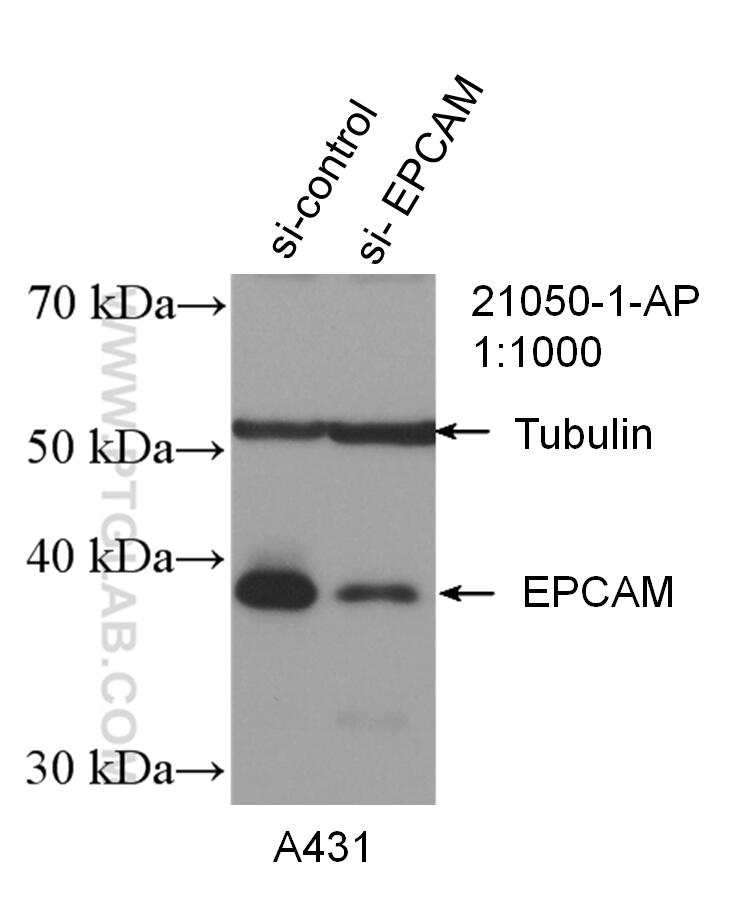
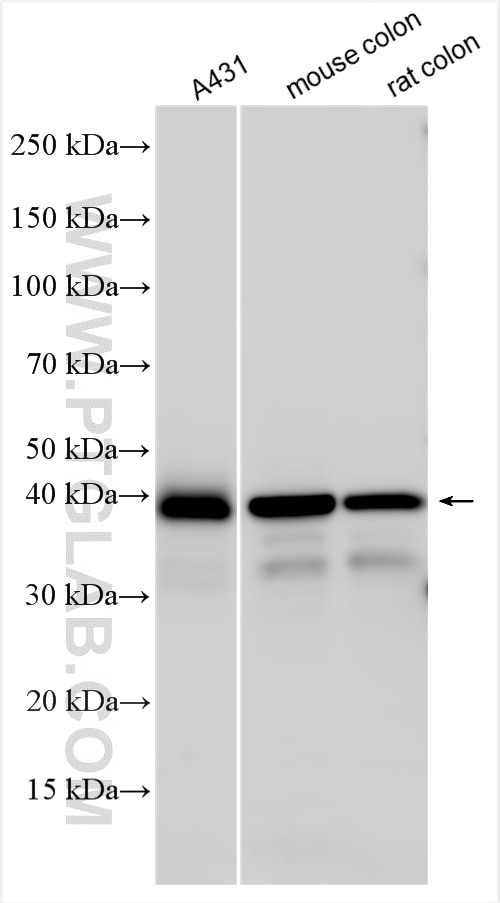
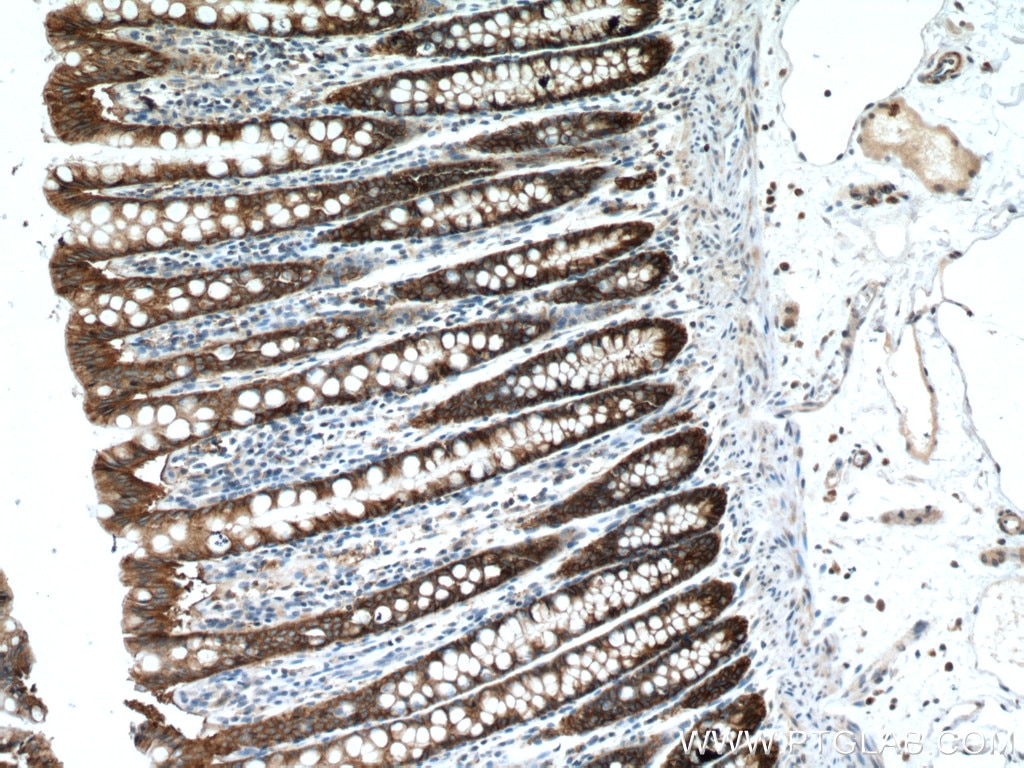
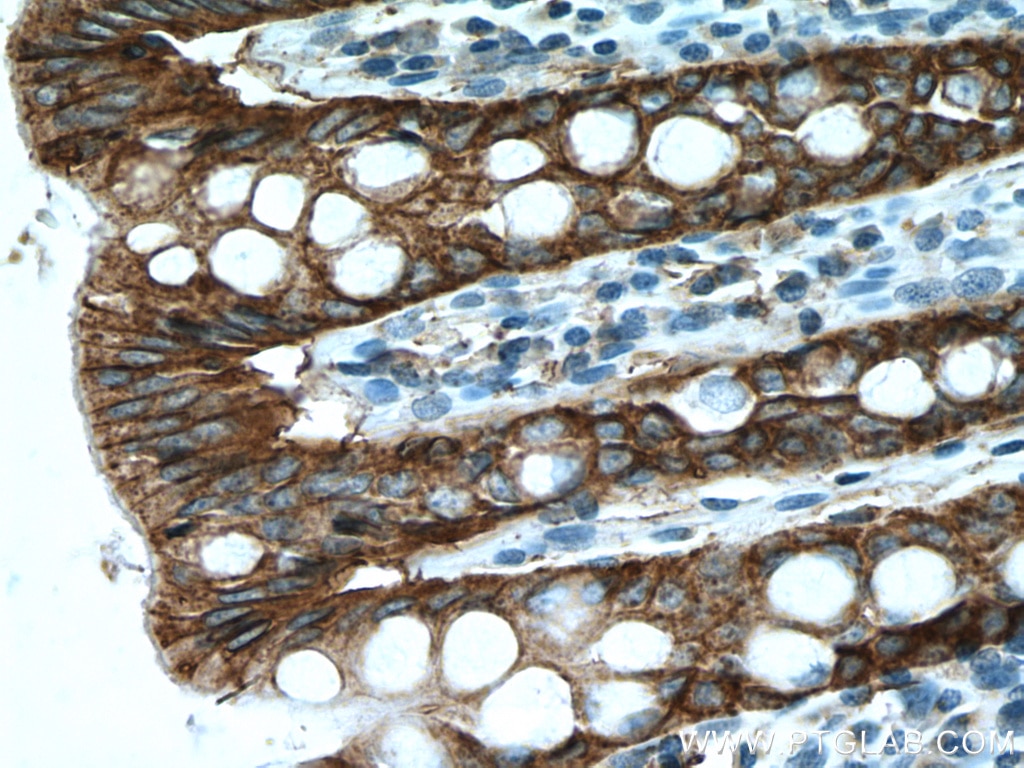
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | A431 cells, mouse colon tissue, rat colon tissue |
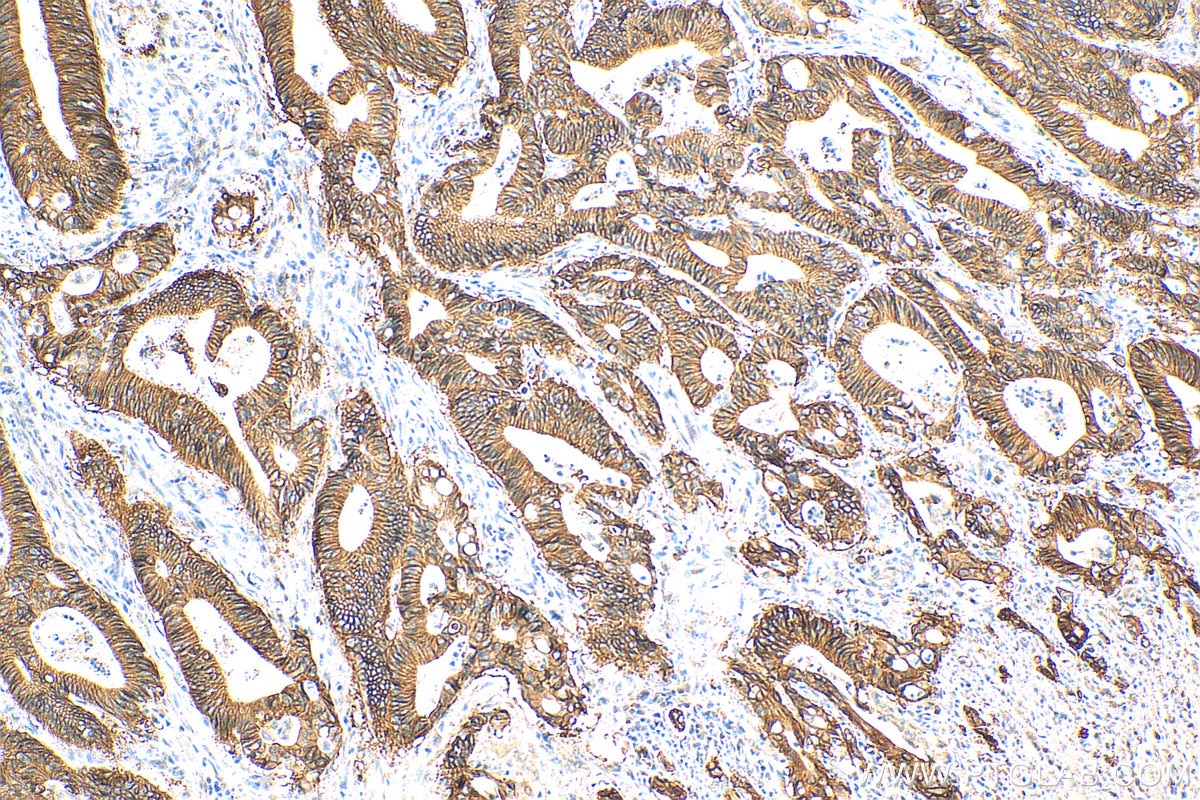
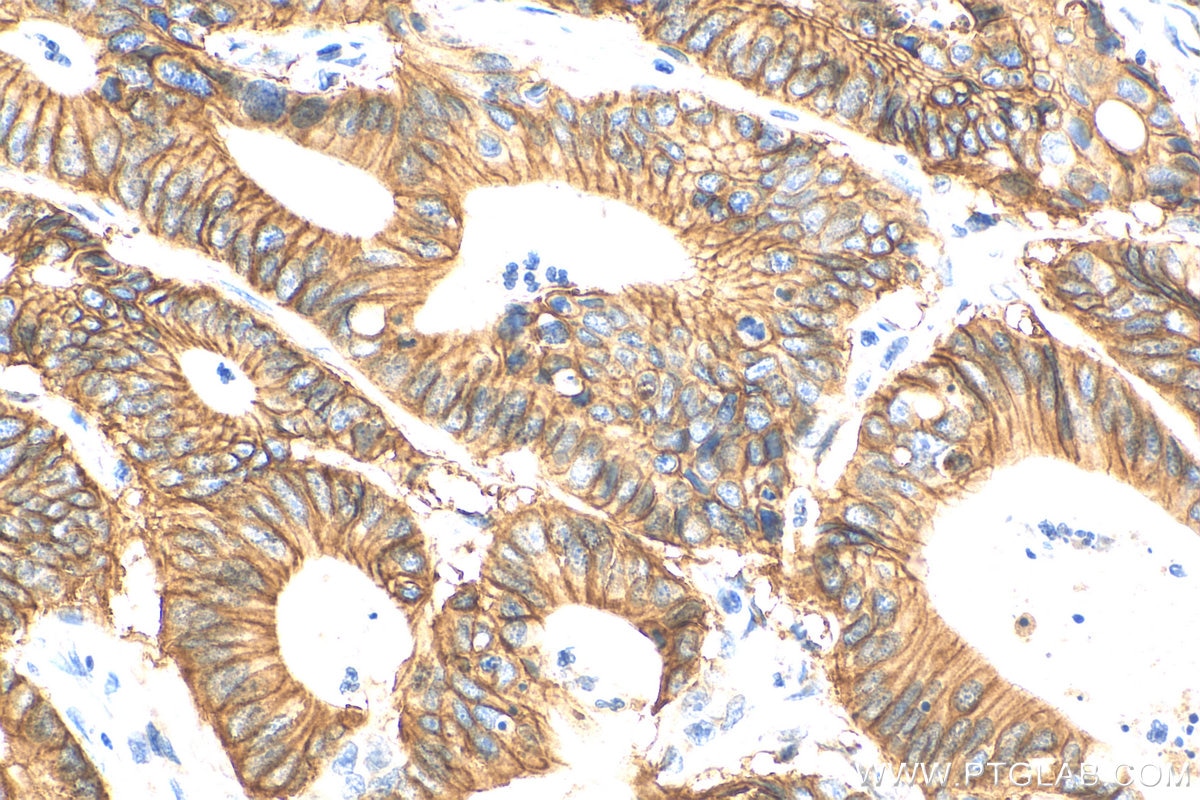
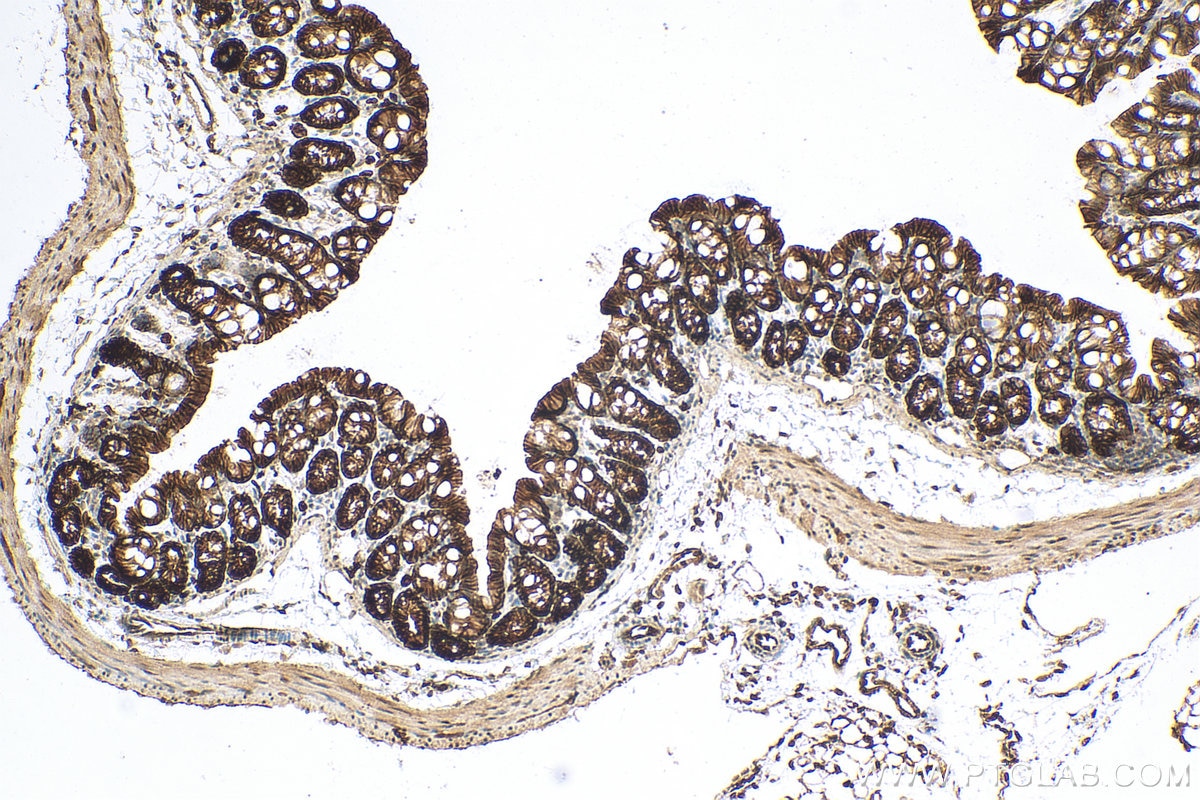
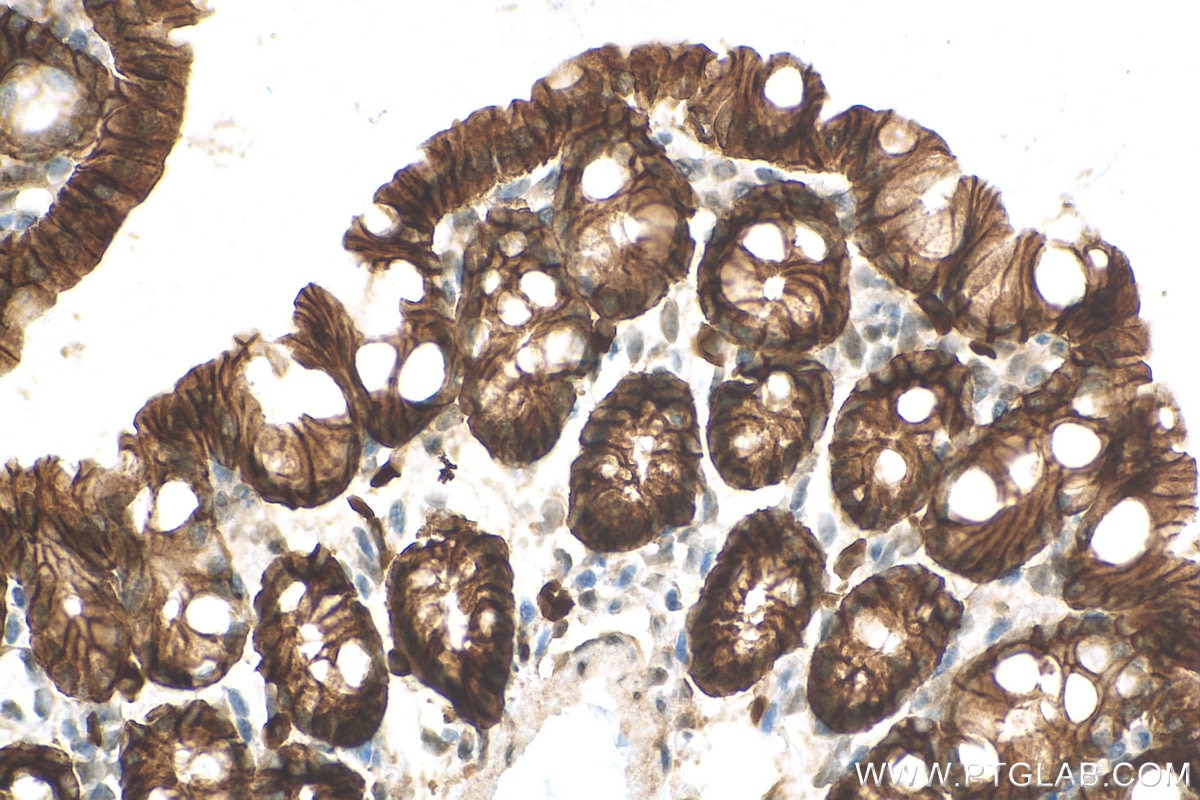
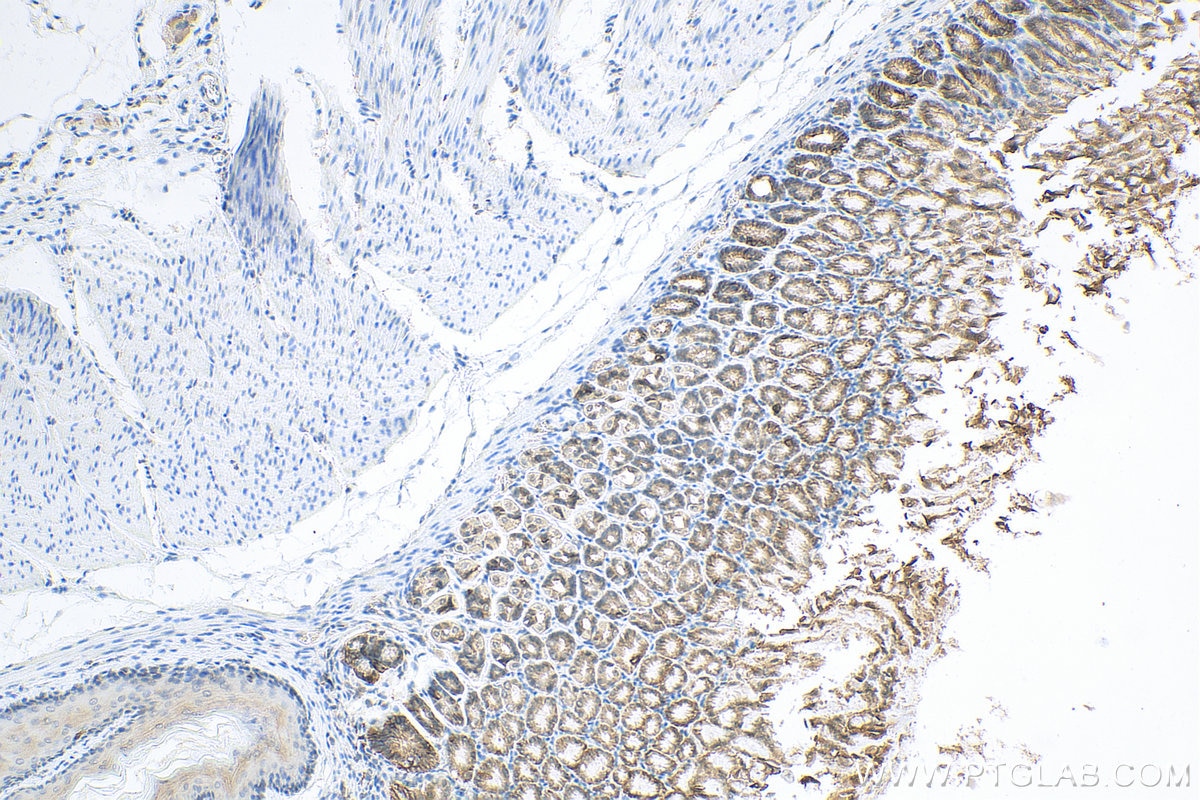
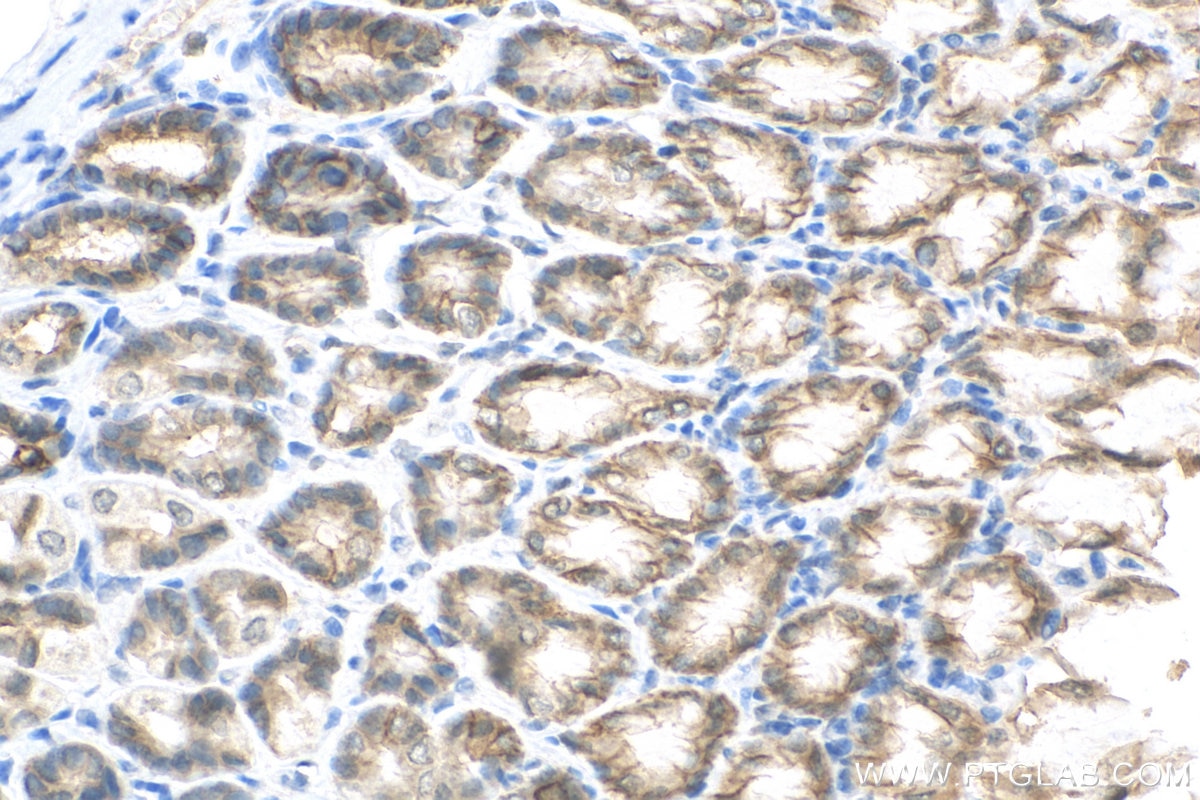
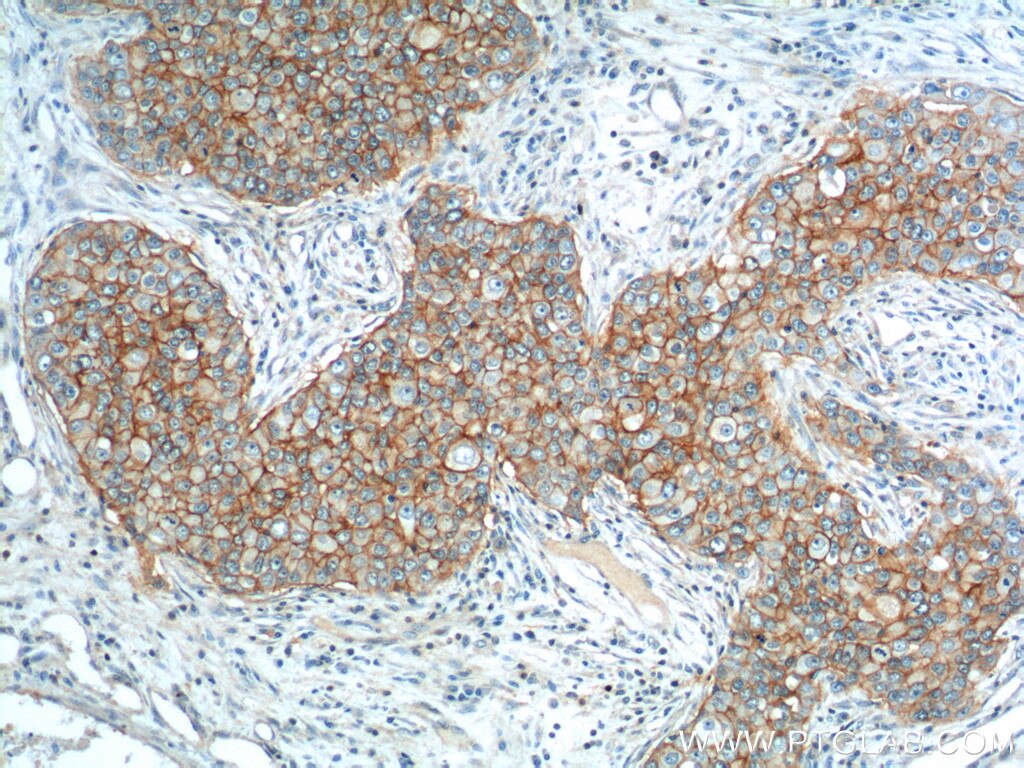
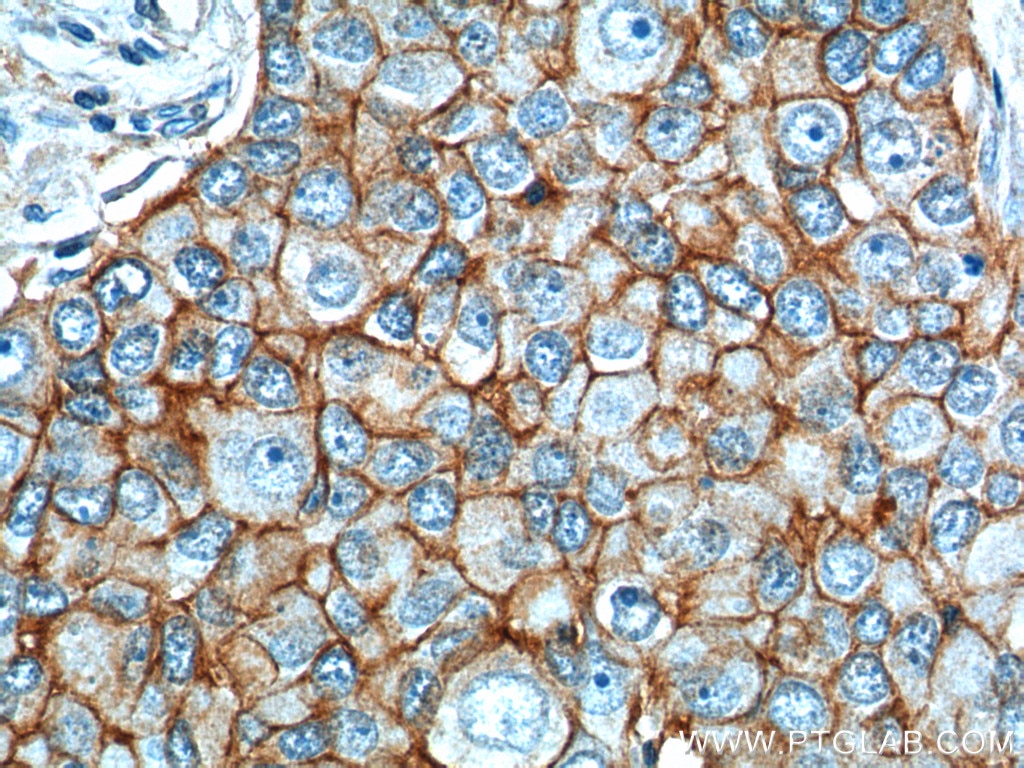
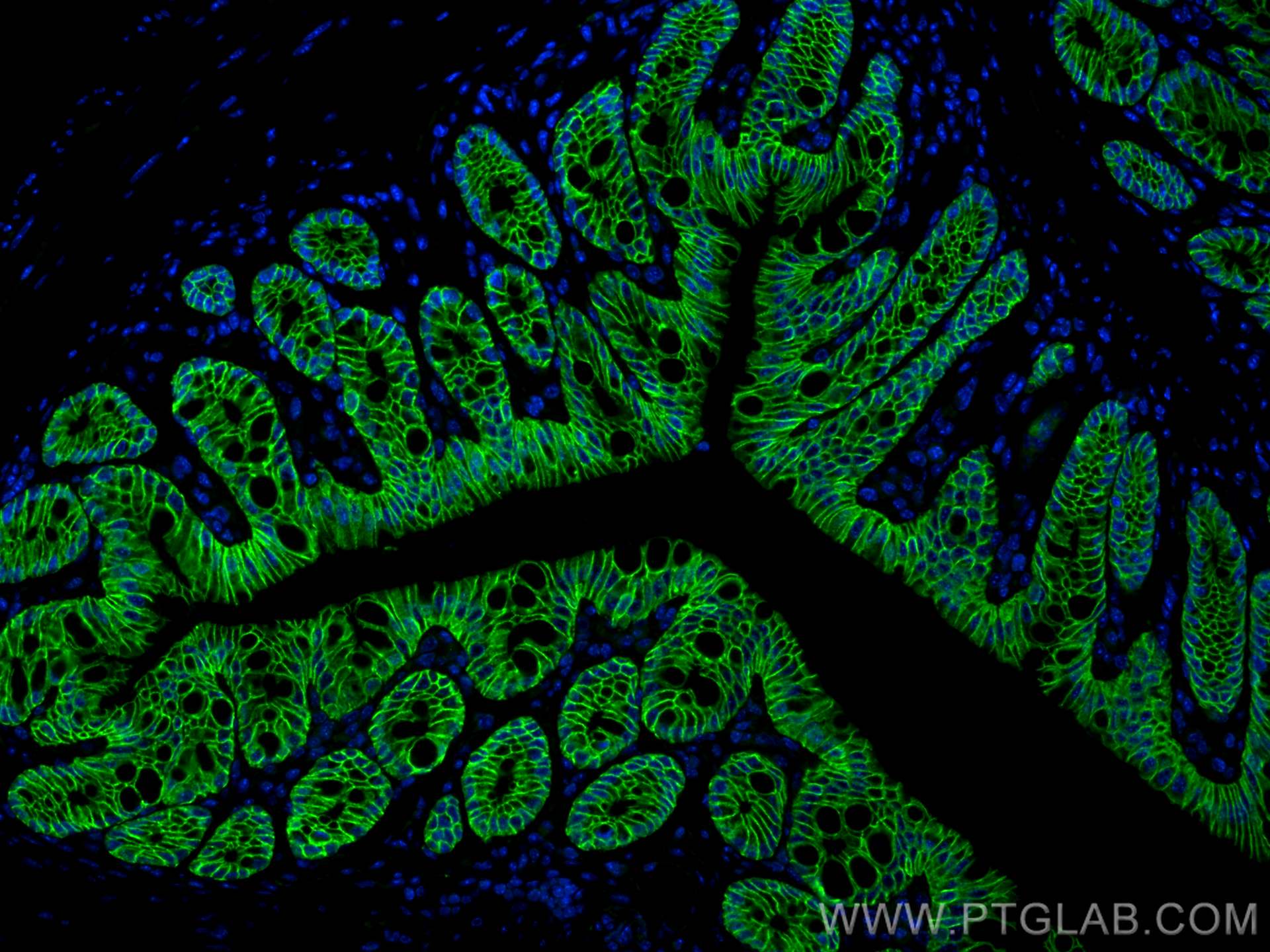
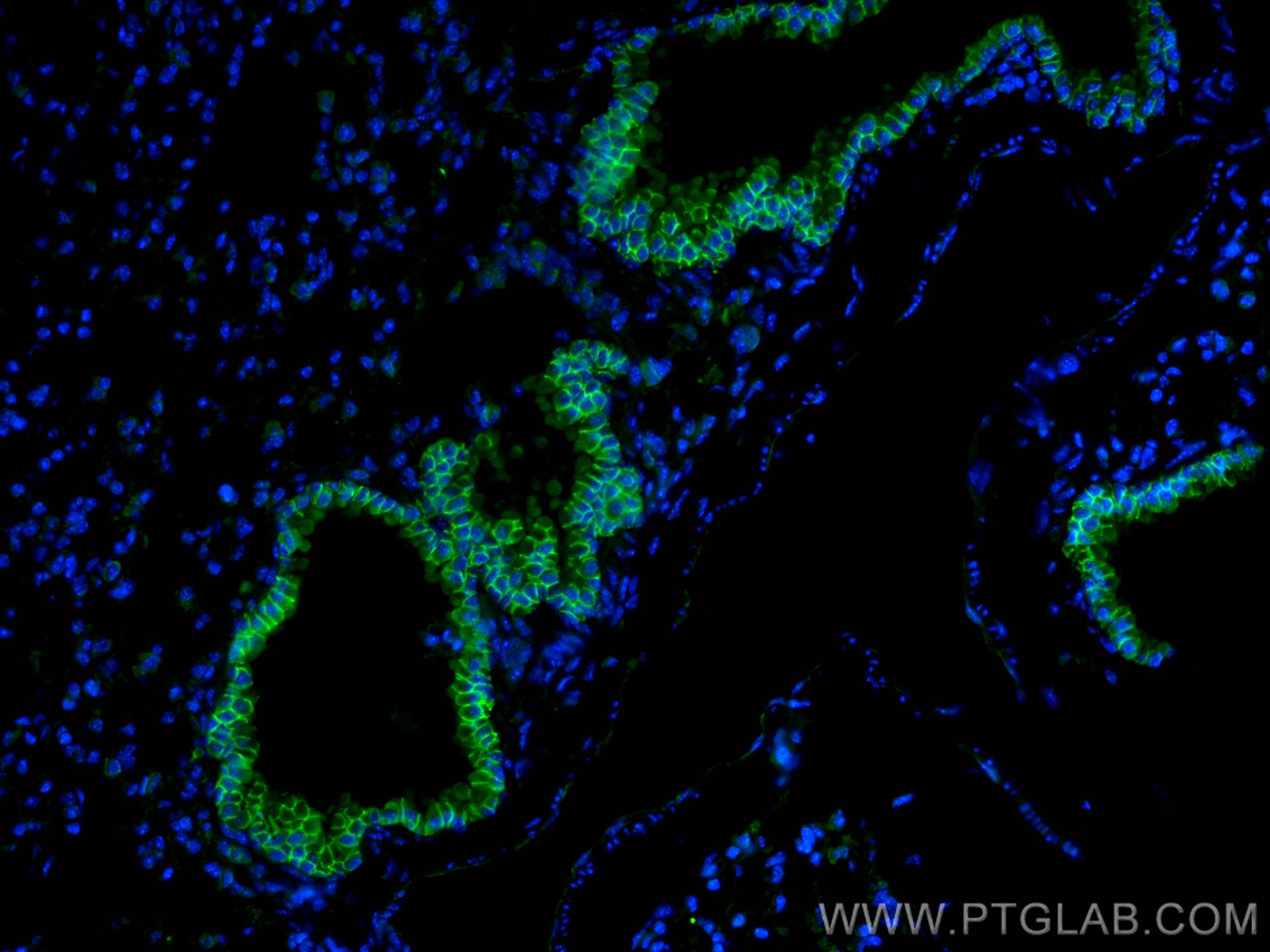
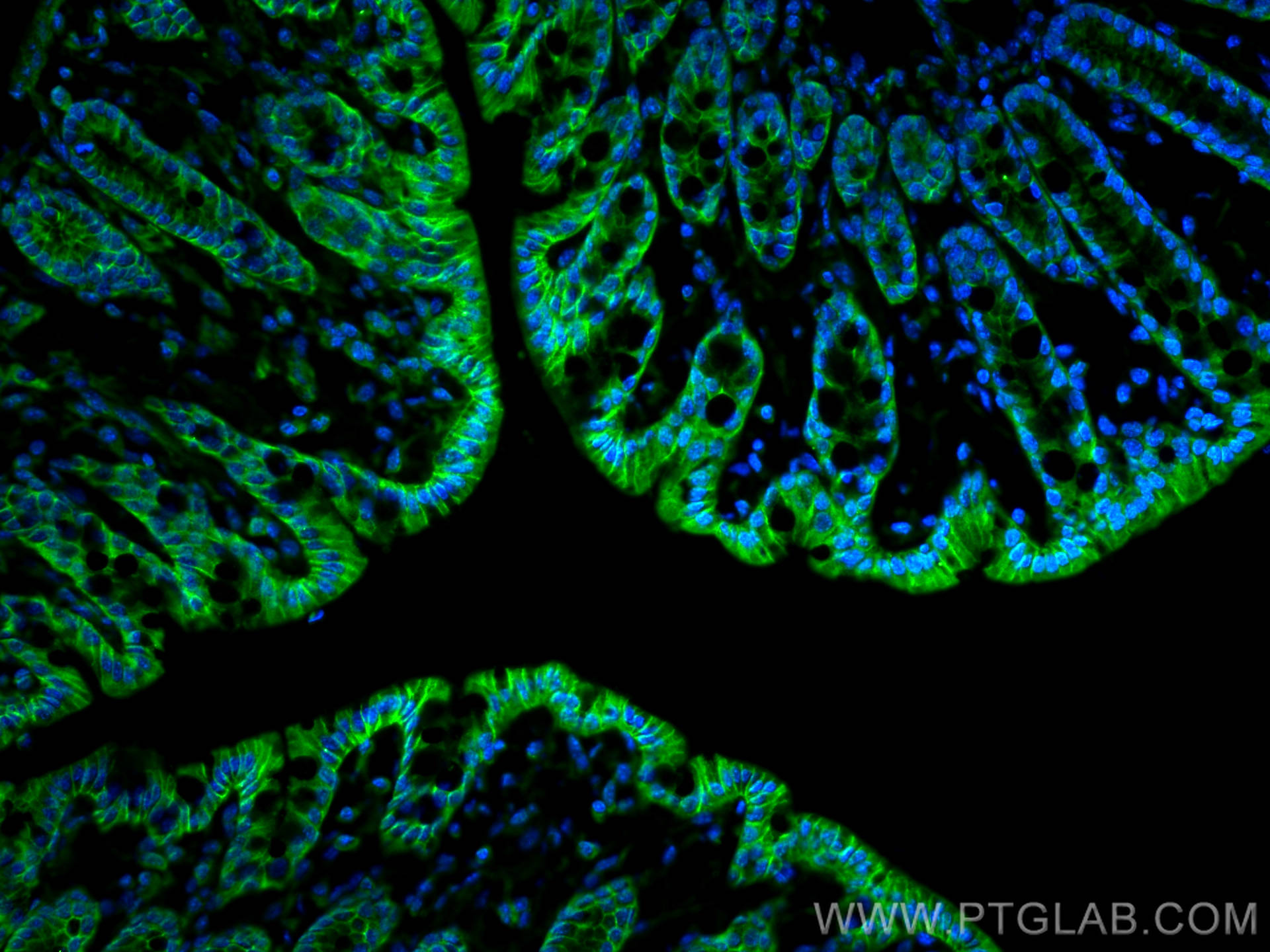
| Positive IHC detected in | human colon cancer tissue, mouse colon tissue, human breast cancer tissue, human colon tissue, mouse stomach tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
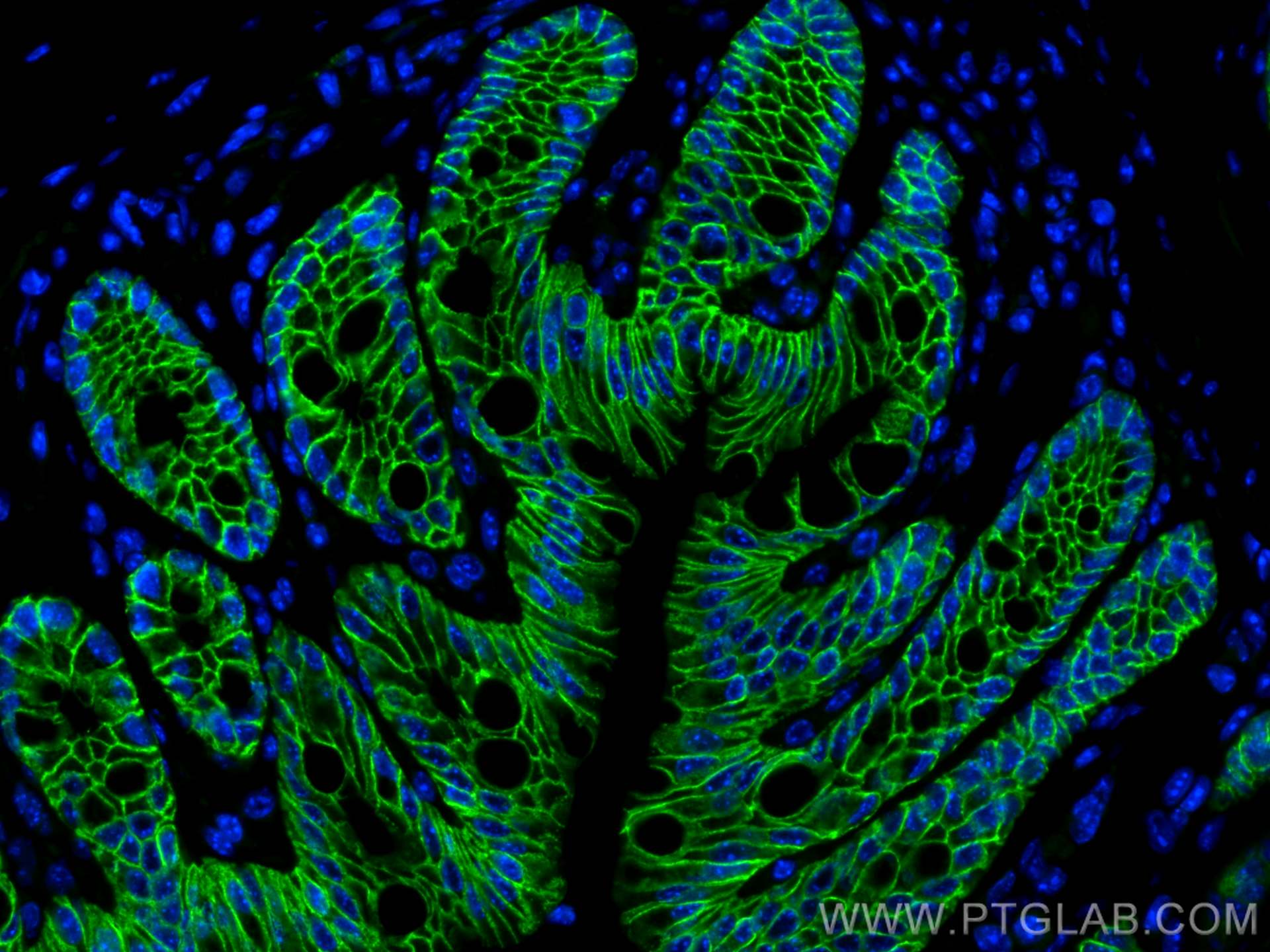
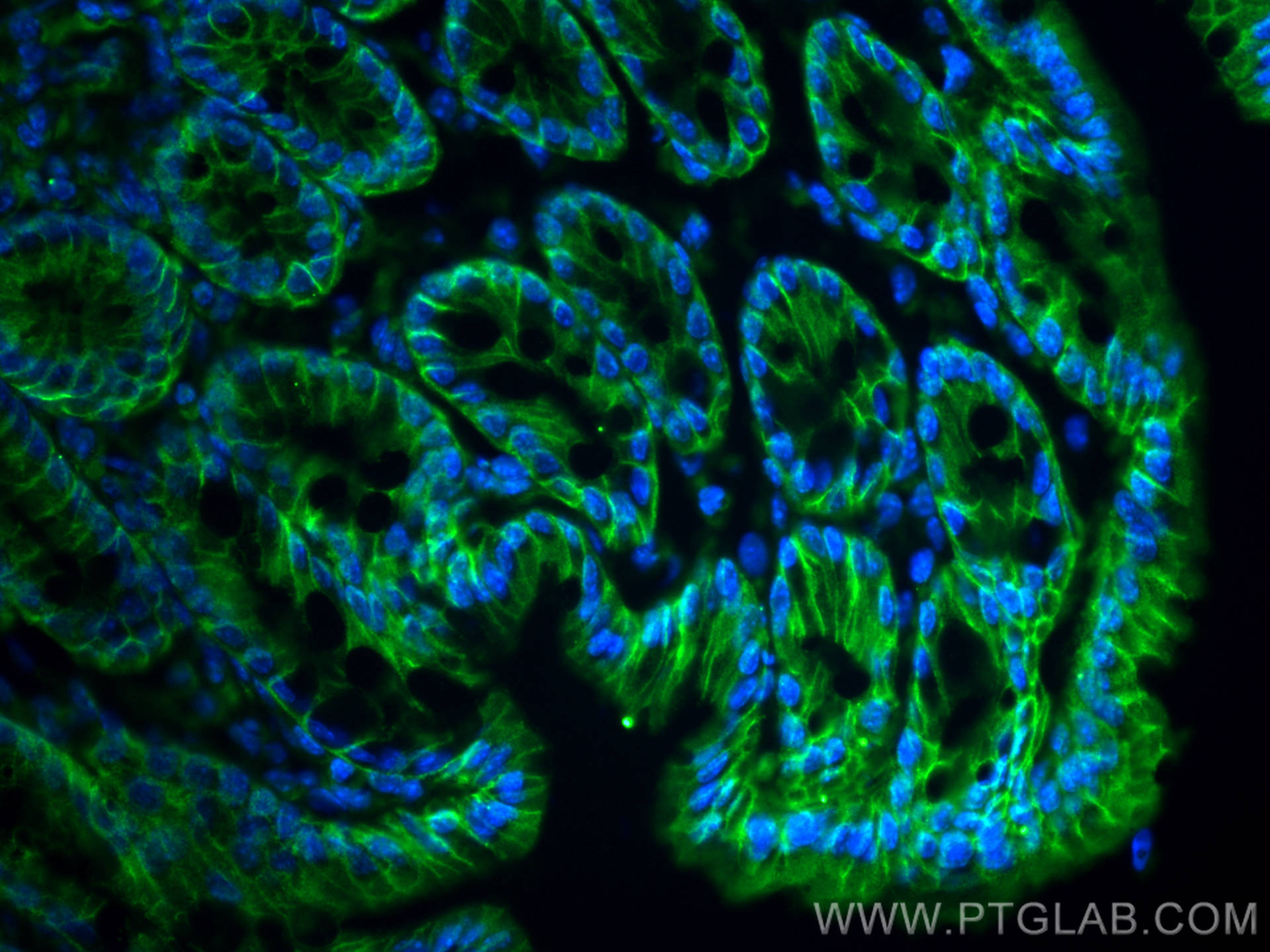
| Positive IF-P detected in | mouse colon tissue, MCF-7 cells, mouse lung tissue |
| Positive IF-Fro detected in | mouse colon tissue |
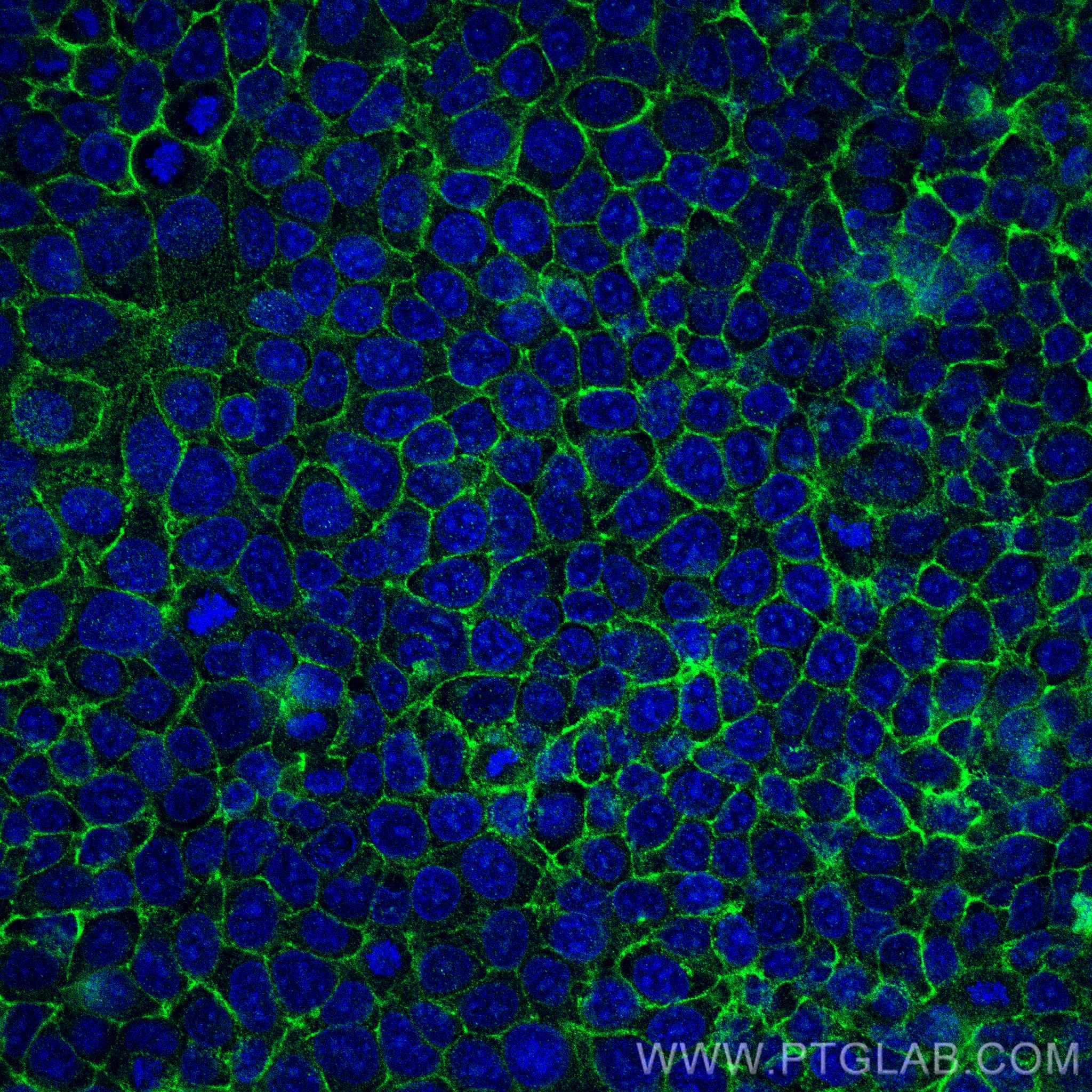
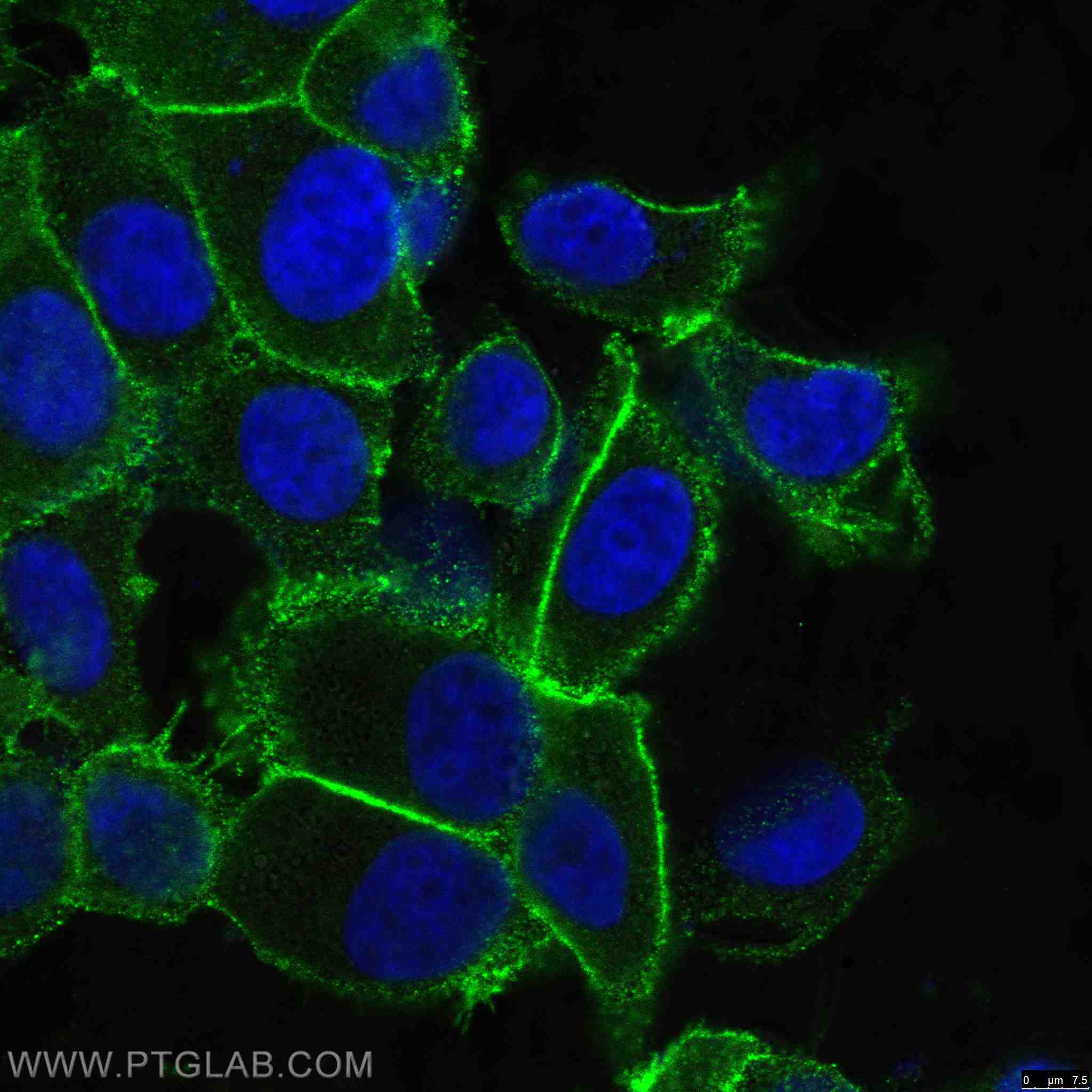
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HT-29 cells, MCF-7 cells |
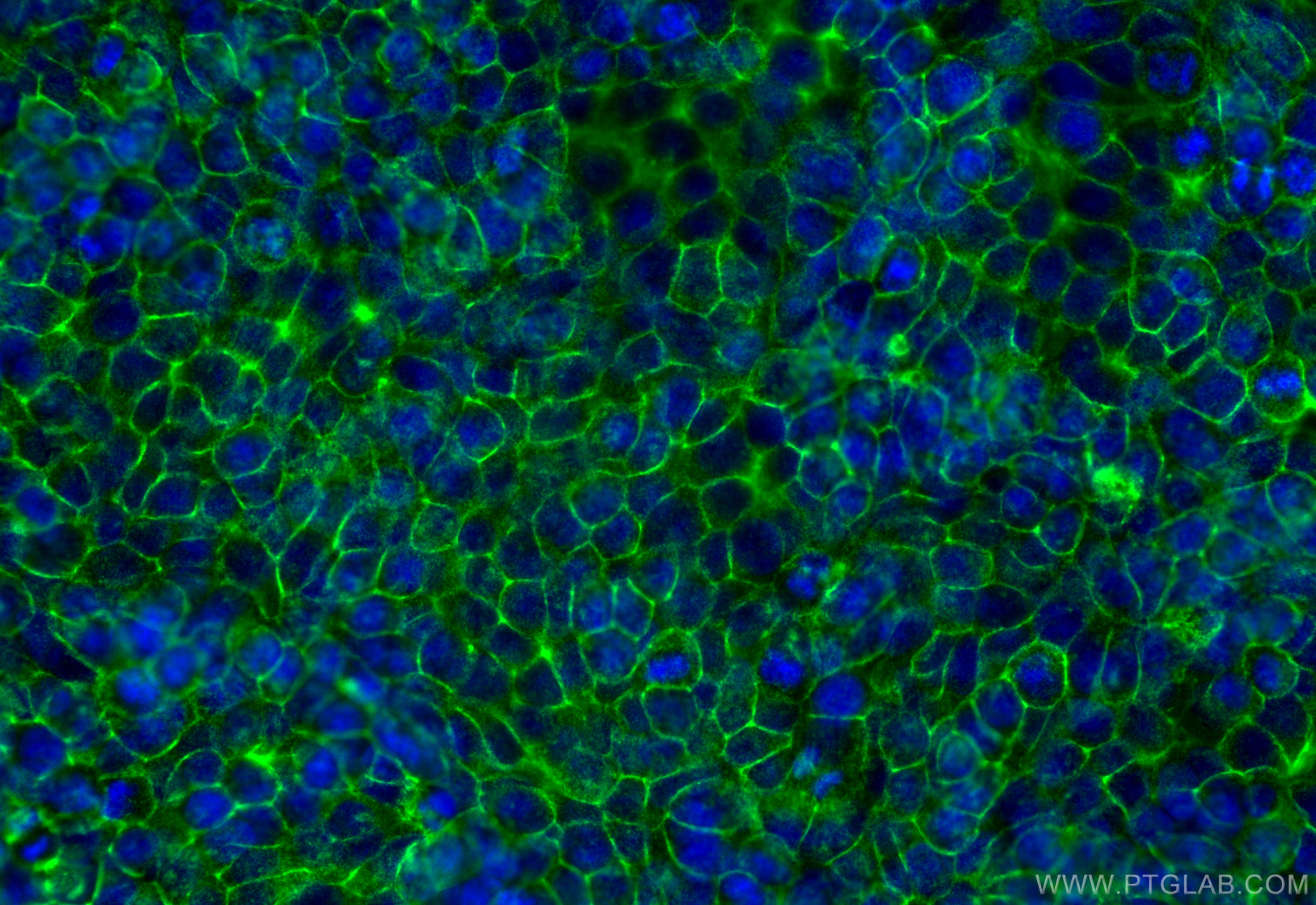
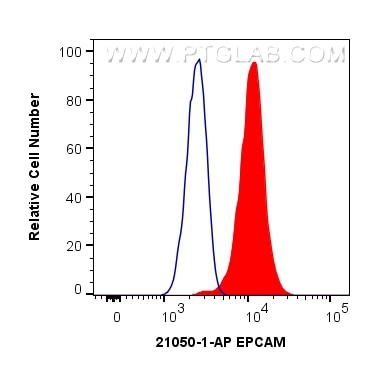
| Positive FC detected in | HT-29 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:10000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-FRO | IF-FRO : 1:200-1:800 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) | FC : 0.50 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
21050-1-AP targets EPCAM/CD326 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IF-Fro, FC, IP, chIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, pig, canine |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag15393 Product name: Recombinant human EPCAM protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 24-264 aa of BC014785 Sequence: QEECVCENYKLAVNCFVNNNRQCQCTSVGAQNTVICSKLAAKCLVMKAEMNGSKLGRRAKPEGALQNNDGLYDPDCDESGLFKAKQCNGTSTCWCVNTAGVRRTDKDTEITCSERVRTYWIIIELKHKAREKPYDSKSLRTALQKEITTRYQLDPKFITSILYENNVITIDLVQNSSQKTQNDVDIADVAYYFEKDVKGESLFHSKKMDLTVNGEQLDLDPGQTLIYYVDEKAPEFSMQGL Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | epithelial cell adhesion molecule |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 314 aa, 35 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 35-40 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC014785 |
| Gene Symbol | EPCAM |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4072 |
| RRID | AB_10693684 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P16422 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM, CD326) is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that functions as a homophilic, epithelial-specific intercellular cell-adhesion molecule. In addition to cell adhesion, EpCAM is also involved in cellular signaling, cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation. EpCAM is highly expressed on most carcinomas and therefore of potential use as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for a variety of carcinomas, and has become a therapeutic target. EpCAM may occur in distinct forms due to glycosylation. (PMID: 20837599; 19249674; 21576002; 22647938; 12691820)
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for EPCAM/CD326 antibody 21050-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for EPCAM/CD326 antibody 21050-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for EPCAM/CD326 antibody 21050-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for EPCAM/CD326 antibody 21050-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Mol Cancer m6A methylation reader IGF2BP2 activates endothelial cells to promote angiogenesis and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma | ||
Cell Metab Nicotinamide metabolism face-off between macrophages and fibroblasts manipulates the microenvironment in gastric cancer | ||
Cancer Cell Loss of Lkb1 and Pten leads to lung squamous cell carcinoma with elevated PD-L1 expression. | ||
Gut Cross-talk between the gut microbiota and monocyte-like macrophages mediates an inflammatory response to promote colitis-associated tumourigenesis. | ||
Autophagy Neutrophil-derived serine proteases induce FOXA2-mediated autophagy dysfunction and exacerbate colitis-associated carcinogenesis via F2RL1/protease-activated receptor 2 |
Reviews
The reviews below have been submitted by verified Proteintech customers who received an incentive for providing their feedback.
FH Andrew (Verified Customer) (07-12-2024) | Got a clean band at the desired molecular weight for EPCAM on the first attempt of using this primary antibody for Western Blot. Also, there was very little background. Overall, very happy with this product.
|