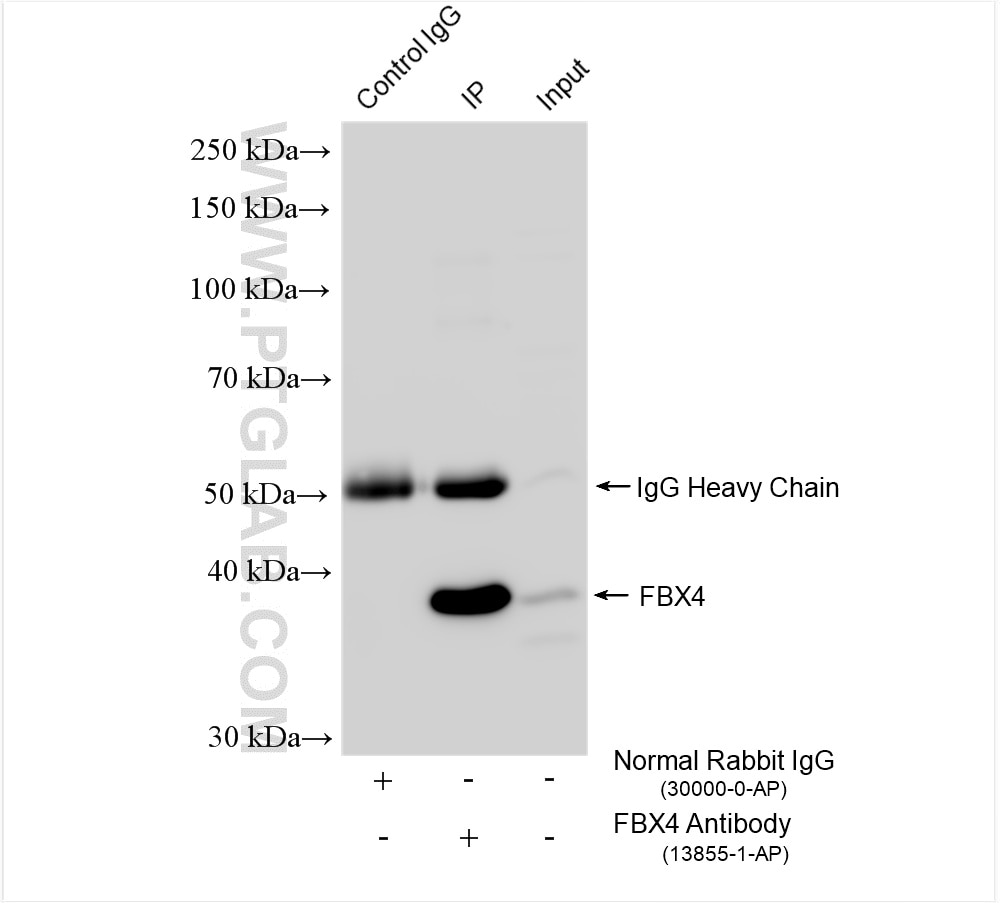
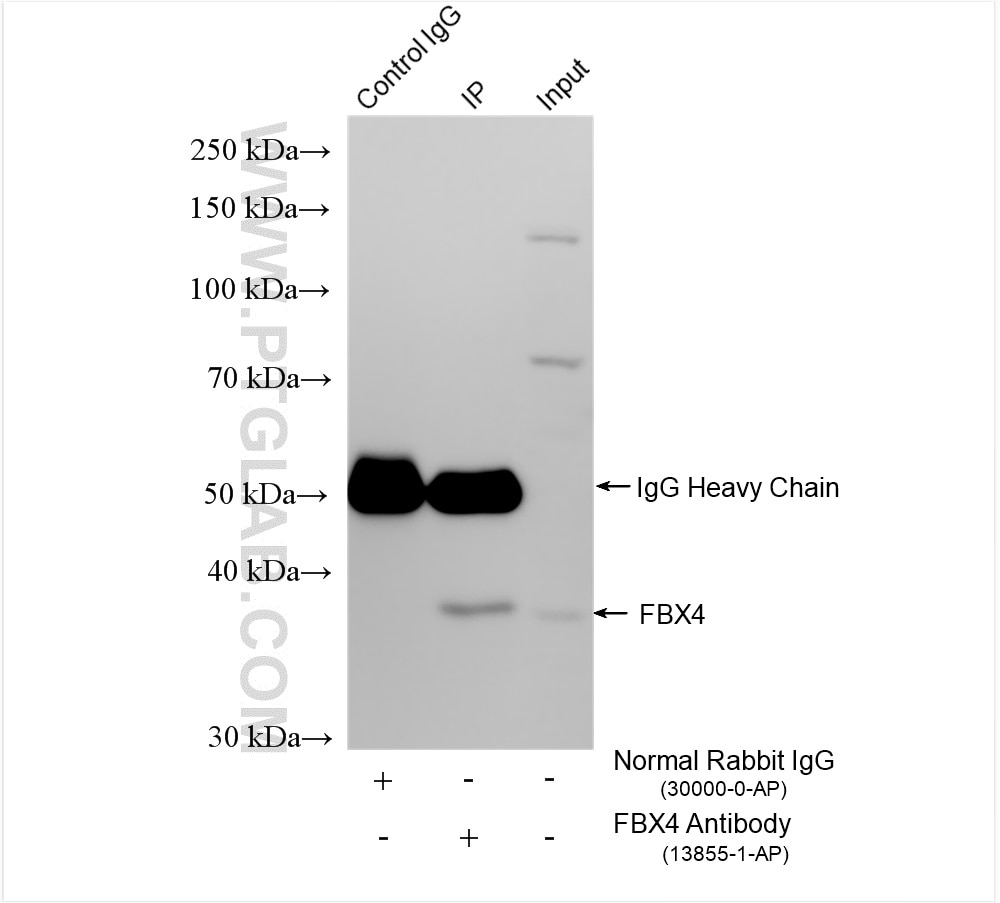
Tested Applications
| Positive IP detected in | HeLa cells, A431 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
13855-1-AP targets FBX4 in IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag4829 Product name: Recombinant human FBX4 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-387 aa of BC048098 Sequence: MAGSEPRSGTNSPPPPFSDWGRLEAAILSGWKTFWQSVSKERVARTTSREEVDEAASTLTRLPIDVQLYILSFLSPHDLCQLGSTNHYWNETVRDPILWRYFLLRDLPSWSSVDWKSLPDLEILKKPISEVTDGAFFDYMAVYRMCCPYTRRASKSSRPMYGAVTSFLHSLIIQNEPRFAMFGPGLEELNTSLVLSLMSSEELCPTAGLPQRQIDGIGSGVNFQLNNQHKFNILILYSTTRKERDRAREEHTSAVNKMFSRHNEGDDQQGSRYSVIPQIQKVCEVVDGFIYVANAEAHKRHEWQDEFSHIMAMTDPAFGSSGRPLLVLSCISQGDVKRMPCFYLAHELHLNLLNHPWLVQDTEAETLTGFLNGIEWILEEVESKRAR Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | F-box protein 4 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 44 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 38 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC048098 |
| Gene Symbol | FBXO4/FBX4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 26272 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9UKT5 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
FBX4 (F-Box Protein 4), also known as FBXO4, is a member of the F-box protein family. FBX4 is involved in the ubiquitination of various target proteins, leading to their degradation. It has been shown to regulate the cell cycle by targeting proteins such as cyclin D1 for ubiquitination and degradation. Mutations in FBX4 have been linked to various diseases, including spermatogenic failure and esophageal cancer. In cancer, FBX4 has been shown to act as a tumor suppressor. Loss of FBX4 function can lead to increased cell proliferation and tumor development. For example, FBX4 knockout mice have been shown to develop various tumors, including lymphoblastic lymphoma and mammary carcinoma. FBX4 has two isforms: 44 kDa and 35 kDa.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IP protocol for FBX4 antibody 13855-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |