3):188-202.