Tested Applications
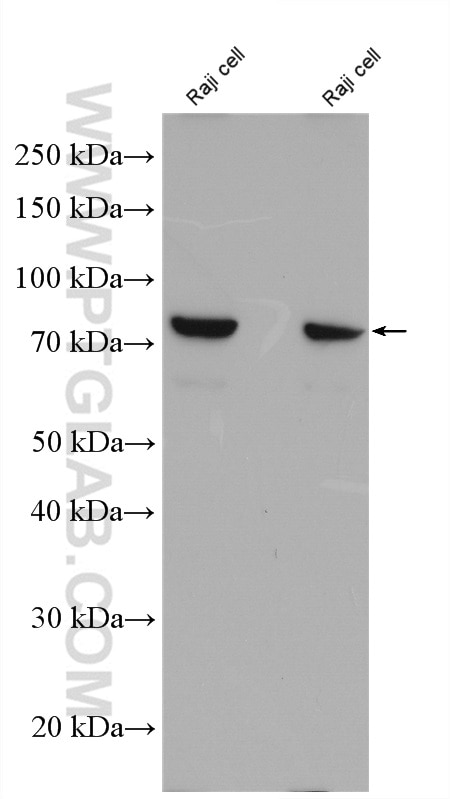
| Positive WB detected in | Raji cells |
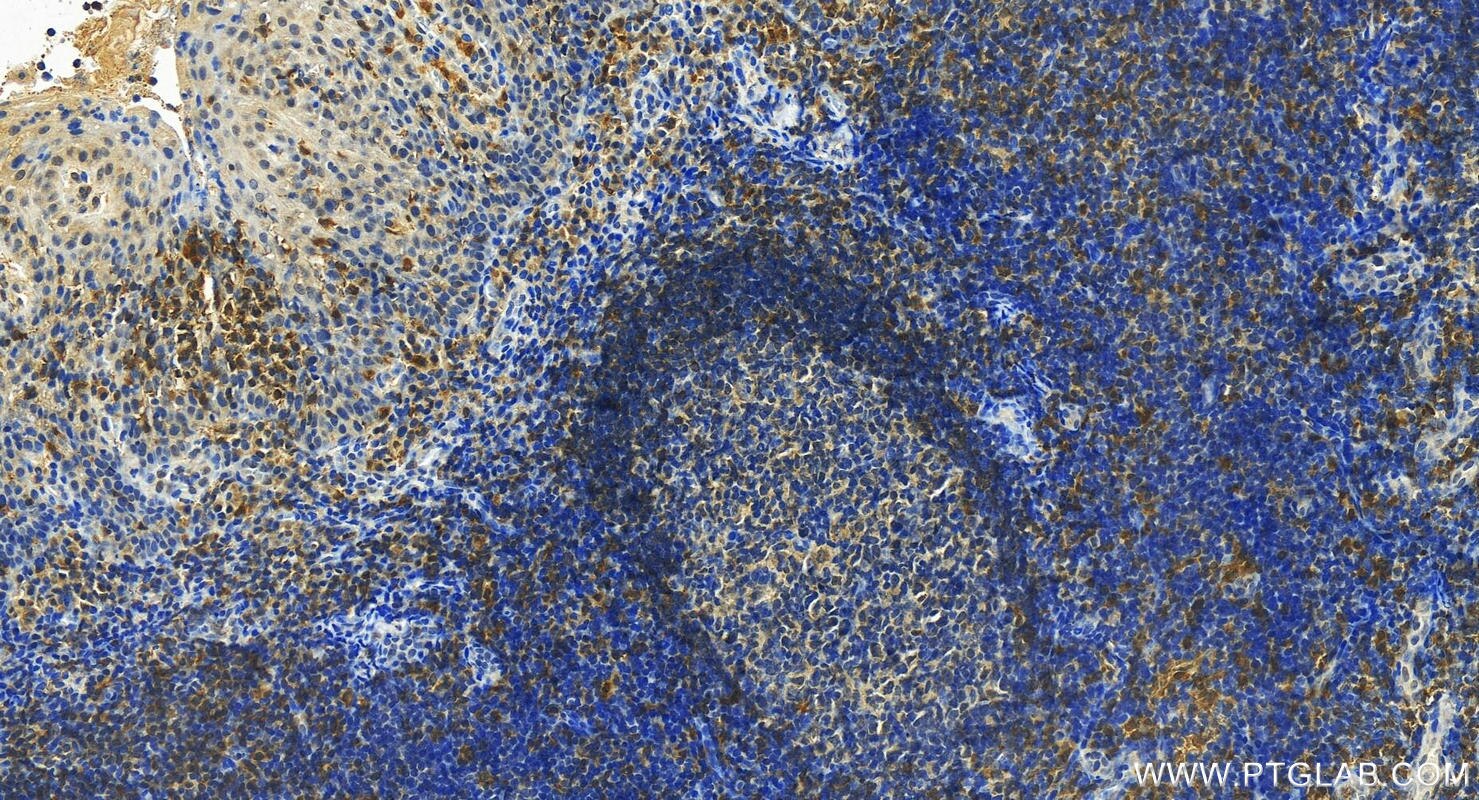
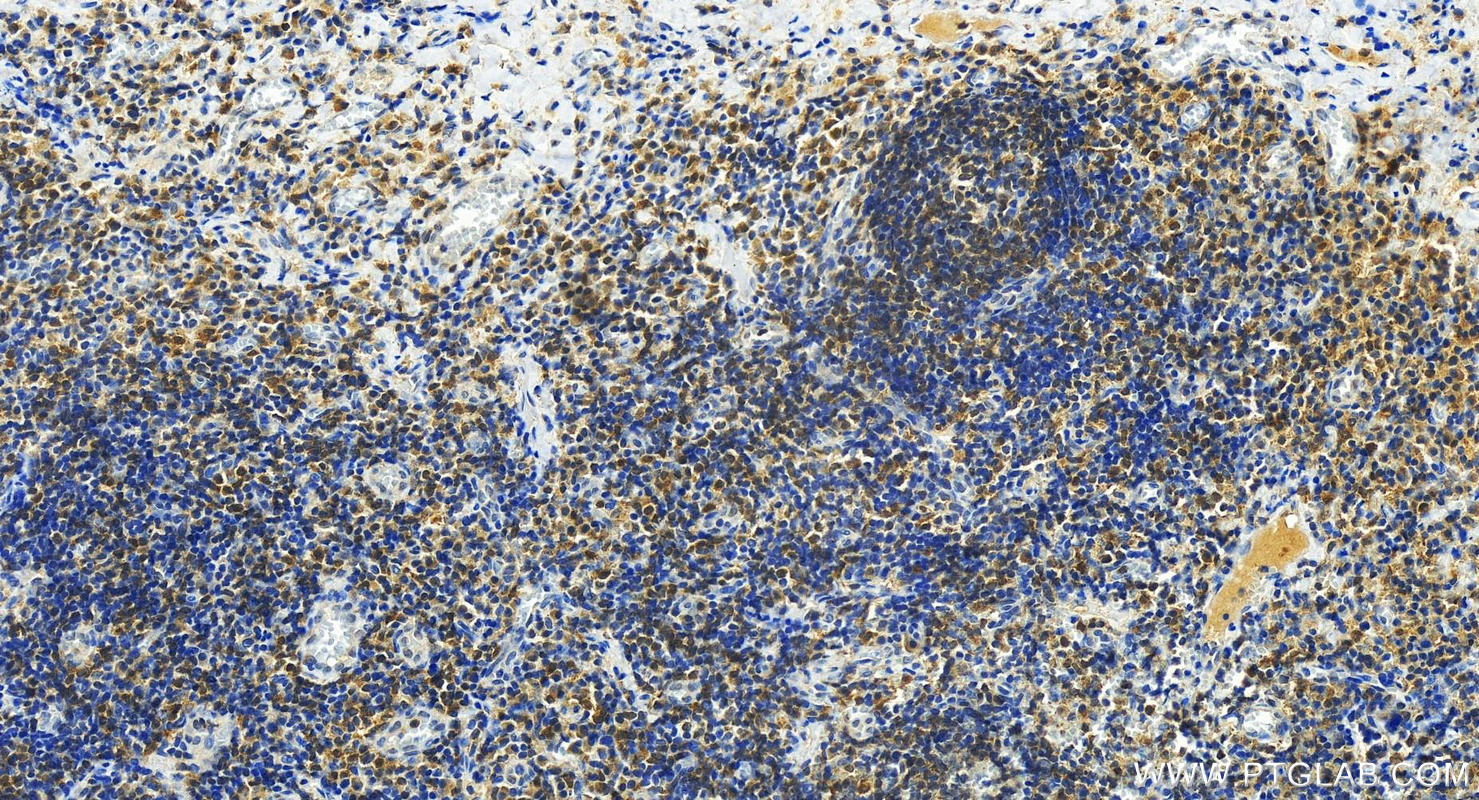
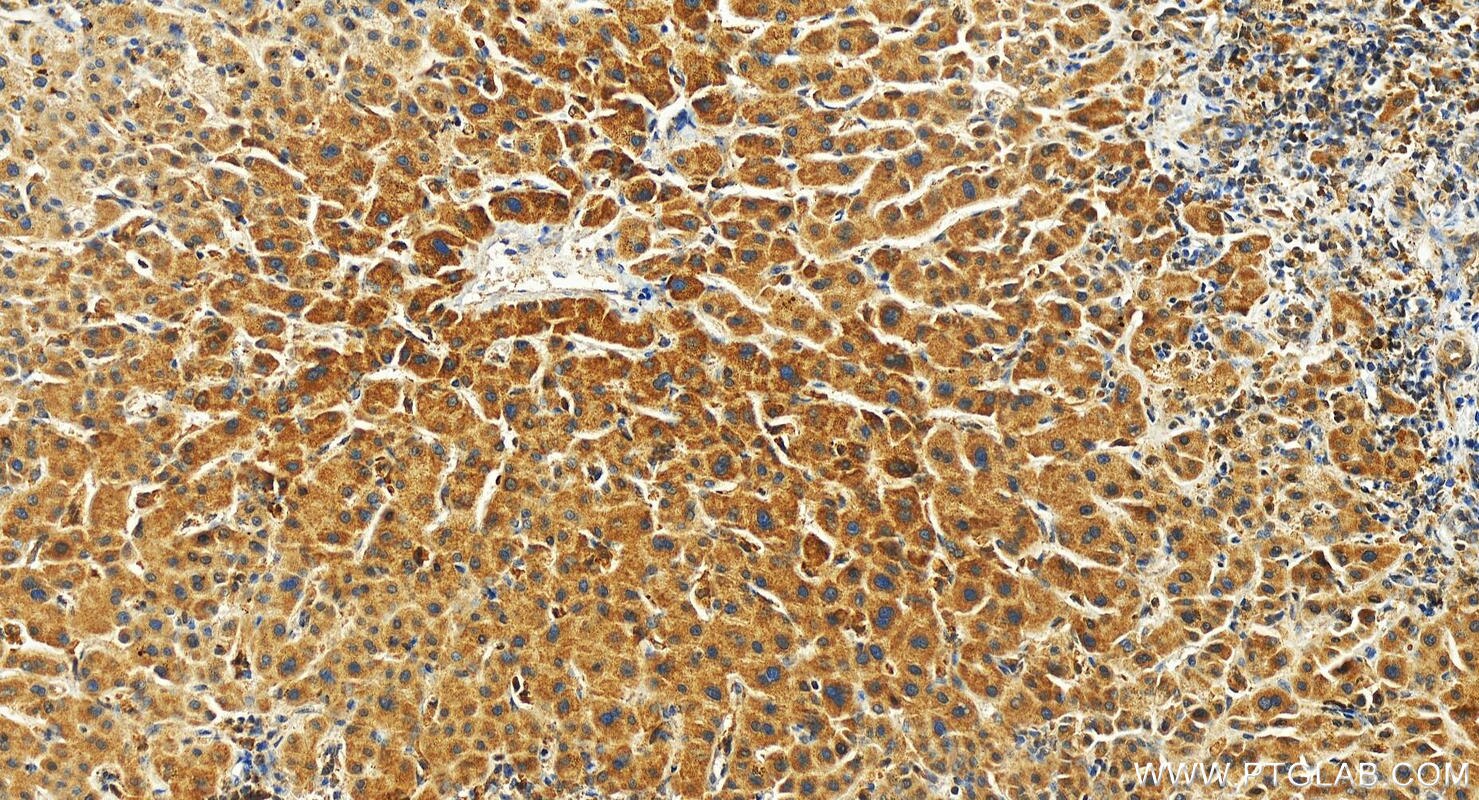
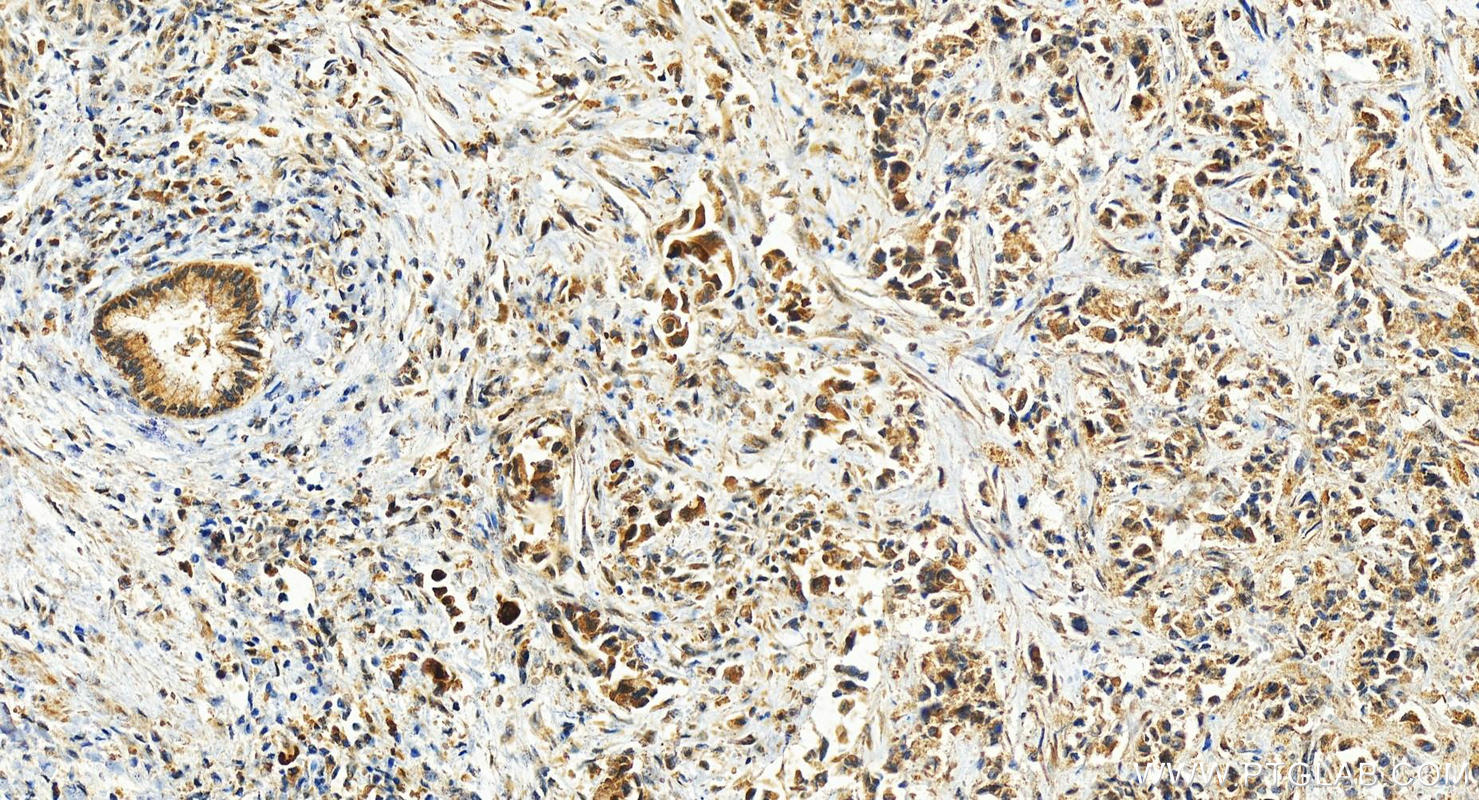
| Positive IHC detected in | human tonsillitis tissue, human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
27068-1-AP targets FGD2 in WB, IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag25782 Product name: Recombinant human FGD2 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-123 aa of BC023645 Sequence: MKGASEEKLASVSNLVTVFENSRTPEAAPRGHRLEDVHHRPECRPPESPGPREKTNVGEAVGSEPRTVSRRYLNSLKNKLSSEAWRKSCQPVTLSGSGTQEPEKKIVQELLETEQAYVARLHL Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain containing 2 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 655 aa, 75 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 75 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC023645 |
| Gene Symbol | FGD2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 221472 |
| RRID | AB_2880740 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q7Z6J4 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
FGD2 is a member of the formin family of proteins, which are known for their role in regulating the assembly of actin filaments. Formins are characterized by their ability to nucleate and elongate actin filaments, and they play a crucial role in processes that require dynamic actin structures, such as cell motility and cell division. Mutations or alterations in FGD2 have been associated with certain developmental disorders and diseases. For example, mutations in FGD2 are a cause of faciogenital dysplasia (Aarskog-Scott syndrome), a condition characterized by facial and genital abnormalities and short stature.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for FGD2 antibody 27068-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for FGD2 antibody 27068-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |