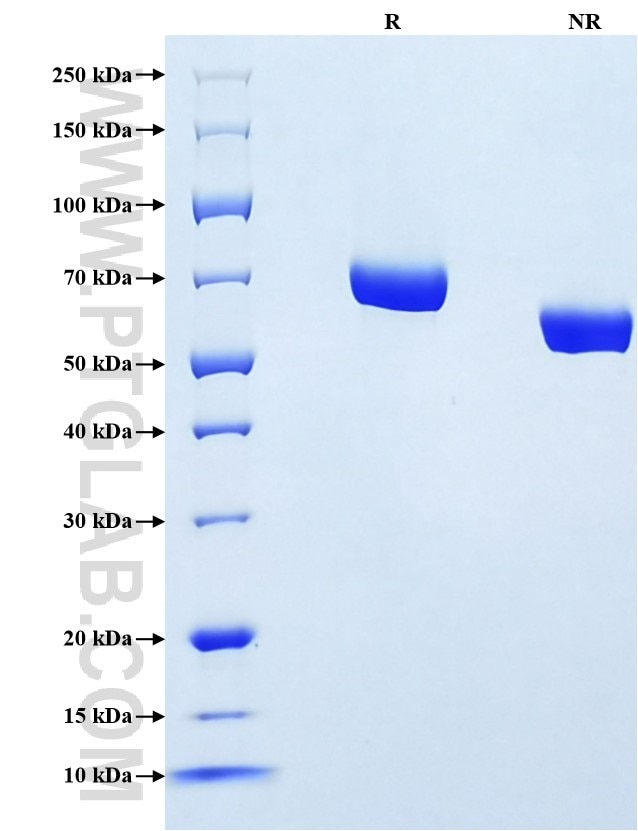
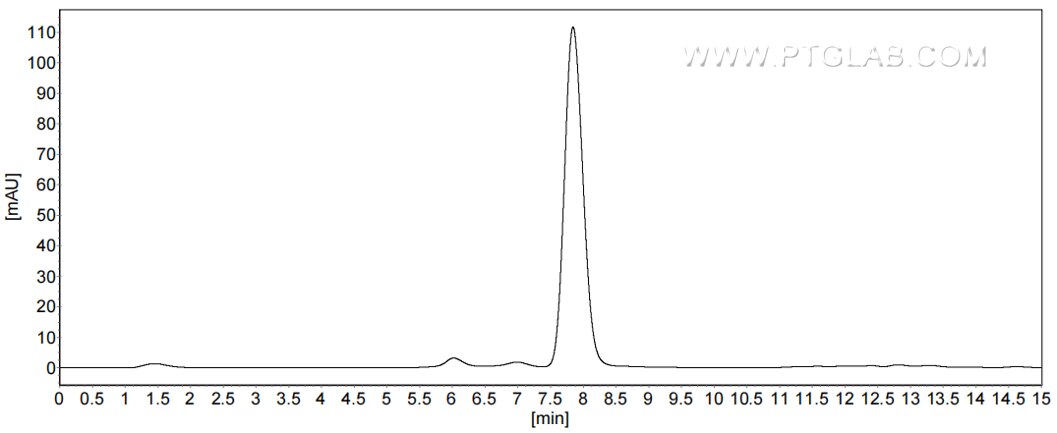
Recombinant Mouse AFP protein (His Tag)(HPLC verified)
Species
Mouse
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
>90 %, SEC-HPLC
Tag
His Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg0670
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE >90 %, SEC-HPLC |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Mouse AFP protein Lys19-Val605 (Accession# P02772) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 11576 |
| Accession | P02772 |
| PredictedSize | 66.4 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 60-75 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
AFP (alpha-fetoprotein) is a major plasma protein found in the fetus while plasma AFP level is decreased rapidly after birth. AFP is a vital marker of the hepatocyte lineage. High AFP concentrations is related with tumor cell growth. Detection of AFP in plasma is important in diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), stomach cancer and germ cell cancers. Altered levels of both fetal and maternal AFP are associated with hypothyroidism, autoimmune disorders, and heart defects. Measurement of AFP in maternal blood or amniotic fluid of pregnant women is used in screening developmental abnormalities such as aneuploidy. Serum AFP level is elevated in people with developmental birth defects and neurologic disorders.
References:
1. Rosen T, et al. (2005). Semin Perinatol. 29(6):367-75. 2. Schieving JH, et al. (2014). Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 18(3):243-8. 3. Wang X, et al. (2018). Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 9;2018:1232785. 4. Başbuğ D, et al. (2017). Ginekol Pol. 88(6):325-330.