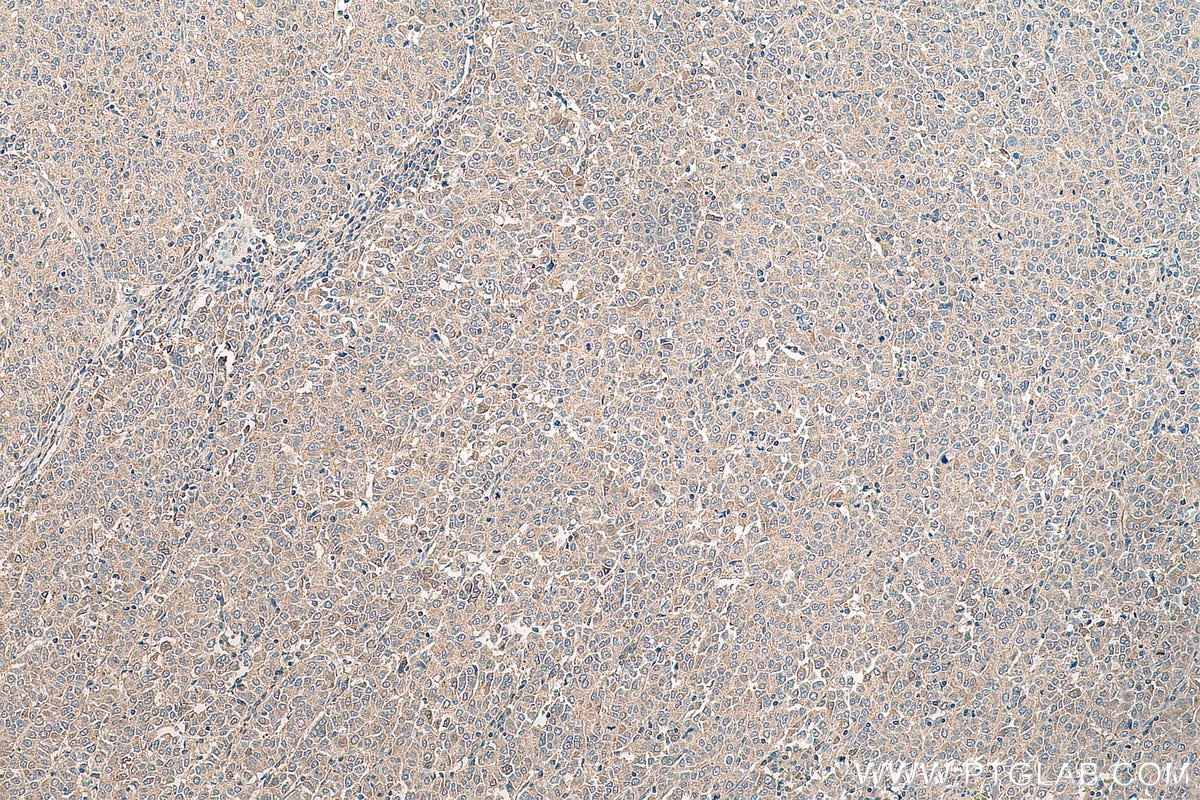
Product Information
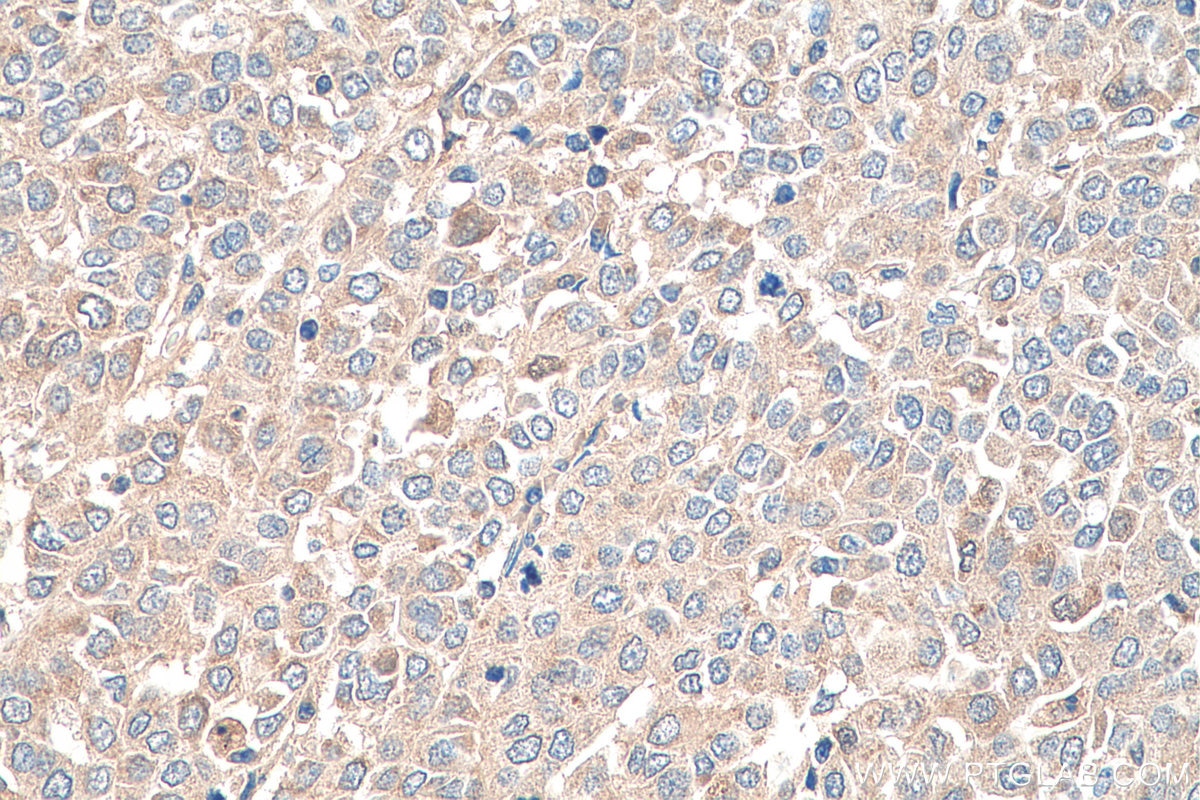
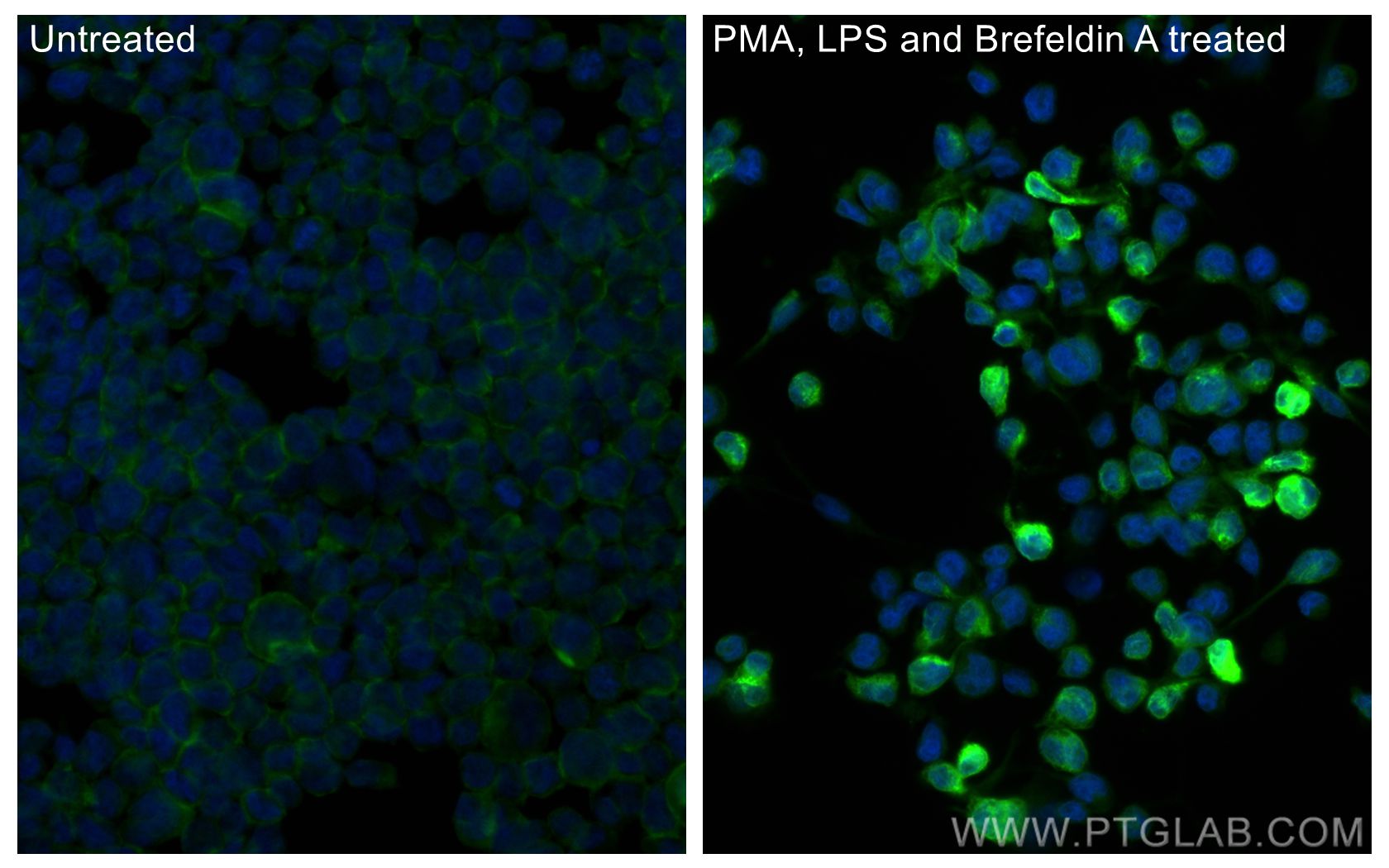
26405-1-PBS targets TNF-alpha in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag24020 Product name: Recombinant human TNF-a protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 77-233 aa of BC028148 Sequence: VRSSSRTPSDKPVAHVVANPQAEGQLQWLNRRANALLANGVELRDNQLVVPSEGLYLIYSQVLFKGQGCPSTHVLLTHTISRIAVSYQTKVNLLSAIKSPCQRETPEGAEAKPWYEPIYLGGVFQLEKGDRLSAEINRPDYLDFAESGQVYFGIIAL Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | tumor necrosis factor (TNF superfamily, member 2) |
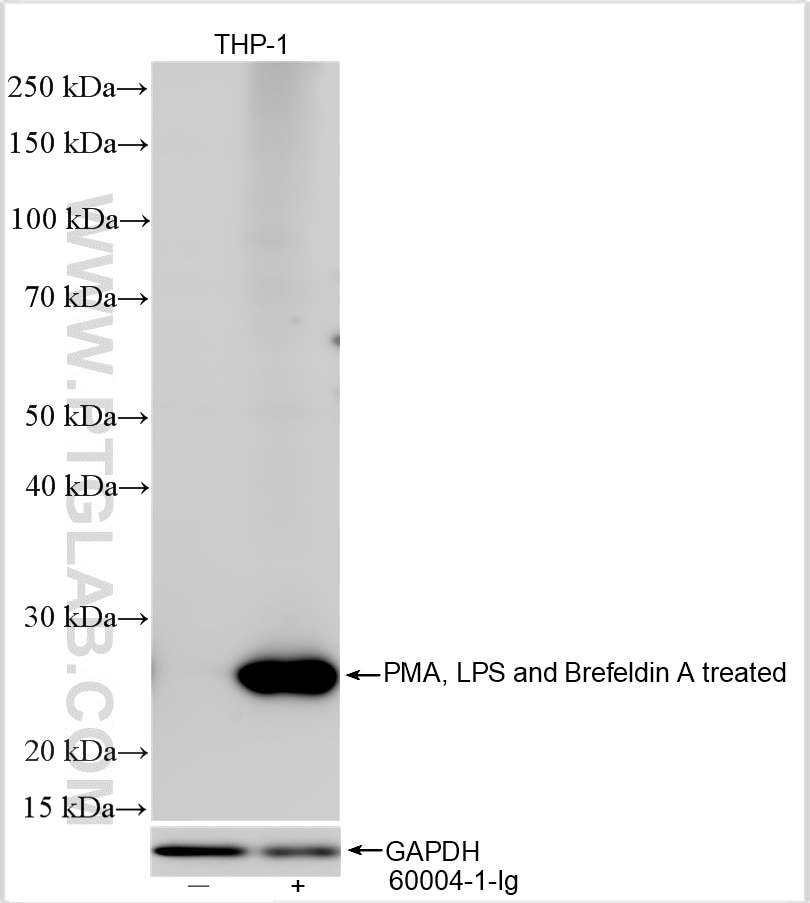
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 233 aa, 26 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 26 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC028148 |
| Gene Symbol | TNF-alpha |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7124 |
| ENSEMBL Gene ID | ENSG00000232810 |
| RRID | AB_2918102 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P01375 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
TNF, as also known as TNF-alpha, or cachectin, is a multifunctional proinflammatory cytokine that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily. It is expressed as a 26 kDa membrane bound protein and is then cleaved by TNF-alpha converting enzyme (TACE) to release the soluble 17 kDa monomer, which forms homotrimers in circulation. It is produced chiefly by activated macrophages, although it can be produced by many other cell types such as CD4+ lymphocytes, NK cells, neutrophils, mast cells, eosinophils, and neurons. It can bind to, and thus functions through its receptors TNFRSF1A/TNFR1 and TNFRSF1B/TNFBR. This cytokine is involved in the regulation of a wide spectrum of biological processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, lipid metabolism, and coagulation. This cytokine has been implicated in a variety of diseases, including autoimmune diseases, ins resistance, and cancer.