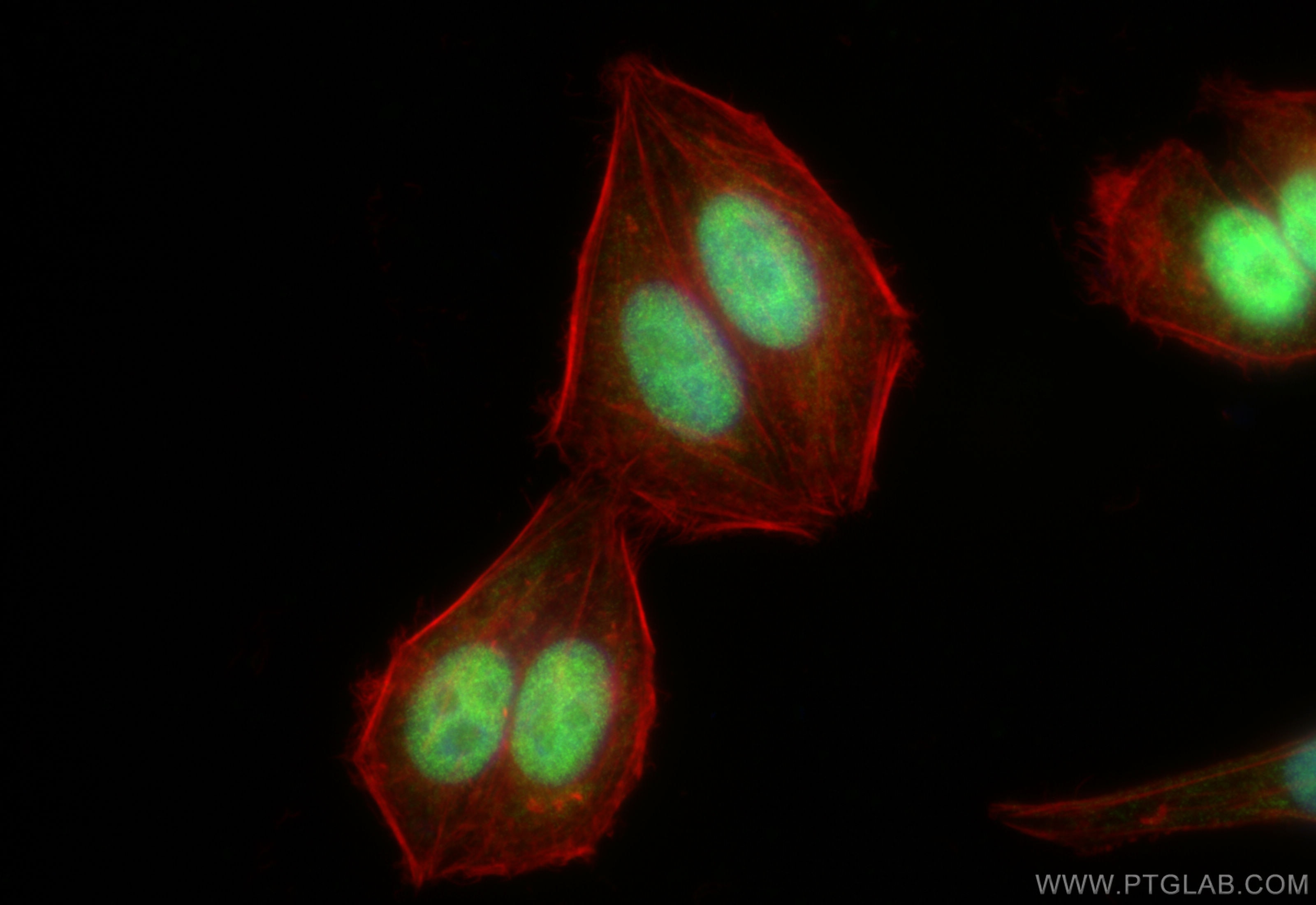
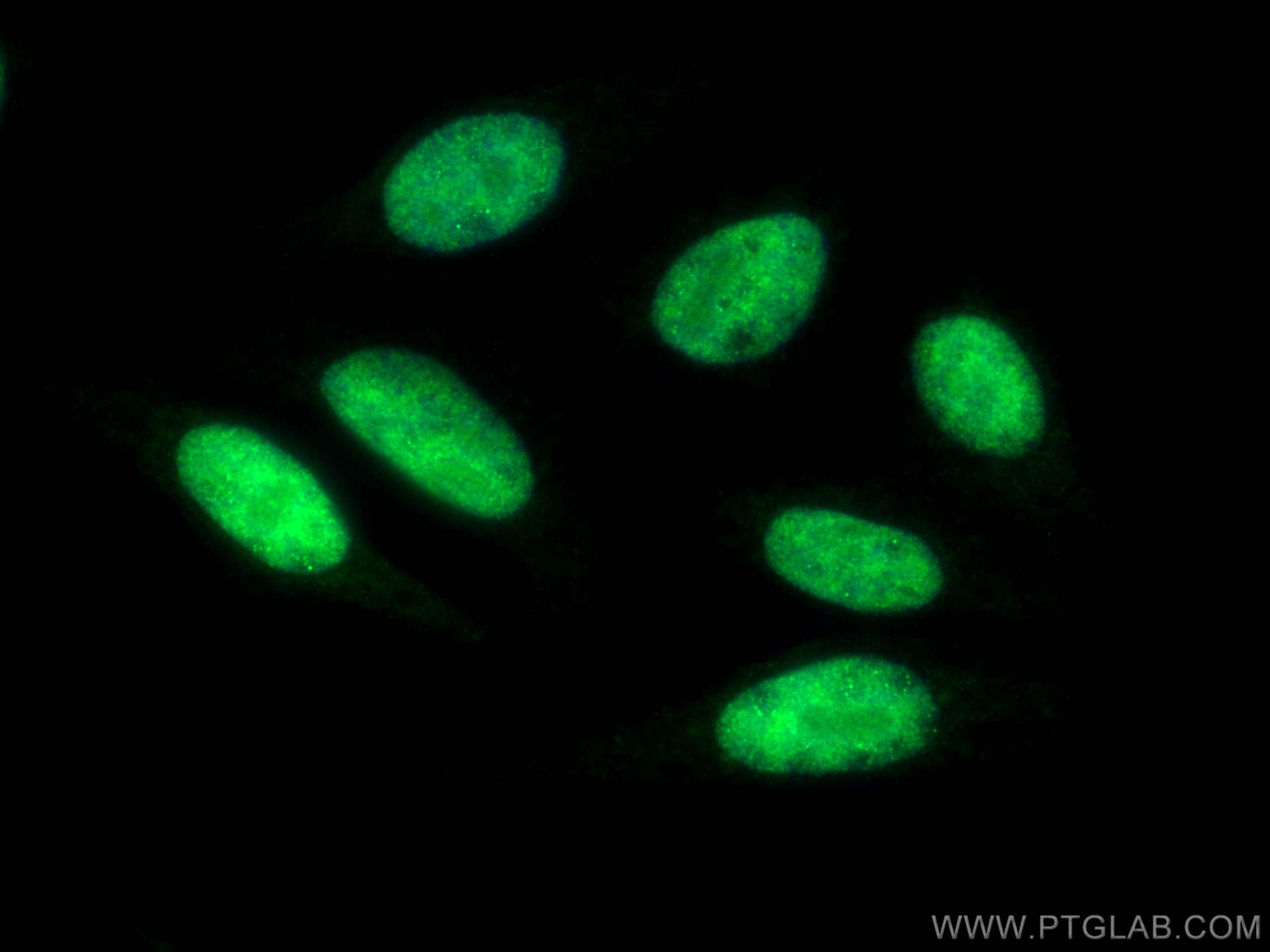
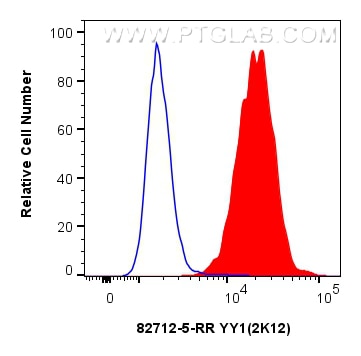
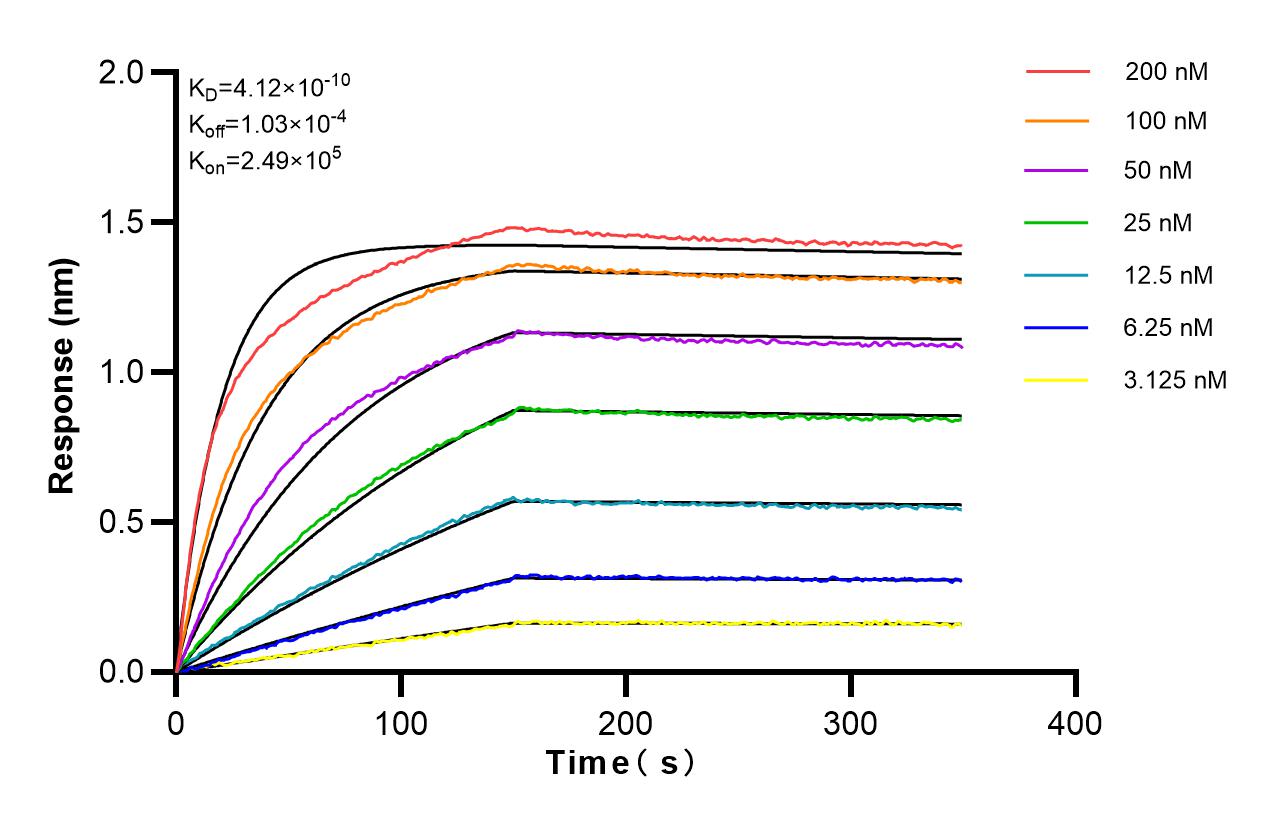
Product Information
82712-5-PBS targets YY1 in IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag17792 Product name: Recombinant human YY1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-414 aa of BC037308 Sequence: MASGDTLYIATDGSEMPAEIVELHEIEVETIPVETIETTVVGEEEEEDDDDEDGGGGDHGGGGGHGHAGHHHHHHHHHHHPPMIALQPLVTDDPTQVHHHQEVILVQTREEVVGGDDSDGLRAEDGFEDQILIPVPAPAGGDDDYIEQTLVTVAAAGKSGGGGSSSSGGGRVKKGGGKKSGKKSYLSGGAGAAGGGGADPGNKKWEQKQVQIKTLEGEFSVTMWSSDEKKDIDHETVVEEQIIGENSPPDYSEYMTGKKLPPGGIPGIDLSDPKQLAEFARMKPRKIKEDDAPRTIACPHKGCTKMFRDNSAMRKHLHTHGPRVHVCAECGKAFVESSKLKRHQLVHTGEKPFQCTFEGCGKRFSLDFNLRTHVRIHTGDRPYVCPFDGCNKKFAQSTNLKSHILTHAKAKNNQ Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | YY1 transcription factor |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 414 aa, 45 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC037308 |
| Gene Symbol | YY1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7528 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P25490 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
YY1, also named as DELTA, INO80S and NF-E1, contains four C2H2-type zinc fingers and belongs to the YY transcription factor family. YY1 is a multifunctional transcription factor that exhibits positive and negative control on a large number of cellular and viral genes by binding to sites overlapping the transcription start site. YY1 may direct histone deacetylases and histone acetyltransferases to a promoter in order to activate or repress the promoter, thus implicating histone modification in the YY1. The open reading frame of the human YY1 cDNA encodes a protein of 414 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of 44 kDa. However, YY1 migrates on SDS gels as a 65-68 kDa protein, probably due to the structure of the protein. It is a ubiquitously expressed transcription factor with fundamental roles in embryogenesis, differentiation, replication and proliferation.