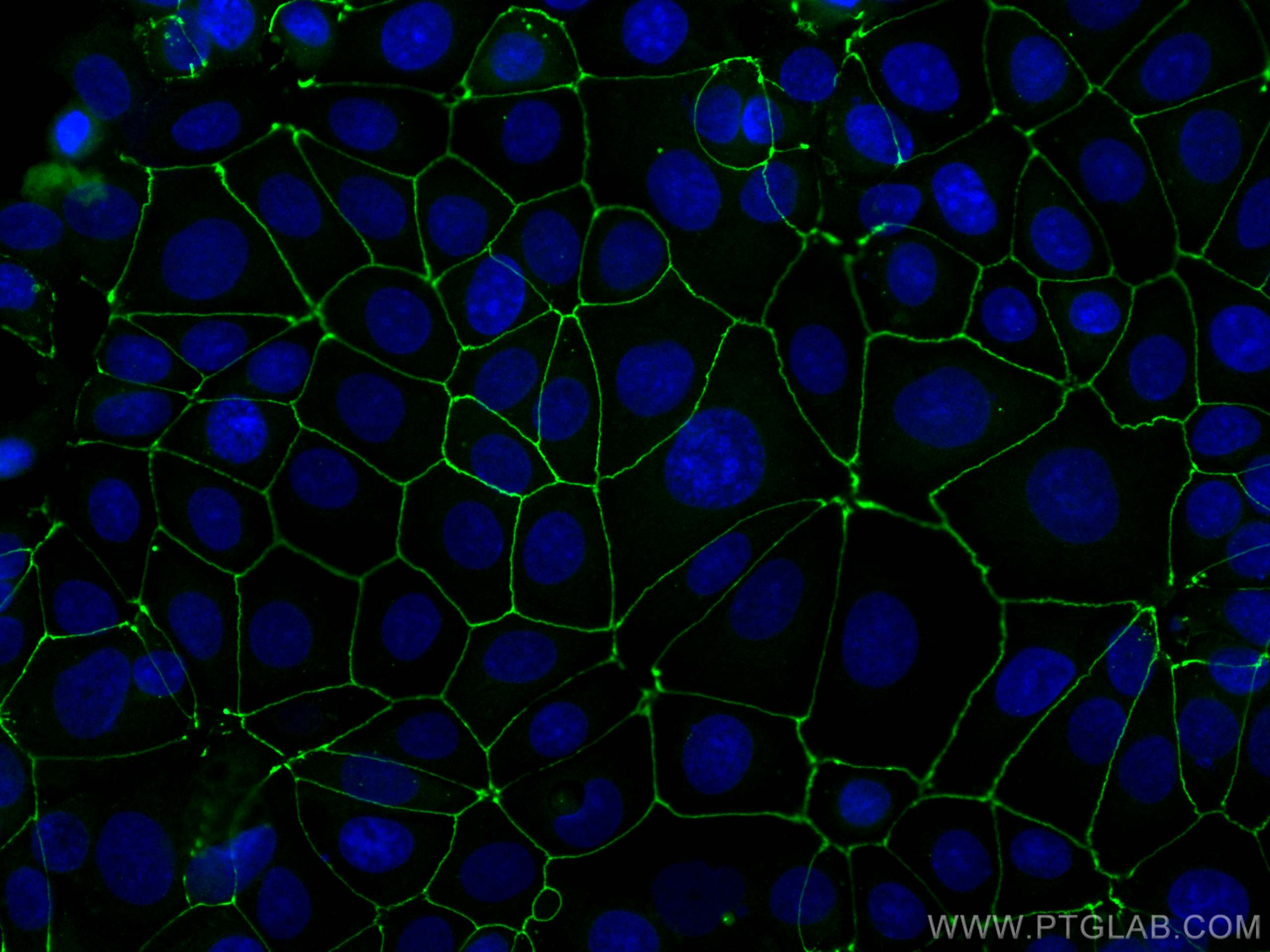
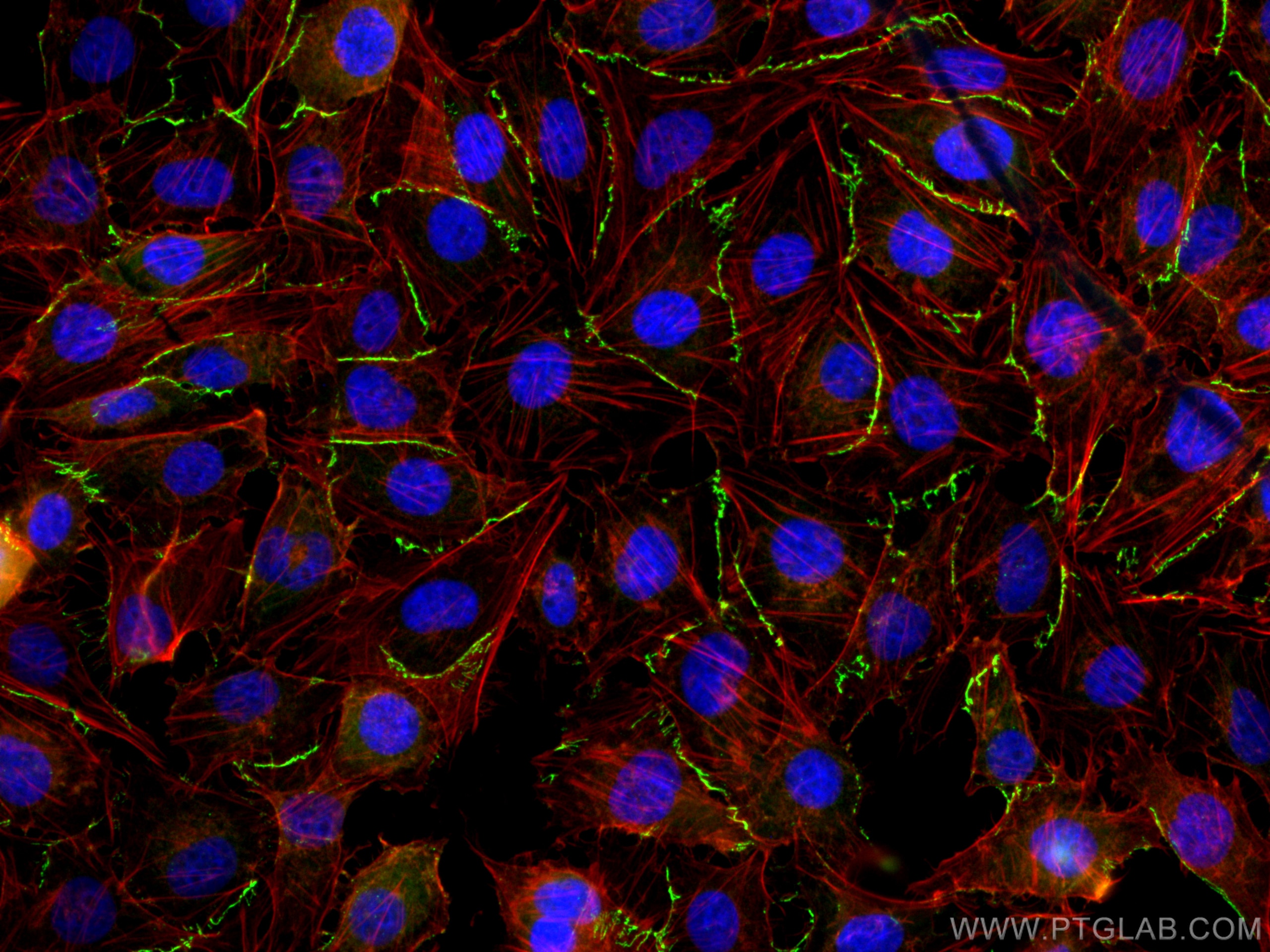
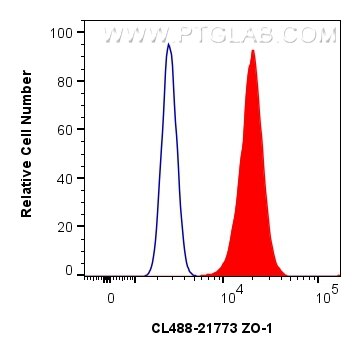
Tested Applications
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | MCF-7 cells, HUVEC cells |
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | MCF-7 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| IF | See 7 publications below |
Product Information
CL488-21773 targets ZO-1 in IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra) applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, canine, hamster samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, canine, hamster |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag16454 Product name: Recombinant human ZO1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1446-1748 aa of BC111712 Sequence: SLHIHSKGAHGEGNSVSLDFQNSLVSKPDPPPSQNKPATFRPPNREDTAQAAFYPQKSFPDKAPVNGTEQTQKTVTPAYNRFTPKPYTSSARPFERKFESPKFNHNLLPSETAHKPDLSSKTPTSPKTLVKSHSLAQPPEFDSGVETFSIHAEKPKYQINNISTVPKAIPVSPSAVEEDEDEDGHTVVATARGIFNSNGGVLSSIETGVSIIIPQGAIPEGVEQEIYFKVCRDNSILPPLDKEKGETLLSPLVMCGPHGLKFLKPVELRLPHCDPKTWQNKCLPGDPNYLVGANCVSVLIDHF Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | tight junction protein 1 (zona occludens 1) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 1748 aa, 195 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 230 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC111712 |
| Gene Symbol | ZO-1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7082 |
| RRID | AB_2919182 |
| Conjugate | CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 493 nm / 522 nm |
| Excitation Laser | Blue laser (488 nm) |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q07157 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
What is the function of ZO-1?
Zona Occludens 1 (ZO-1) is a tight junction (TJ) protein found in complexes at cell-cell contacts. The role of ZO-1 is to recruit other TJ proteins.1,2 The resulting TJ complexes regulate paracellular flow, contribute to apical-basal polarity, and are part of signaling pathways for proliferation and differentiation.3 This protein is useful for highlighting cell-cell contacts both in cultured cells and in tissue samples, outlining cell membranes and specific structures.
Where is ZO-1 expressed?
The protein is localized to the cytoplasmic membrane in most types of cells, particularly where a barrier function is essential. It is common in endothelial cells,4 which line the internal surface of blood and lymph vessels, and in epithelial cells,5 which form the outer barrier of organs.
ZO-1 is expressed in many tissues including the intestine, kidney, liver, and skeletal muscle cells.
What proteins does ZO-1 interact with?
The molecular weight of ZO-1 is 220kDa6 and it contains multiple distinct protein domains that allow bind to other junctional proteins at the cytoplasmic membrane. The N-terminal of ZO-1 can dimerize with other ZO proteins and bind directly to other TJ proteins including claudins, connexions, and JAMs,7-10 which allows it to assemble TJ complexes. The C-terminal can interact with actin and cortactin, anchoring the TJ complexes to the cytoskeleton.8,11 This suggests that ZO-1 forms a link between the outer cell-cell contacts and the inner actin.
1. McNeil, E., Capaldo, C. T. & Macara, I. G. Zonula occludens-1 function in the assembly of tight junctions in Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 17, 1922-32 (2006).
2. Kratzer, I. et al. Complexity and developmental changes in the expression pattern of claudins at the blood-CSF barrier. Histochem. Cell Biol. (2012). doi:10.1007/s00418-012-1001-9
3. Guillemot, L., Paschoud, S., Pulimeno, P., Foglia, A. & Citi, S. The cytoplasmic plaque of tight junctions: A scaffolding and signalling center. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Biomembr. 1778, 601-613 (2008).
4. Tornavaca, O. et al. ZO-1 controls endothelial adherens junctions, cell-cell tension, angiogenesis, and barrier formation. J. Cell Biol. 208, 821-38 (2015).
5. Umeda, K. et al. Establishment and characterization of cultured epithelial cells lacking expression of ZO-1. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 44785-94 (2004).
6. Stevenson, B. R. Identification of ZO-1: a high molecular weight polypeptide associated with the tight junction (zonula occludens) in a variety of epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 103, 755-766 (1986).
7. Itoh, M. et al. Direct Binding of Three Tight Junction-Associated Maguks, Zo-1, Zo-2, and Zo-3, with the Cooh Termini of Claudins. J. Cell Biol. 147, 1351-1363 (1999).
8. Fanning, A. S., Jameson, B. J., Jesaitis, L. A. & Anderson, J. M. The Tight Junction Protein ZO-1 Establishes a Link between the Transmembrane Protein Occludin and the Actin Cytoskeleton. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 29745-29753 (1998).
9. Kausalya, P. J., Reichert, M. & Hunziker, W. Connexin45 directly binds to ZO-1 and localizes to the tight junction region in epithelial MDCK cells. FEBS Lett. 505, 92-96 (2001).
10. Itoh, M. et al. Junctional adhesion molecule (JAM) binds to PAR-3. J. Cell Biol. 154, 491-498 (2001).
11. Itoh, M., Nagafuchi, A., Moroi, S. & Tsukita, S. Involvement of ZO-1 in Cadherin-based Cell Adhesion through Its Direct Binding to α Catenin and Actin Filaments. J. Cell Biol. 138, 181-192 (1997).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for CL Plus 488 ZO-1 antibody CL488-21773 | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for CL Plus 488 ZO-1 antibody CL488-21773 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Commun The role of extracellular vesicle fusion with target cells in triggering systemic inflammation | ||
J Nanobiotechnology Orally biomimetic metal-phenolic nanozyme with quadruple safeguards for intestinal homeostasis to ameliorate ulcerative colitis | ||
Int Immunopharmacol Hernandezine alleviates inflammatory bowel disease by enhancing gut barrier integrity via the AMPK/NRF2 pathway and regulating immune-metabolic balance | ||
Microbiol Spectr Characteristics of upper respiratory tract rhinovirus in children with allergic rhinitis and its role in disease severity | ||
Am J Pathol Restorative Effects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids on Corneal Homeostasis Disrupted by Antibiotic-Induced Gut Dysbiosis | ||
Int J Mol Sci In Vitro Analysis of Probiotic Properties Related to the Adaptation of Levilactobacillus brevis to Intestinal Microenvironment and Involvement of S-Layer Proteins |