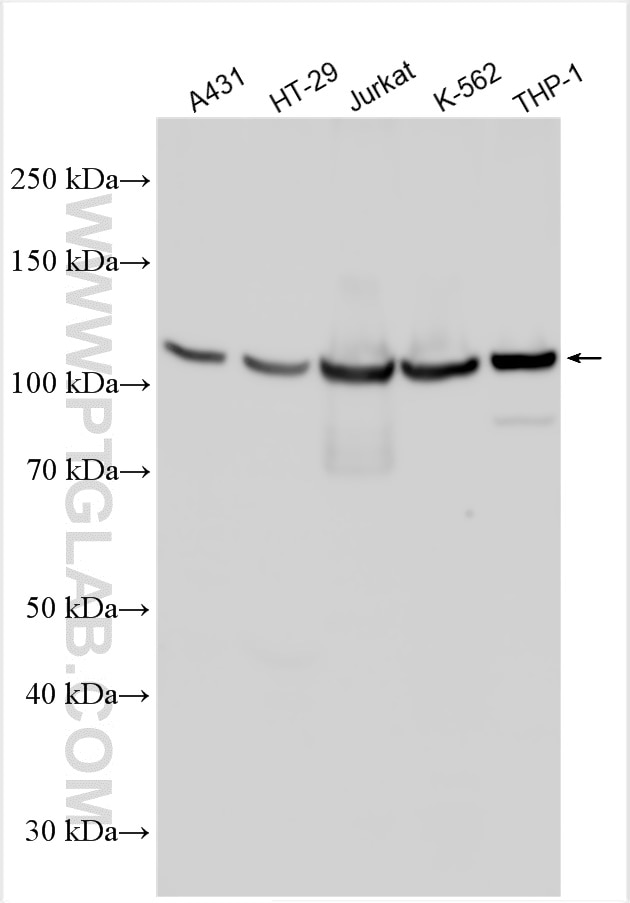
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | A431 cells, HT-29 cells, Jurkat cells, K-562 cells, THP-1 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
20703-1-AP targets ABCB5 in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Peptide Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (MDR/TAP), member 5 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 90 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 90-110 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_178559 |
| Gene Symbol | ABCB5 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 340273 |
| RRID | AB_3085616 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q2M3G0 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
ABCB5 is an 812 amino acid multi-pass membrane protein and belongs to the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily of integral membrane proteins (PMID: 15760339). ABCB5 is an Energy-dependent efflux transporter responsible for decreased drug accumulation in multidrug-resistant cells(PMID: 15899824, 15205344). ABCB5 acts as a marker of stem-like cells (CSC) in several malignancies and is responsible for the resistance to doxorubicin of a subset of malignant melanomas (PubMed:24934811, 15760339). Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for ABCB5 antibody 20703-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |