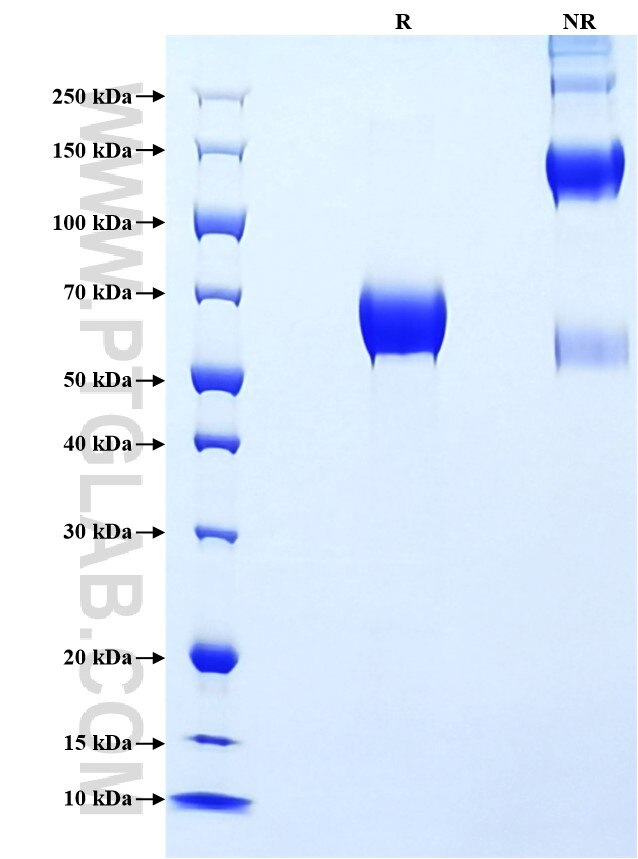
Recombinant Human TACSTD2/TROP2 protein (rFc Tag)
Species
Human
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg3329
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human TACSTD2 protein His27-Thr274 (Accession# P09758) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 4070 |
| Accession | P09758 |
| PredictedSize | 54.2 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 55-70 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
TACSTD2 encodes a transmembrane glycoprotein Trop2, that is overexpressed in most carcinomas where it has been associated with cancer cell plasticity, tumor growth, metastasis and prognosis. In humans, congenital mutations of TACSTD2 cause a gelatinous drop-like corneal disease (GDLD), a rare autosomal recessive disease characterized by the development of bilateral corneal amyloidosis and eventually blindness.Overexpression of TROP2/TACSTD2 has been shown to confer a poor prognosis, notably among patients with gynecologic or gastrointestinal tumors. TROP2/TACSTD2 has also been shown to have some impact on the tumor immune microenvironment and may modulate immunotherapy response. In cervical cancer, TROP2 levels were associated with increased intratumoral tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression.Conversely, TROP2/TACSTD2-high tumors had lower gene expression of immune cell markers in breast and non–small cell lung cancer and were independently associated with poor response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs).
References:
1.Lenárt, Sára. et al. (2022) Sci Rep. 12(1):9583. 2.Morgenstern-Kaplan, Dan. et al. (2024) Oncologist. 29(11):e1480-e1491. 3.Abbas, Mahmoud. et al. (2023) Oncol Lett. 26(6):527.