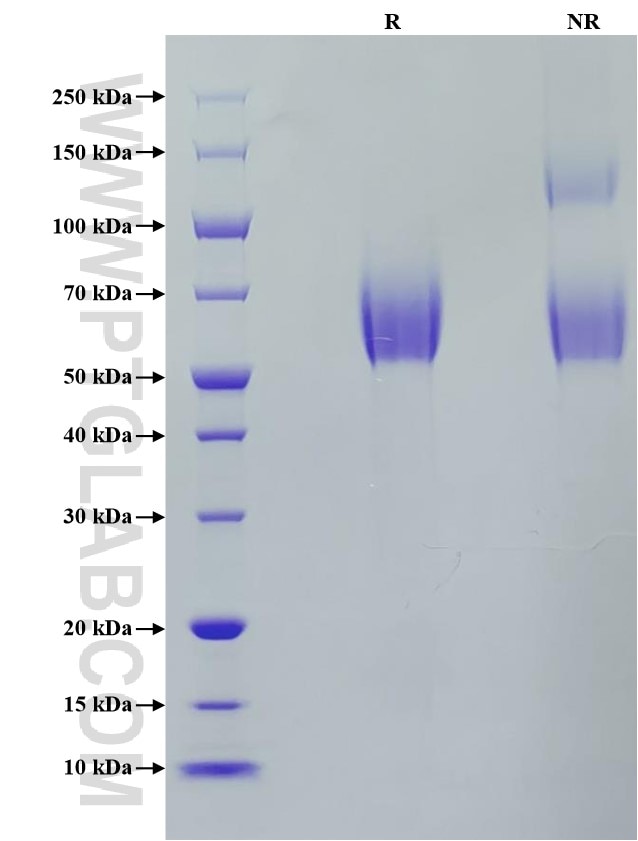
Recombinant Human CEACAM-8 protein (Myc Tag, His Tag)
Species
Human
Purity
>95 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
Myc Tag, His Tag
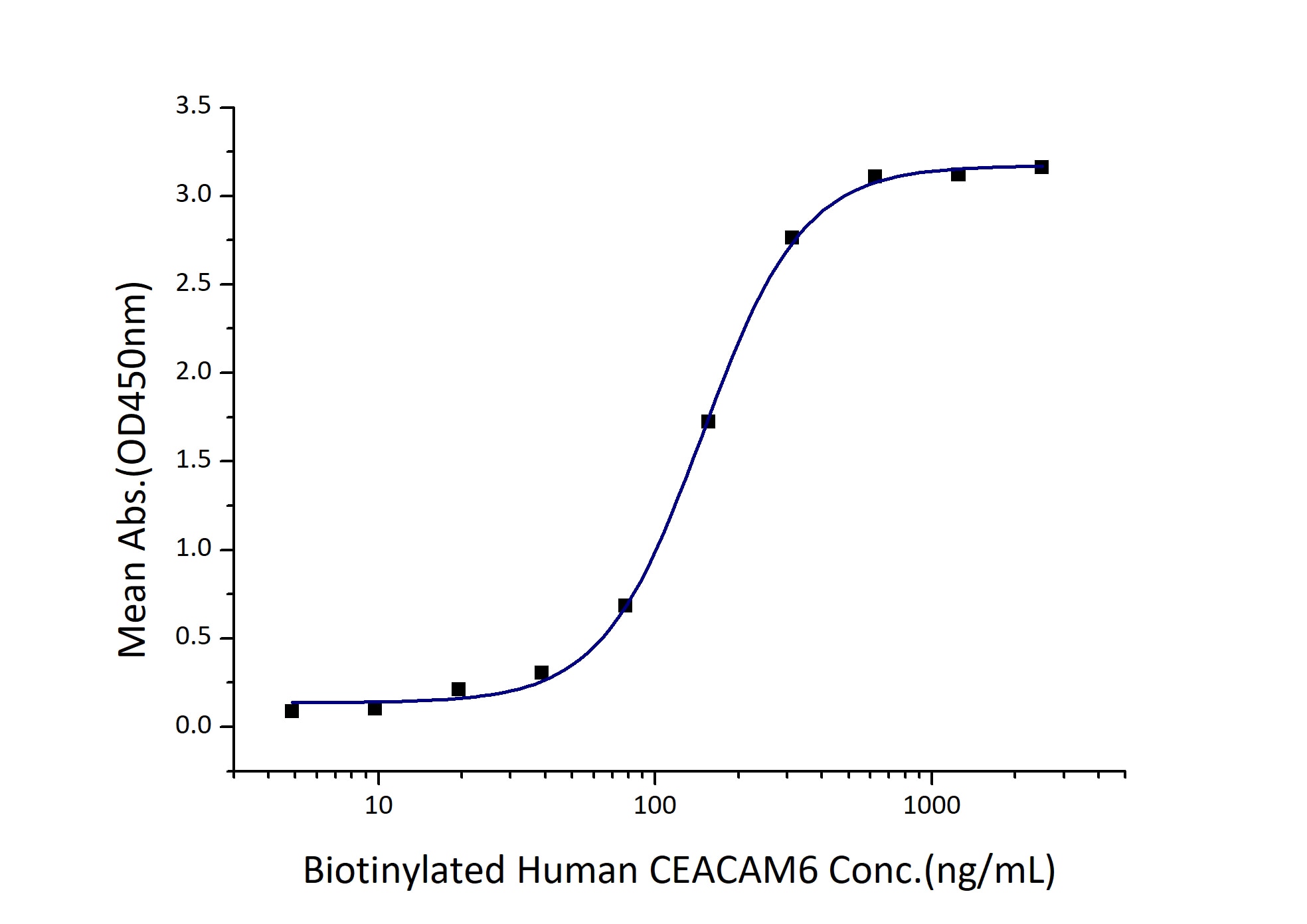
Activity
EC50: 75-300 ng/mL
Cat no : Eg32133
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >95 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Immobilized Human CEACAM-8 (Myc tag, His tag) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Biotinylated Human CEACAM-6 (Myc tag, His tag) with a linear range of 75-300 ng/mL. |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human CEACAM-8 protein Gln35-Ser319 (Accession# P31997) with a Myc tag and a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 1088 |
| Accession | P31997 |
| PredictedSize | 36.4 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 55-70 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
A glycosylphosphatidyl-inositol-(GPI)-anchored glycoprotein, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-related cell adhesion molecule 8 (CEACAM8), also known as CD66b, NCA-95 and CD67, was identified in human neutrophils. It is solely expressed by granulocytes, of which 95% are polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN). CEACAM8 is cell-adhesion proteins on neutrophils that belong to the human carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) family. CEA family members are believed to function as intercellular adhesion molecules in vitro. CEACAM8 has been shown to adhere to the closely related molecule CEACAM6 (NCA-50/90 and CD66c), suggesting a role in the interaction between granulocytes or between granulocytes and epithelial cells expressing CEACAM6 in vivo.
References:
1.F Buchegger. et al. (1984). Int J Cancer. 33(5):643-649. 2.Linshu Zhao. et al. (2004). Br J Haematol. 125(5):666-673. 3.M Kuroki. et al. (2001). J Leukoc Biol. 70(4):543-550. 4.S Oikawa. et al. (1991). J Biol Chem. 266(13):7995-8001. 5.T Yamanka. et al. (1996). Biochem Biophys Res Commun.219(3):842-847.