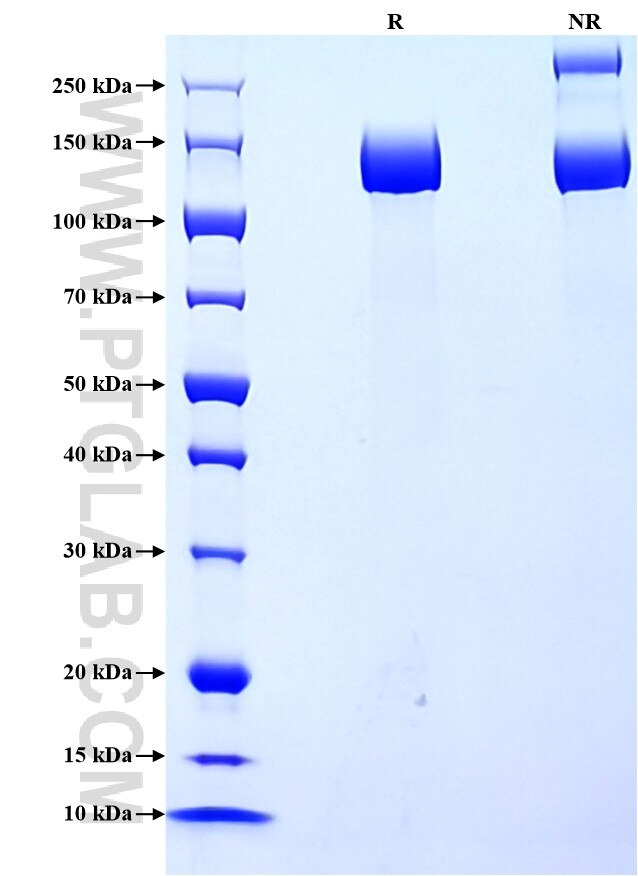
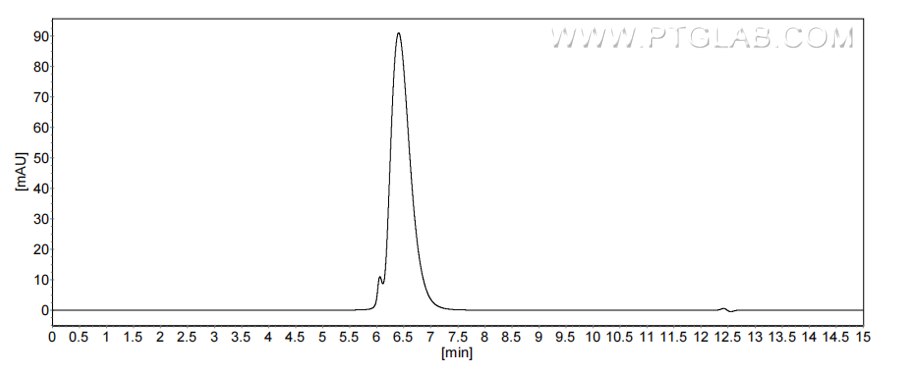
Recombinant Human CD13 protein (rFc Tag)(HPLC verified)
Species
Human
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
>90%, SEC-HPLC
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg3748
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE >90%, SEC-HPLC |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human CD13 protein Lys69-Lys967 (Accession# P15144) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 290 |
| Accession | P15144 |
| PredictedSize | 129.0 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 130-150 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
ANPEP (Aminopeptidase N) is a membrane-associated exonuclease, also known as CD13 or basic amino acid peptidase, that plays a role in glutathione metabolism and exhibits broad substrate specificity. The primary function of ANPEP is the N-terminal amino acid shearing of peptide chains, which participates in the degradation process of proteins, and is also implicated in the regulation of cell-surface antigen expression. ANPEP has been identified as a susceptibility gene for type 2 diabetes (T2D), but the mechanism by which it contributes to the development of the disease is not fully understood, and it has been suggested that it may be mediated through disruption of glutathione metabolism and redox homeostasis.
References:
1. Kim JH,et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2022;21(11):100424. 2. Korvyakova Y, et al. Gene. 2025;935:149050.