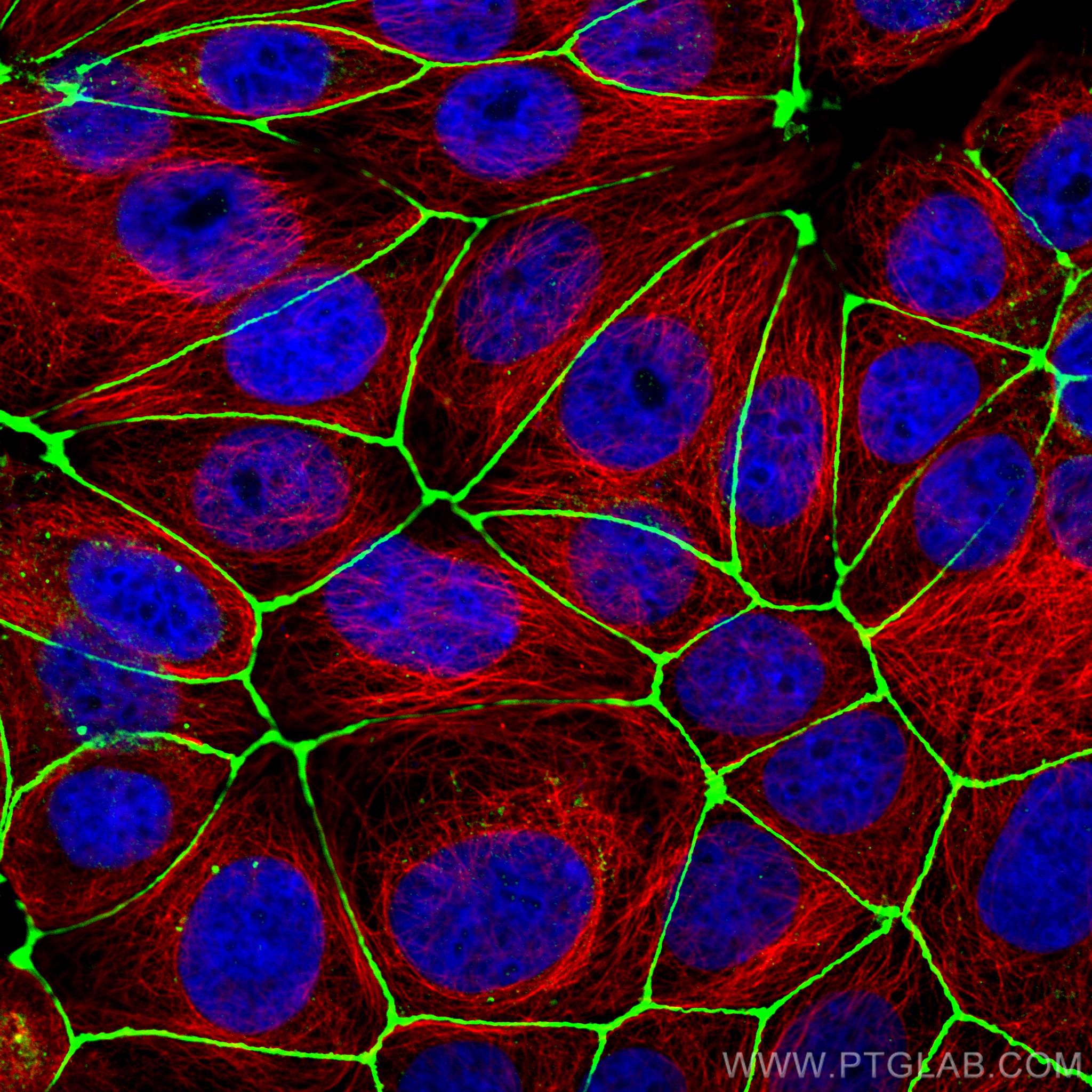
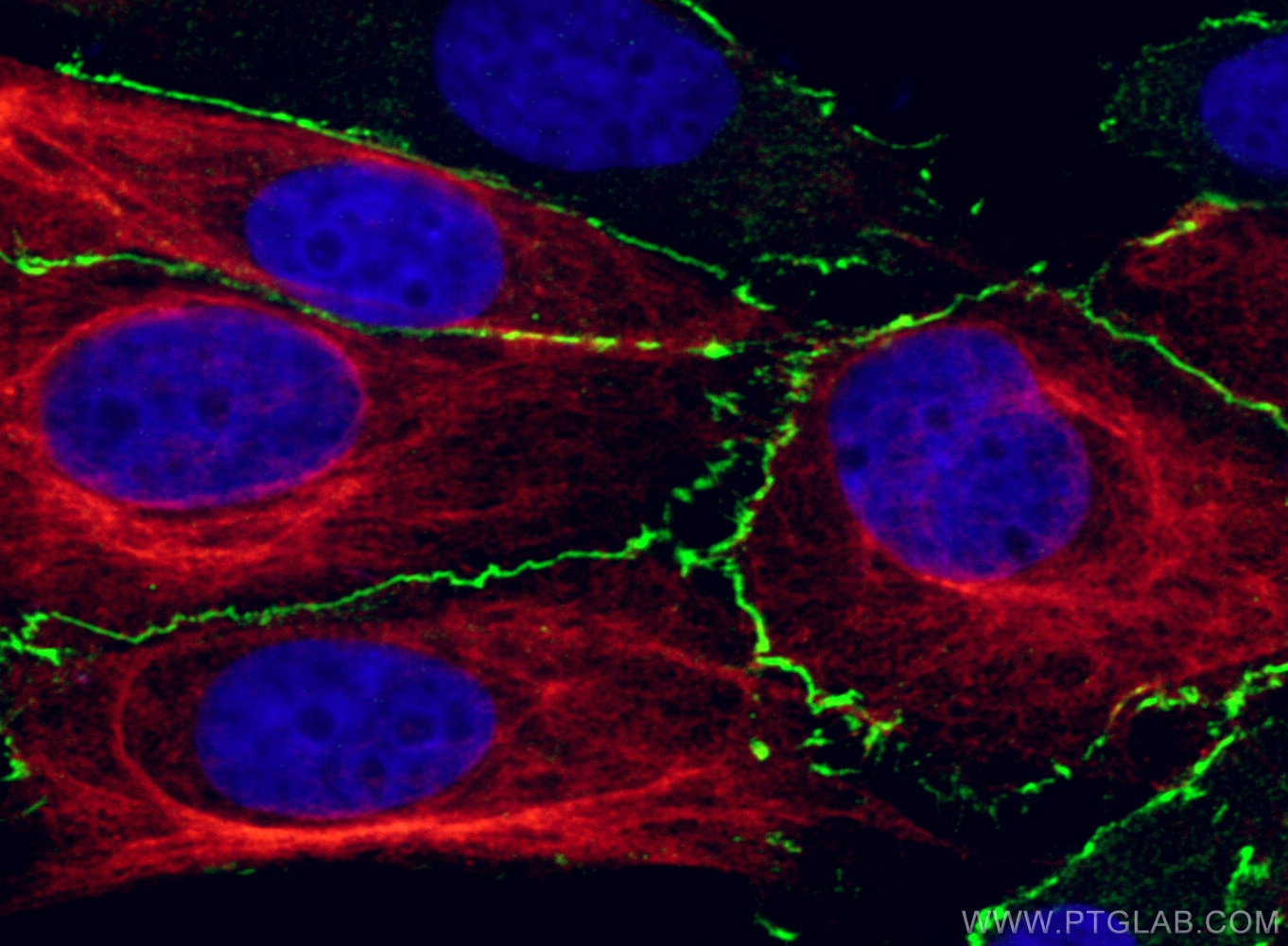
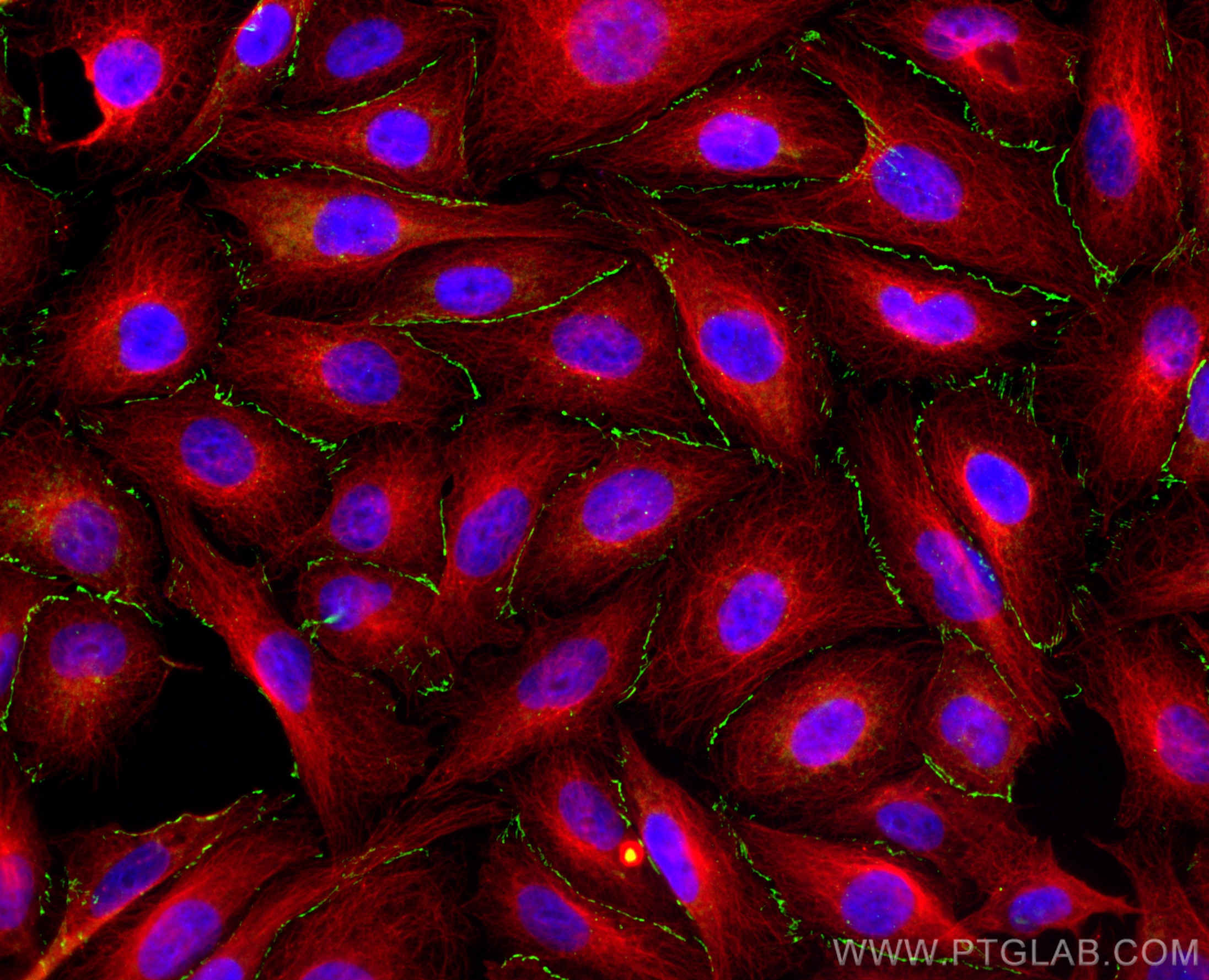
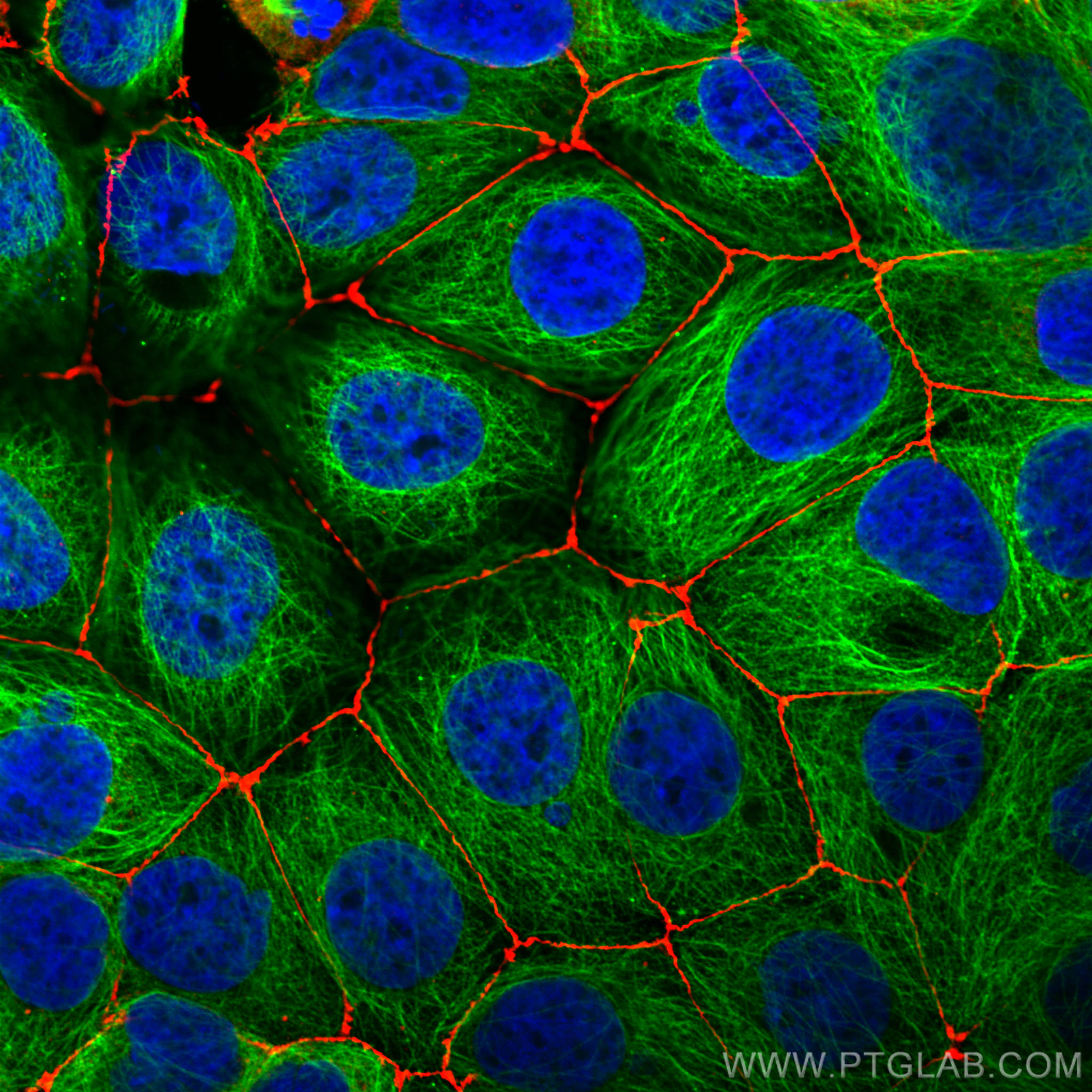
Tested Applications
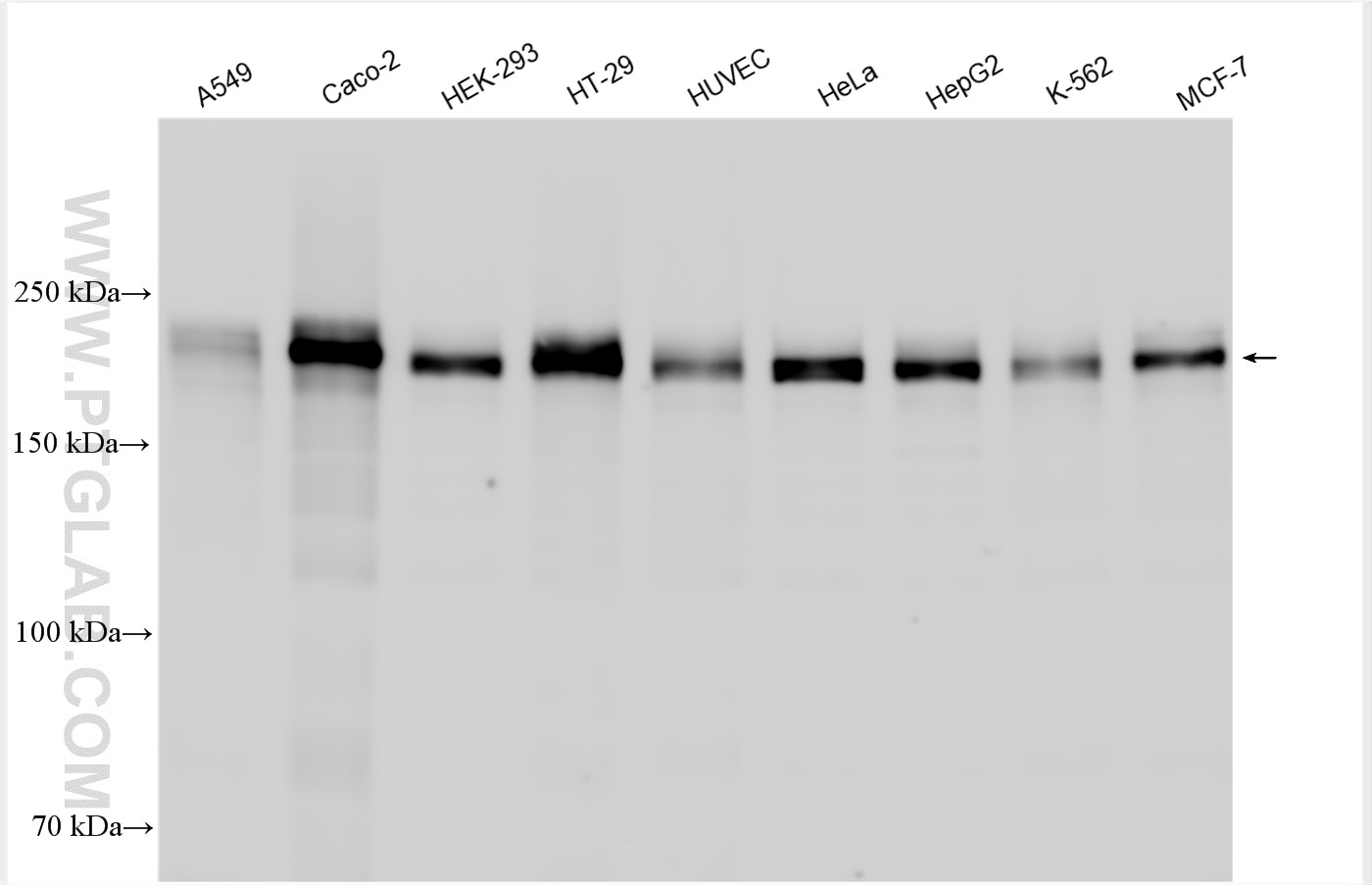
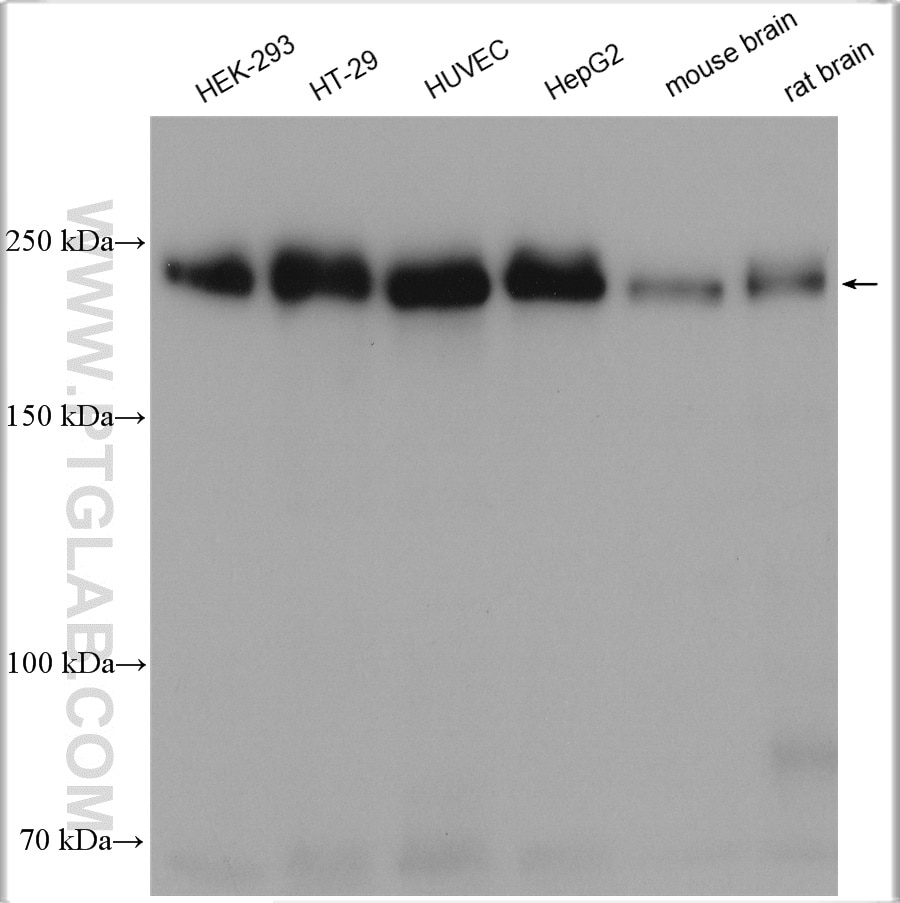
| Positive WB detected in | A549 cells, HEK-293 cells, NIH/3T3 cells, Caco-2 cells, HT-29 cells, HUVEC cells, HeLa cells, HepG2 cells, K-562 cells, MCF-7 cells, mouse brain tissue, rat brain tissue, Neuro-2a cells |
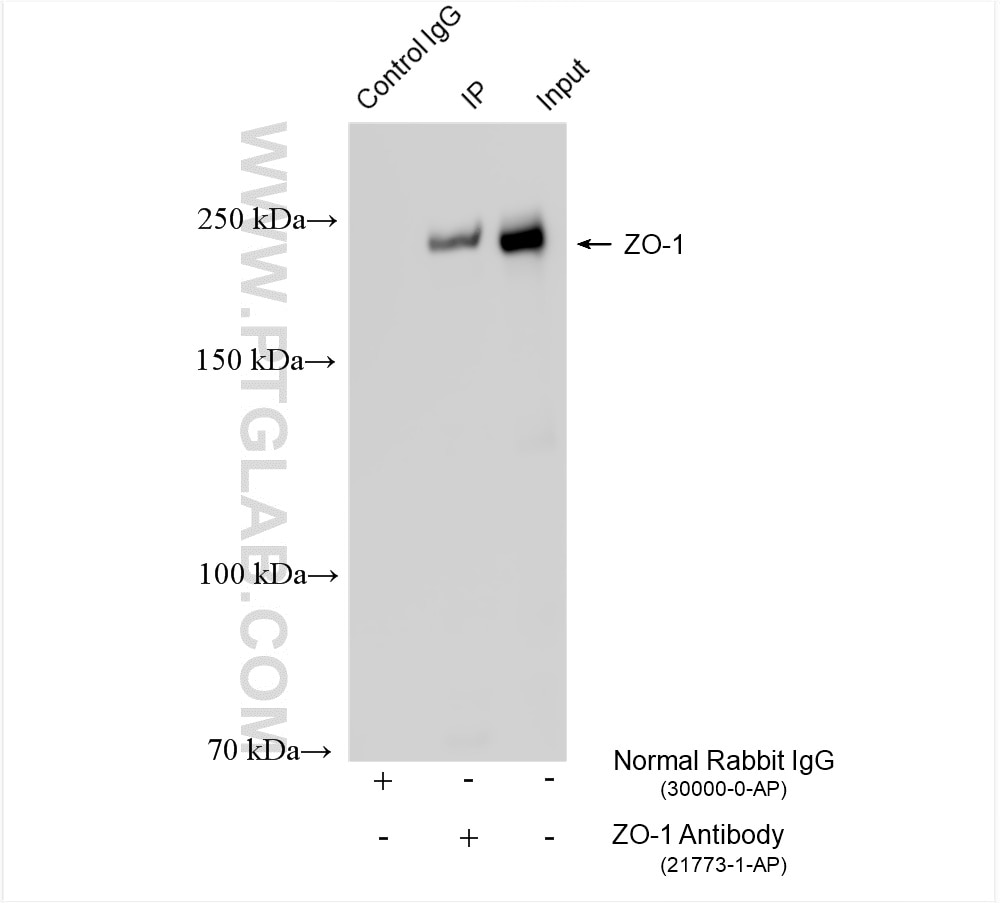
| Positive IP detected in | HEK-293 cells |
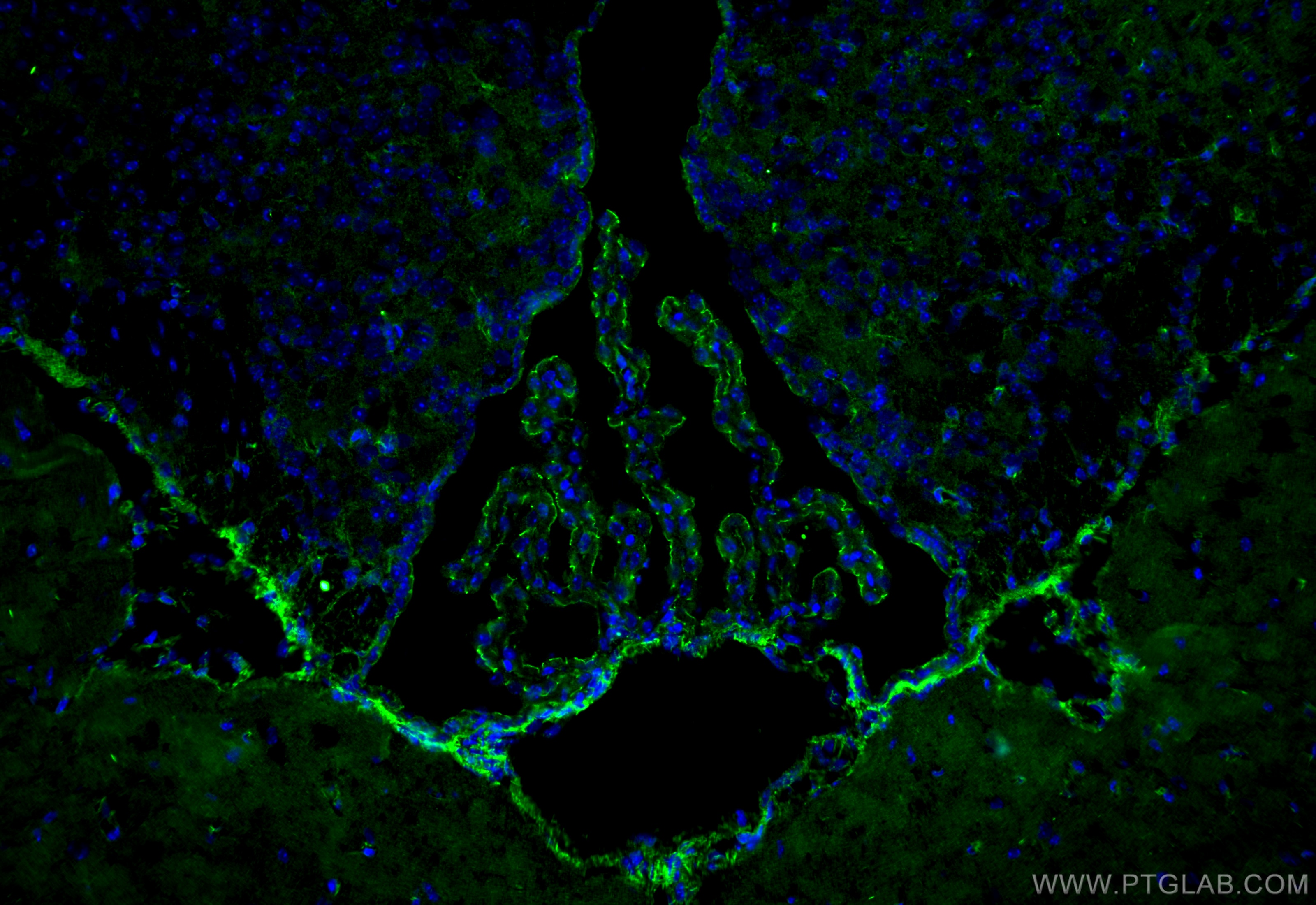
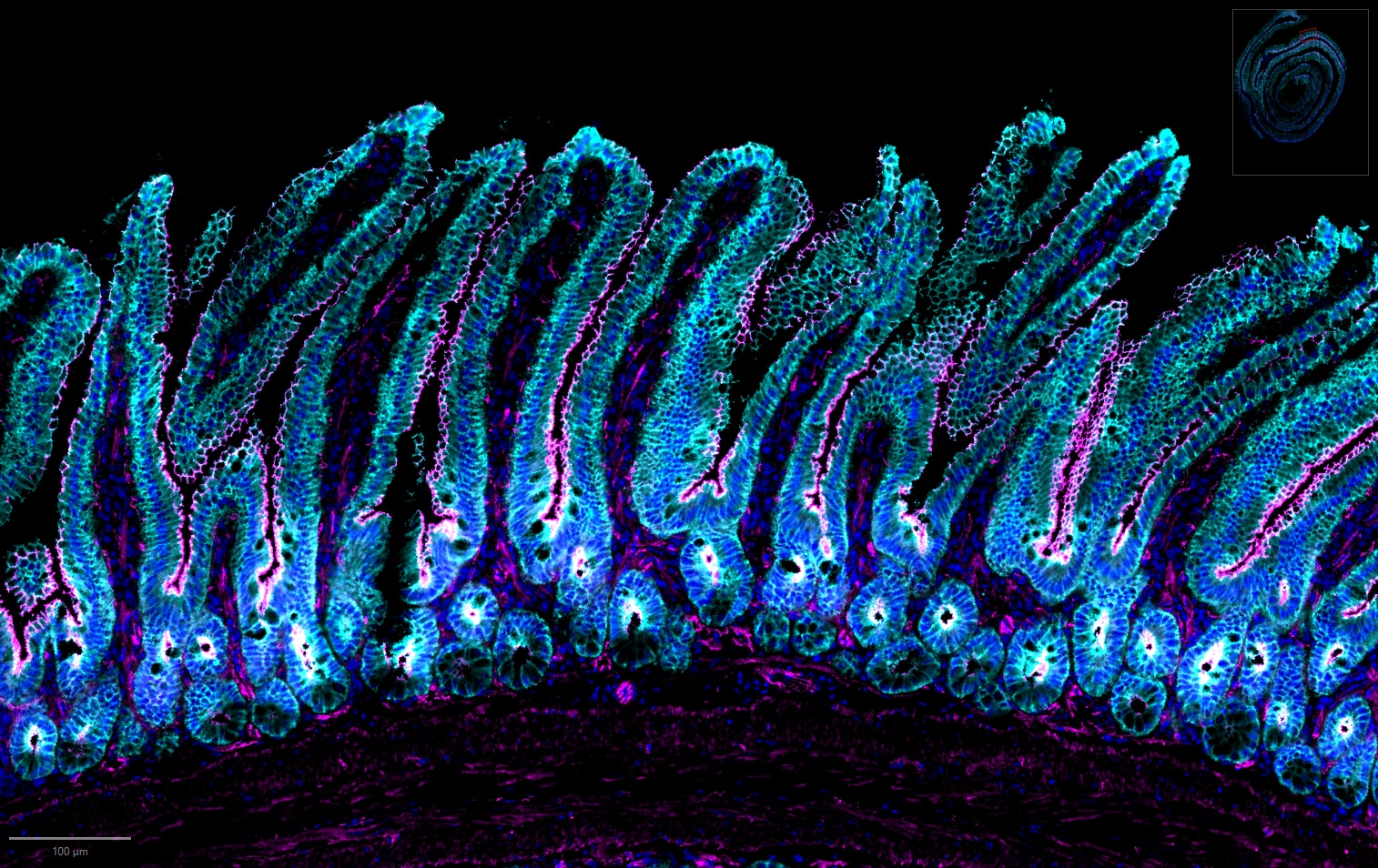
| Positive IF-Fro detected in | mouse brain tissue |
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | MCF-7 cells, MDCK cells, HUVEC cells |
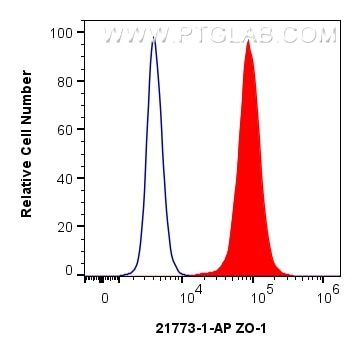
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | MCF-7 cells |
Freshly prepared samples are recommended.
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-FRO | IF-FRO : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:100-1:2000 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.80 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 4 publications below |
| WB | See 1191 publications below |
| IHC | See 228 publications below |
| IF | See 686 publications below |
| ELISA | See 1 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
| RIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
21773-1-AP targets ZO-1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-Fro, FC (Intra), IP, CoIP, RIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, canine, hamster samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, canine, hamster |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, pig, rabbit, canine, chicken, bovine, goat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag16454 Product name: Recombinant human ZO1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1446-1748 aa of BC111712 Sequence: SLHIHSKGAHGEGNSVSLDFQNSLVSKPDPPPSQNKPATFRPPNREDTAQAAFYPQKSFPDKAPVNGTEQTQKTVTPAYNRFTPKPYTSSARPFERKFESPKFNHNLLPSETAHKPDLSSKTPTSPKTLVKSHSLAQPPEFDSGVETFSIHAEKPKYQINNISTVPKAIPVSPSAVEEDEDEDGHTVVATARGIFNSNGGVLSSIETGVSIIIPQGAIPEGVEQEIYFKVCRDNSILPPLDKEKGETLLSPLVMCGPHGLKFLKPVELRLPHCDPKTWQNKCLPGDPNYLVGANCVSVLIDHF Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | tight junction protein 1 (zona occludens 1) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 1748 aa, 195 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 230 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC111712 |
| Gene Symbol | ZO-1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7082 |
| RRID | AB_10733242 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q07157 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
What is the function of ZO-1?
Zona Occludens 1 (ZO-1) is a tight junction (TJ) protein found in complexes at cell-cell contacts. The role of ZO-1 is to recruit other TJ proteins.1,2 The resulting TJ complexes regulate paracellular flow, contribute to apical-basal polarity, and are part of signaling pathways for proliferation and differentiation.3 This protein is useful for highlighting cell-cell contacts both in cultured cells and in tissue samples, outlining cell membranes and specific structures.
Where is ZO-1 expressed?
The protein is localized to the cytoplasmic membrane in most types of cells, particularly where a barrier function is essential. It is common in endothelial cells,4 which line the internal surface of blood and lymph vessels, and in epithelial cells,5 which form the outer barrier of organs.
ZO-1 is expressed in many tissues including the intestine, kidney, liver, and skeletal muscle cells.
What proteins does ZO-1 interact with?
ZO-1 contains multiple distinct protein domains that allow bind to other junctional proteins at the cytoplasmic membrane. The N-terminal of ZO-1 can dimerize with other ZO proteins and bind directly to other TJ proteins including claudins, connexions, and JAMs,6-10 which allows it to assemble TJ complexes. The C-terminal can interact with actin and cortactin, anchoring the TJ complexes to the cytoskeleton.8,11 This suggests that ZO-1 forms a link between the outer cell-cell contacts and the inner actin.
What is the molecular weight of ZO-1?
ZO-1 has an apparent molecular weight of 210-225 kDa. There are two isoforms of ZO-1, α+ and α-, which are produced by alternative RNA splicing and differ in the presence or absence of an internal 80-amino acid domain12,13. In some literature, the bands with a molecular weight of 250-260 kDa can also be detected for ZO-114,15,16,17.
1. McNeil, E., Capaldo, C. T. & Macara, I. G. Zonula occludens-1 function in the assembly of tight junctions in Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 17, 1922-32 (2006).
2. Kratzer, I. et al. Complexity and developmental changes in the expression pattern of claudins at the blood-CSF barrier. Histochem. Cell Biol. (2012). doi:10.1007/s00418-012-1001-9
3. Guillemot, L., Paschoud, S., Pulimeno, P., Foglia, A. & Citi, S. The cytoplasmic plaque of tight junctions: A scaffolding and signalling center. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Biomembr. 1778, 601-613 (2008).
4. Tornavaca, O. et al. ZO-1 controls endothelial adherens junctions, cell-cell tension, angiogenesis, and barrier formation. J. Cell Biol. 208, 821-38 (2015).
5. Umeda, K. et al. Establishment and characterization of cultured epithelial cells lacking expression of ZO-1. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 44785-94 (2004).
6. Stevenson, B. R. Identification of ZO-1: a high molecular weight polypeptide associated with the tight junction (zonula occludens) in a variety of epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 103, 755-766 (1986).
7. Itoh, M. et al. Direct Binding of Three Tight Junction-Associated Maguks, Zo-1, Zo-2, and Zo-3, with the Cooh Termini of Claudins. J. Cell Biol. 147, 1351-1363 (1999).
8. Fanning, A. S., Jameson, B. J., Jesaitis, L. A. & Anderson, J. M. The Tight Junction Protein ZO-1 Establishes a Link between the Transmembrane Protein Occludin and the Actin Cytoskeleton. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 29745-29753 (1998).
9. Kausalya, P. J., Reichert, M. & Hunziker, W. Connexin45 directly binds to ZO-1 and localizes to the tight junction region in epithelial MDCK cells. FEBS Lett. 505, 92-96 (2001).
10. Itoh, M. et al. Junctional adhesion molecule (JAM) binds to PAR-3. J. Cell Biol. 154, 491-498 (2001).
11. Itoh, M., Nagafuchi, A., Moroi, S. & Tsukita, S. Involvement of ZO-1 in Cadherin-based Cell Adhesion through Its Direct Binding to α Catenin and Actin Filaments. J. Cell Biol. 138, 181-192 (1997).
12. Balda MS, Anderson JM. Two classes of tight junctions are revealed by ZO-1 isoforms. Am J Physiol. 264, (4 Pt 1):C918-24 (1993).
13. Sheth B, Fesenko I, Collins JE, Moran B, Wild AE, Anderson JM, Fleming TP. Tight junction assembly during mouse blastocyst formation is regulated by late expression of ZO-1 alpha+ isoform. Development. 124, (10):2027-37(1997).
14. Lassiter R, Merchen TD, Fang X, Wang Y. Protective Role of Kynurenine 3-Monooxygenase in Allograft Rejection and Tubular Injury in Kidney Transplantation. Front Immunol. 7, 12:671025 (2021).
15. Rempe RG, Hartz AMS, Soldner ELB, Sokola BS, Alluri SR, Abner EL, Kryscio RJ, Pekcec A, Schlichtiger J, Bauer B. Matrix Metalloproteinase-Mediated Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Epilepsy. J Neurosci. 2, 38(18):4301-4315 (2018).
16. Lin SC, Way EL. Effects of morphine and B-endorphin on Ca2+-ATPase activity of synaptic plasma membranes. NIDA Res Monogr. 75, 117-20(1986).
17. Wu Z, Mirza H, Teo JD, Tan KS. Strain-dependent induction of human enterocyte apoptosis by blastocystis disrupts epithelial barrier and ZO-1 organization in a caspase 3- and 9-dependent manner. Biomed Res Int. 2014, 209163(2014).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for ZO-1 antibody 21773-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for ZO-1 antibody 21773-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for ZO-1 antibody 21773-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for ZO-1 antibody 21773-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Am J Respir Crit Care Med Ezrin, a Membrane Cytoskeleton Cross Linker Protein, as a Marker of Epithelial Damage in Asthma. | ||
Cell Metab Gut microbiota modulate distal symmetric polyneuropathy in patients with diabetes | ||
Cell Stem Cell Human branching cholangiocyte organoids recapitulate functional bile duct formation. | ||
Nat Commun Calcium transients regulate the apical emergence of basally located progenitors during Xenopus skin development | ||
Microbiome Arula-7 powder improves diarrhea and intestinal epithelial tight junction function associated with its regulation of intestinal flora in calves infected with pathogenic Escherichia coli O1 | ||
Microbiome Dietary emulsifier carboxymethylcellulose-induced gut dysbiosis and SCFA reduction aggravate acute pancreatitis through classical monocyte activation |
Reviews
The reviews below have been submitted by verified Proteintech customers who received an incentive for providing their feedback.
FH Lee (Verified Customer) (02-04-2026) | ZO-1 Polyclonal antibody has worked well in our study for immunostaining of ZO-1 on rd12 mcie in genome editing projects
|
FH Emily (Verified Customer) (07-31-2025) | Worked well. Images looked good. Murine lung was paraffin fixed and antigen retrieval was conducted prior to the staining. Antibody was diluted 1:400 and incubated for 2hr in a humidity chamber in the dark.
|
FH Ling (Verified Customer) (10-09-2024) | I tried different antibody before I found this one. All didn't work, but this one works well.
|
FH Natalia (Verified Customer) (07-10-2024) | Used the dilution recommended (1:2000) and did not work. Haven't had the chance to re-try yet
|
FH Sarah (Verified Customer) (03-20-2024) | The antibody works perfect.
 |
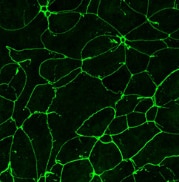
FH Xie (Verified Customer) (10-26-2021) | Efficient Labelling from proteintech ZO1 Antibody
 |
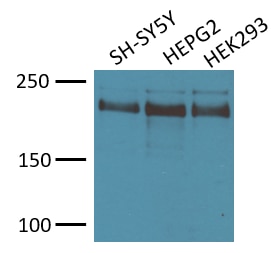
FH Samuel (Verified Customer) (08-06-2021) | Clean and strong band at 220-230 kDa in WB (reducing and denaturing conditions). I used the antibody at a 1:2500 dilution in 5% milk, incubation overnight at 4 degrees Celsius. 30ug loaded per sample.
 |