Tested Applications
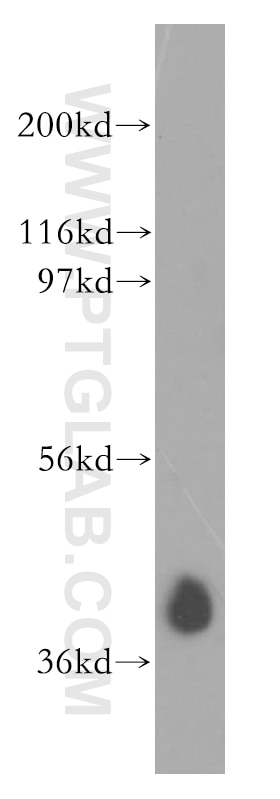
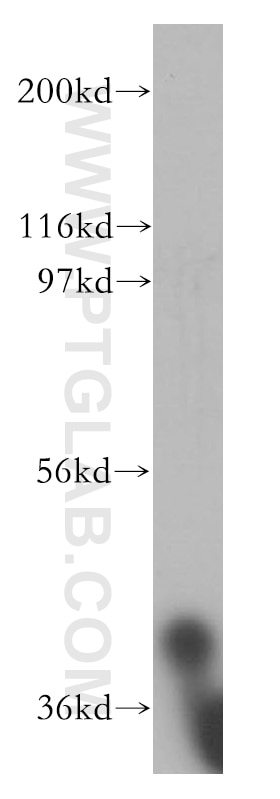
| Positive WB detected in | K-562 cells, HEK-293 cells, Jurkat cells |
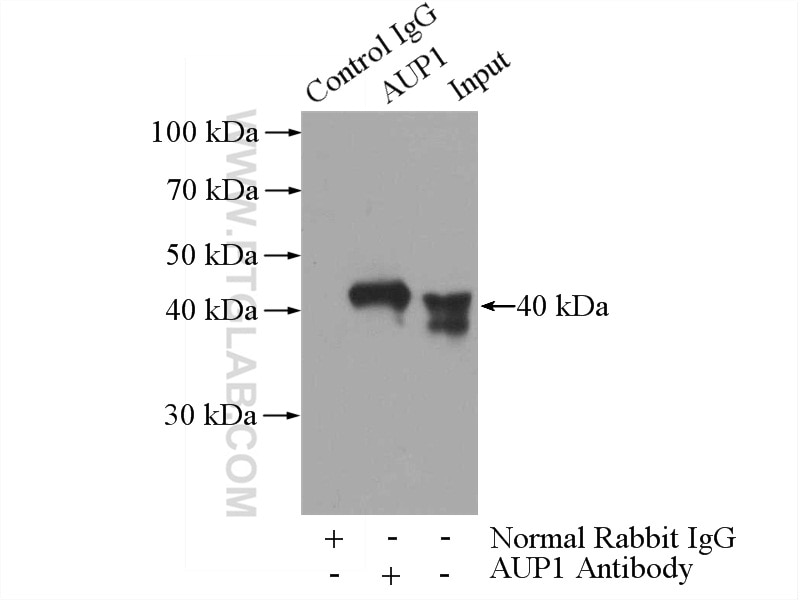
| Positive IP detected in | HEK-293 cells |
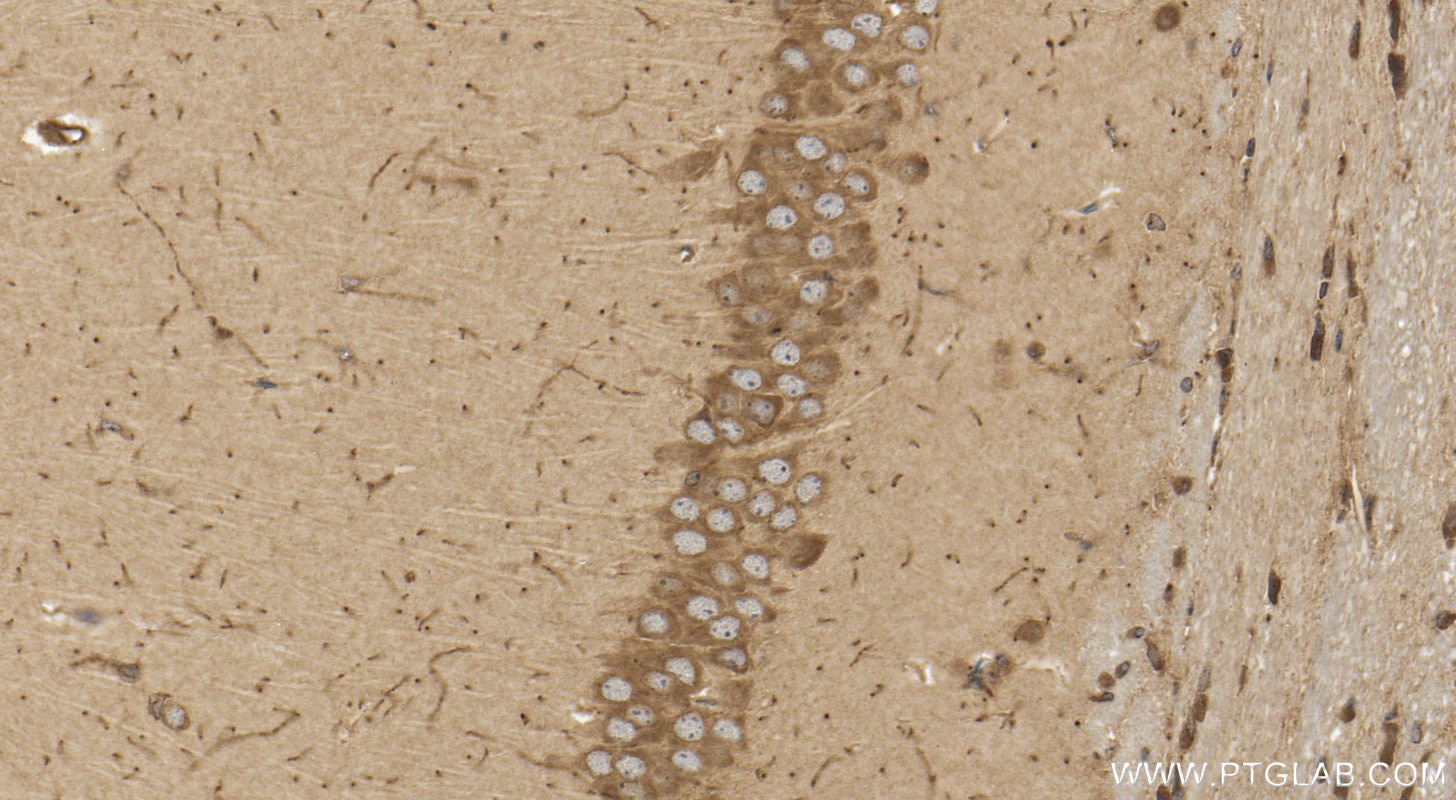
| Positive IHC detected in | mouse brain tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | A431 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 7 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
13726-1-AP targets AUP1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, zebrafish |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag4680 Product name: Recombinant human AUP1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 134-437 aa of BC033646 Sequence: LLTTCSTPLLNSPPSFVCWSRGFMEMNGRGELVESLKRFCASTRLPPTPLLLFPEEEATNGREGLLRFSSWPFSIQDVVQPLTLQVQRPLVSVTVSDASWVSELLWSLFVPFTVYQVRWLRPVHRQLGEANEEFALRVQQLVAKELGQTGTRLTPADKAEHMKRQRHPRLRPQSAQSSFPPSPGPSPDVQLATLAQRVKEVLPHVPLGVIQRDLAKTGCVDLTITNLLEGAVAFMPEDITKGTQSLPTASASKFPSSGPVTPQPTALTFAKSSWARQESLQERKQALYEYARRRFTERRAQEAD Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | ancient ubiquitous protein 1 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 416 aa, 45 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 40 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC033646 |
| Gene Symbol | AUP1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 550 |
| RRID | AB_2258768 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9Y679 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
AUP1 (Ancient ubiquitous protein 1) is a protein associated with lipid metabolism, which is widely expressed on the surface of ER and Lipid droplets, involved in the degradation of misfolded proteins through autophagy (PMID: 37029364). In addition, AUP1 also controls lipid synthesis as it induces ubiquitination and the subsequent degradation of several key regulators of lipid biosynthesis, such as the cholesterol biosynthetic enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (PMID: 28330944).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for AUP1 antibody 13726-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for AUP1 antibody 13726-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for AUP1 antibody 13726-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for AUP1 antibody 13726-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Mol Biol Cell Lipid disequilibrium disrupts ER proteostasis by impairing ERAD substrate glycan trimming and dislocation. | ||
PLoS One Chlamydia trachomatis Infection Leads to Defined Alterations to the Lipid Droplet Proteome in Epithelial Cells. | ||
Mol Biol Cell A VCP inhibitor substrate trapping approach (VISTA) enables proteomic profiling of endogenous ERAD substrates. | ||
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids The role of ancient ubiquitous protein 1 (Aup1) in regulating hepatic lipid droplet levels, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and inflammation in zebrafish (Danio rerio) | ||
bioRxiv Cancer-associated snaR-A noncoding RNA interacts with core splicing machinery and disrupts processing of mRNA subpopulations | ||
Comput Struct Biotechnol J Featured interactome of homocysteine-inducible endoplasmic reticulum protein uncovers novel binding partners in response to ER stress |