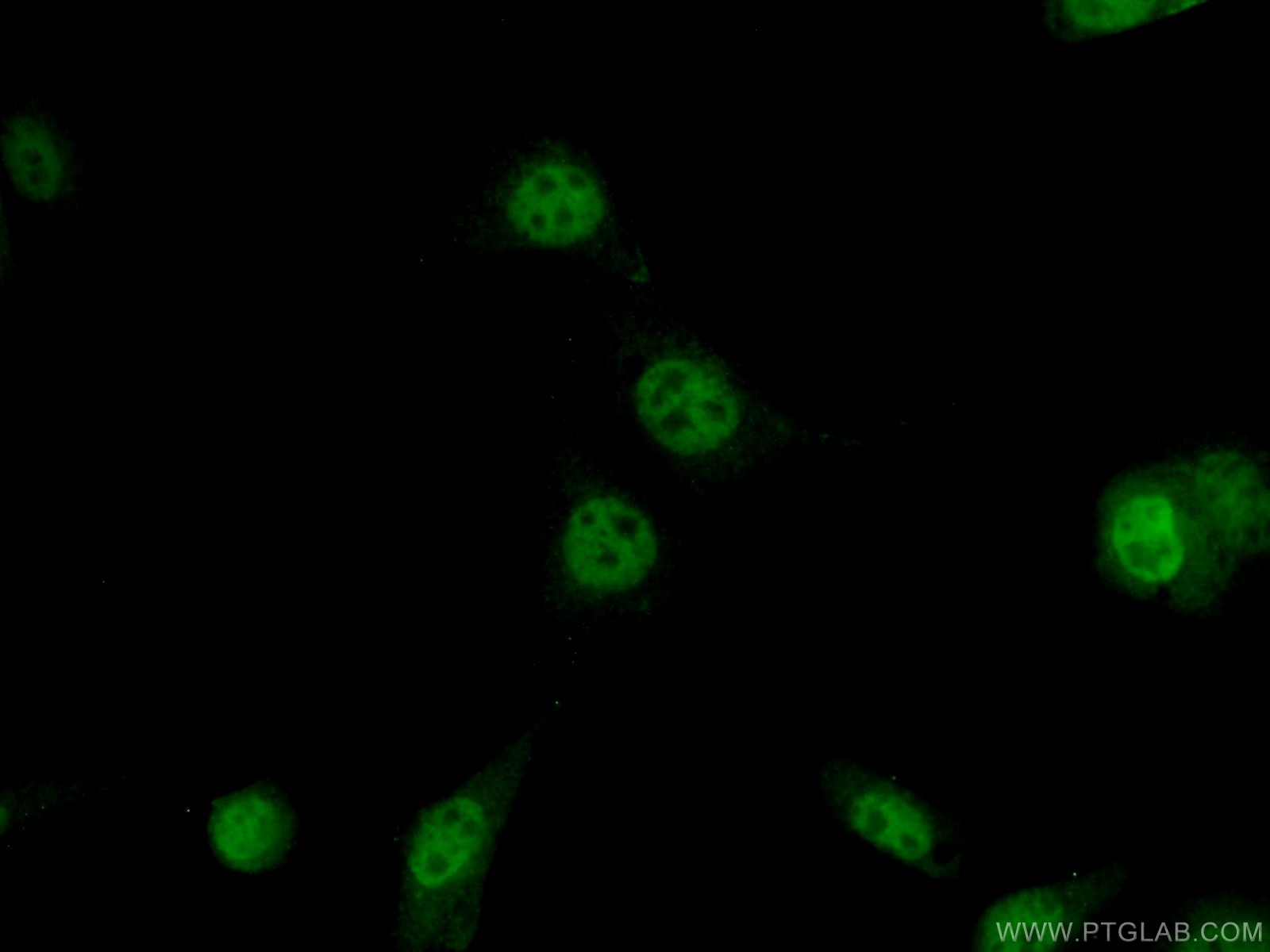
Tested Applications
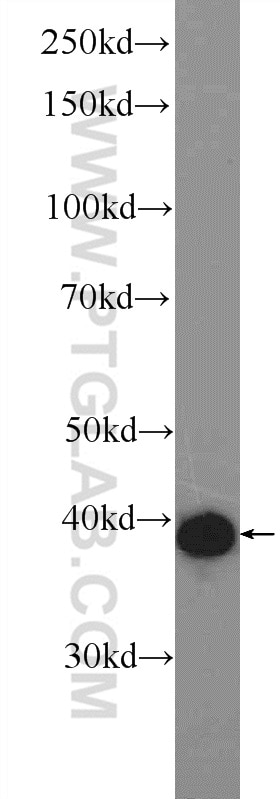
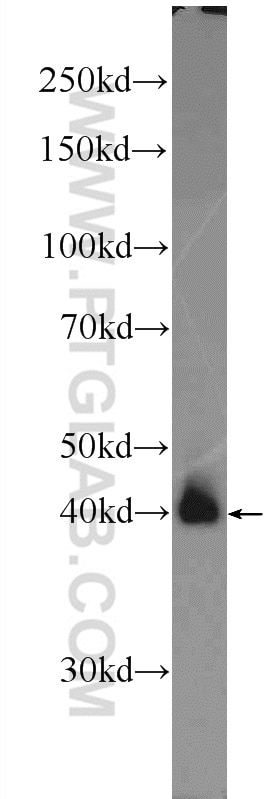
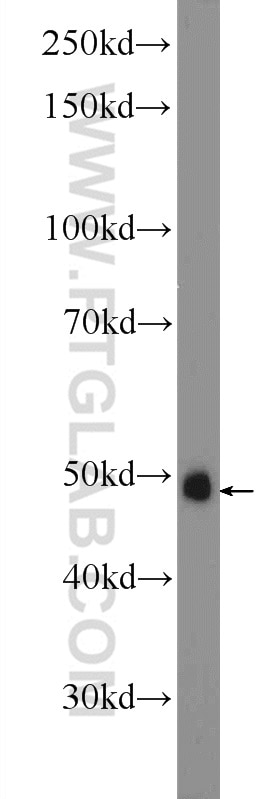
| Positive WB detected in | NIH/3T3 cells, rat brain tissue, HEK-293 cells |
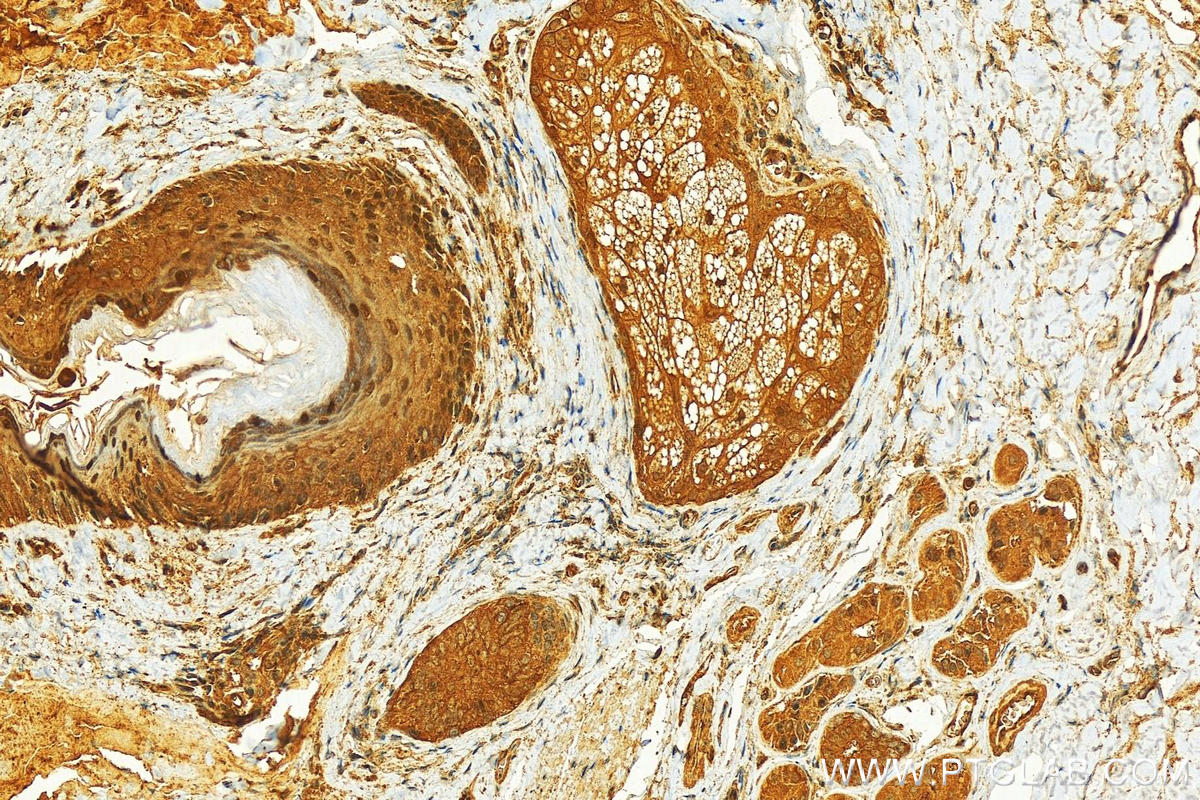
| Positive IHC detected in | human skin cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | NIH/3T3 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 9 publications below |
| ChIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
22114-1-AP targets JUN in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ChIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, monkey samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, monkey |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag17419 Product name: Recombinant human AP1,JUN,P39 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1-331 aa of BC002646 Sequence: MTAKMETTFYDDALNASFLPSESGPYGYSNPKILKQSMTLNLADPVGSLKPHLRAKNSDLLTSPDVGLLKLASPELERLIIQSSNGHITTTPTPTQFLCPKNVTDEQEGFAEGFVRALAELHSQNTLPSVTSAAQPVNGAGMVAPAVASVAGGSGSGGFSASLHSEPPVYANLSNFNPGALSSGGGAPSYGAAGLAFPAQPQQQQQPPHHLPQQMPVQHPRLQALKEEPQTVPEMPGETPPLSPIDMESQERIKAERKRMRNRIAASKCRKRKLERIARLEEKVKTLKAQNSELASTANMLREQVAQLKQKVMNHVNSGCQLMLTQQLQTF Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | jun oncogene |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 331 aa, 36 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 40-46 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC002646 |
| Gene Symbol | JUN |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3725 |
| RRID | AB_2750860 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P05412 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
JUN is also named as c-Jun and AP1, belongs to the bZIP family and Jun subfamily. JUN, the most extensively studied protein of the activator protein-1 (AP-1) complex, is involved in numerous cell activities, such as proliferation, apoptosis, survival, tumorigenesis and tissue morphogenesis (PMID: 22180088). JUN is a transcription factor that recognizes and binds to the enhancer heptamer motif 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3'. It promotes activity of NR5A1 when phosphorylated by HIPK3 leading to increased steroidogenic gene expression upon cAMP signaling pathway stimulation. JUN is a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor that acts as homo- or heterodimer, binding to DNA and regulating gene transcription (PMID: 9732876). In additon, extracellular signals can induce post-translational modifications of JUN, resulting in altered transcriptional activity and target gene expression (PMID:8464713). More over, it has uncovered multiple layers of a complex regulatory scheme in which JUN is able to crosstalk, amplify and integrate different signals for tissue development and disease. Jun is predominantly nuclear, ubiquitinated Jun colocalizes with lysosomal proteins (PMID: 15469925). This antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against a region of human JUN. Both phosphorylated (p-c-Jun) and unphosphorylated forms of c-Jun, with sizes of 42-45 kDa and 36-39 kDa, respectively are obtain in some experiments (PMID:17210646).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for JUN antibody 22114-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for JUN antibody 22114-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for JUN antibody 22114-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Neuroinflammation Downregulation of CD151 restricts VCAM-1 mediated leukocyte infiltration to reduce neurobiological injuries after experimental stroke. | ||
Int Immunopharmacol IL17A/F secreted by ASCT2-overexpression ovarian cancer cells contributes to immune escape through the suppression of natural killer (NK) cells cytotoxicity by the activation of c-JUN/ PTGS2 pathway | ||
Int Immunopharmacol Anti-osteosarcoma activity of Corynoline via Src/JNK signaling-mediated cell cycle arrest and mitochondrial apoptosis | ||
Molecules Effects of the total saponins from Rosa laevigata Michx fruit against acetaminophen-induced liver damage in mice via induction of autophagy and suppression of inflammation and apoptosis. | ||
Exp Ther Med Naringin attenuates renal interstitial fibrosis by regulating the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway and inflammation. | ||
Adv Sci (Weinh) Autophagy Deficiency Induced by SAT1 Potentiates Tumor Progression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer |