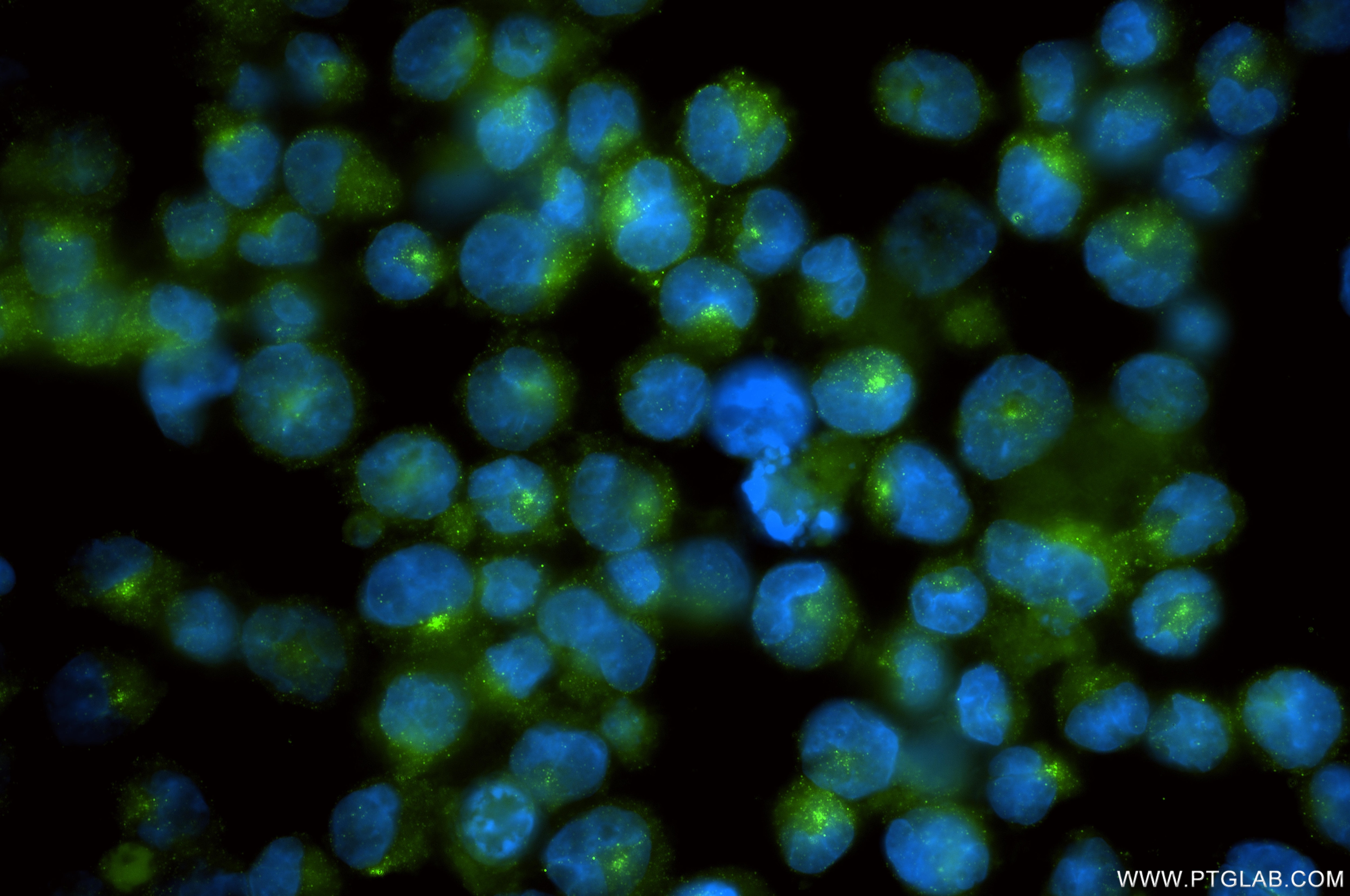
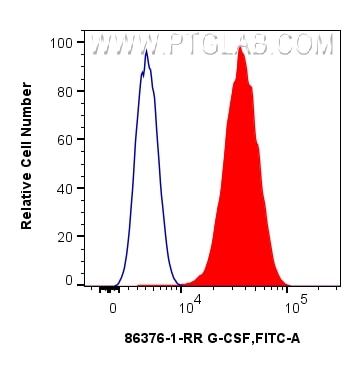
Product Information
86376-1-PBS targets G-CSF as part of a matched antibody pair:
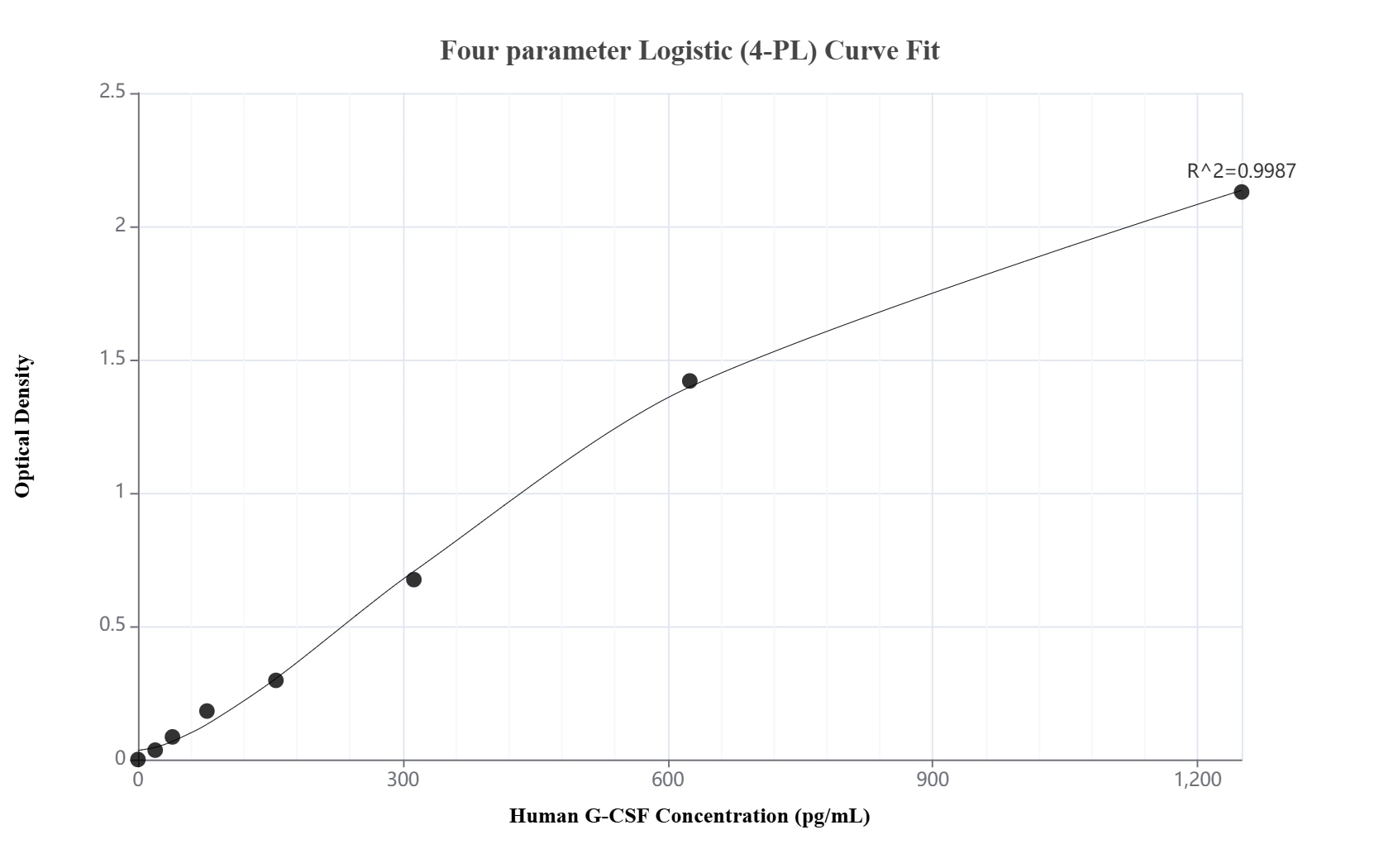
MP02556-1: 86376-1-PBS capture and 86376-2-PBS detection (validated in Sandwich ELISA)
Unconjugated rabbit recombinant monoclonal antibody in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation. Created using Proteintech’s proprietary in-house recombinant technology. Recombinant production enables unrivalled batch-to-batch consistency, easy scale-up, and future security of supply.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Product name: HumanKine® recombinant human G-CSF protein Source: -derived, Tag: Sequence: Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | colony stimulating factor 3 (granulocyte) |
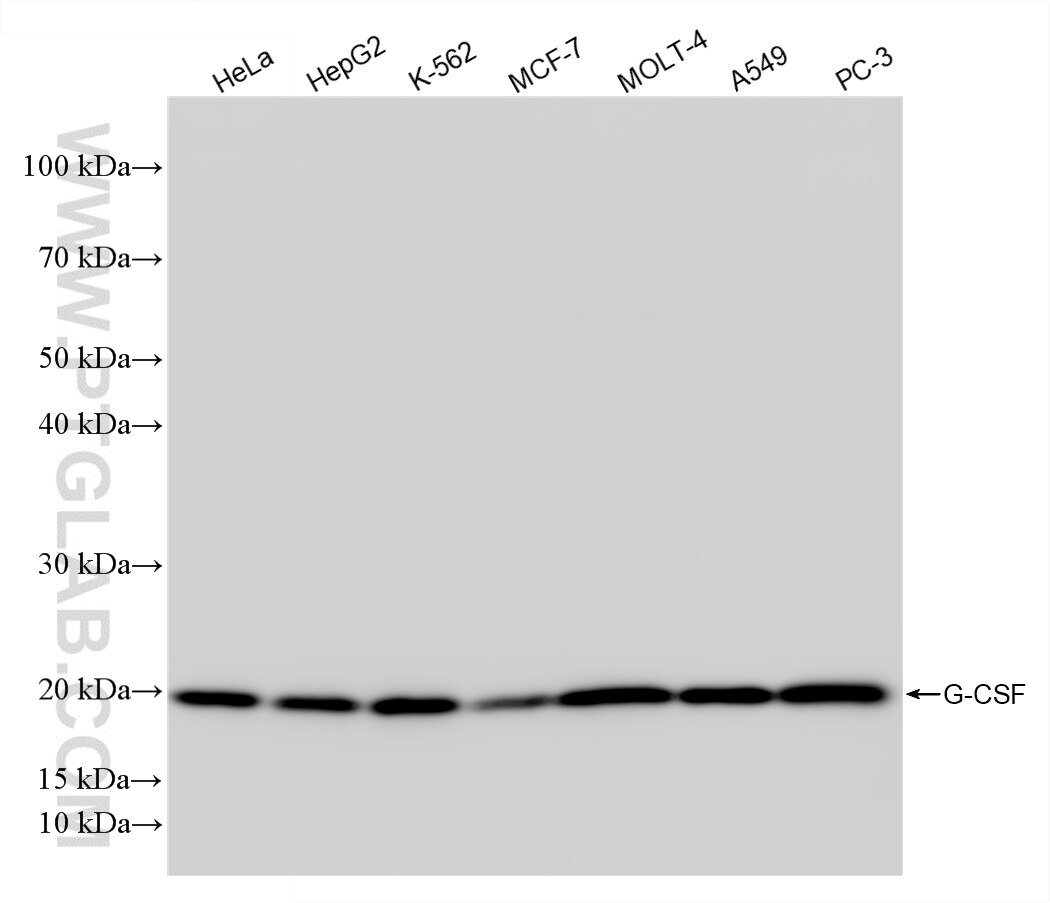
| Observed Molecular Weight | 20 kDa |
| Gene Symbol | G-CSF |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1440 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P09919 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
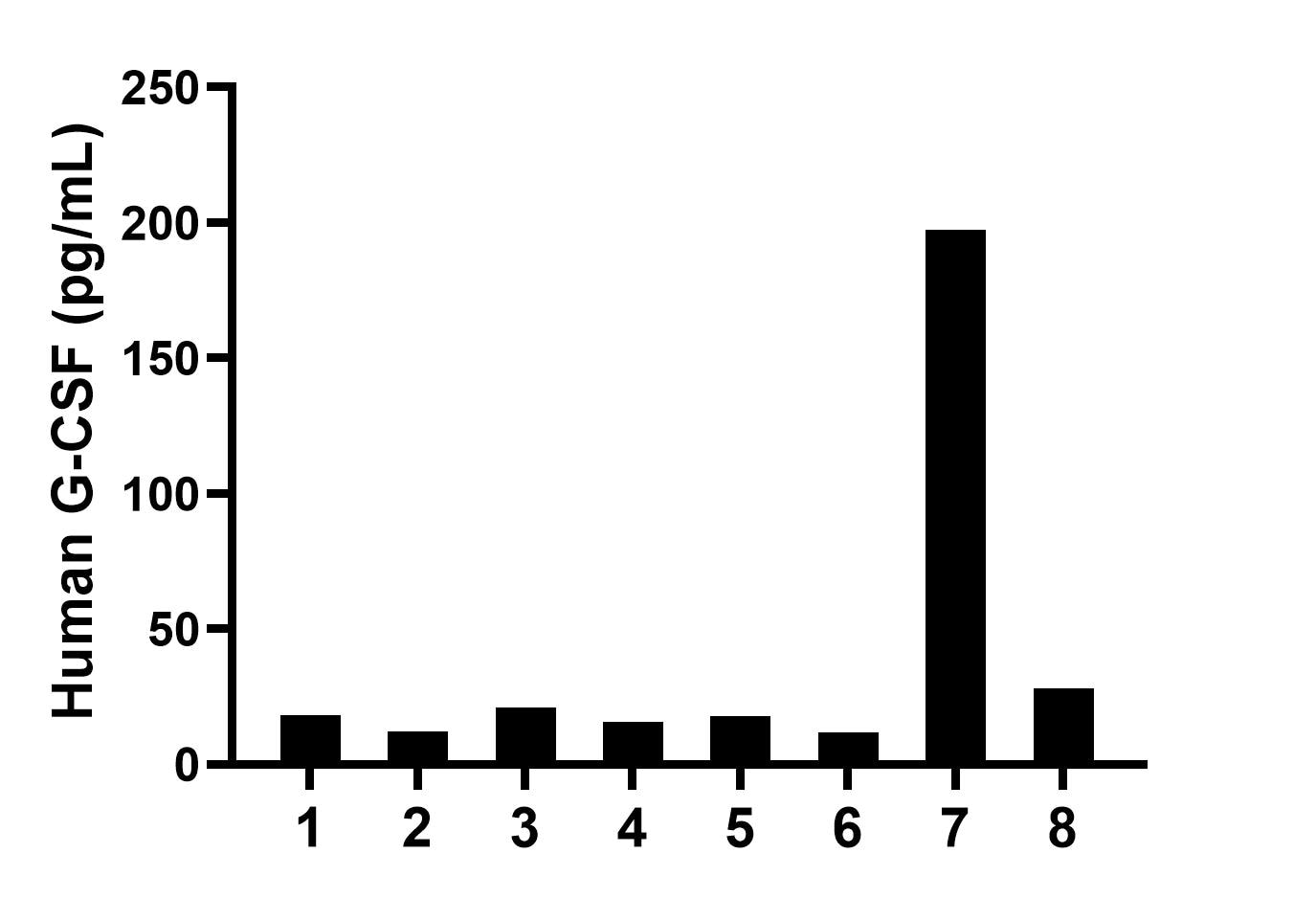
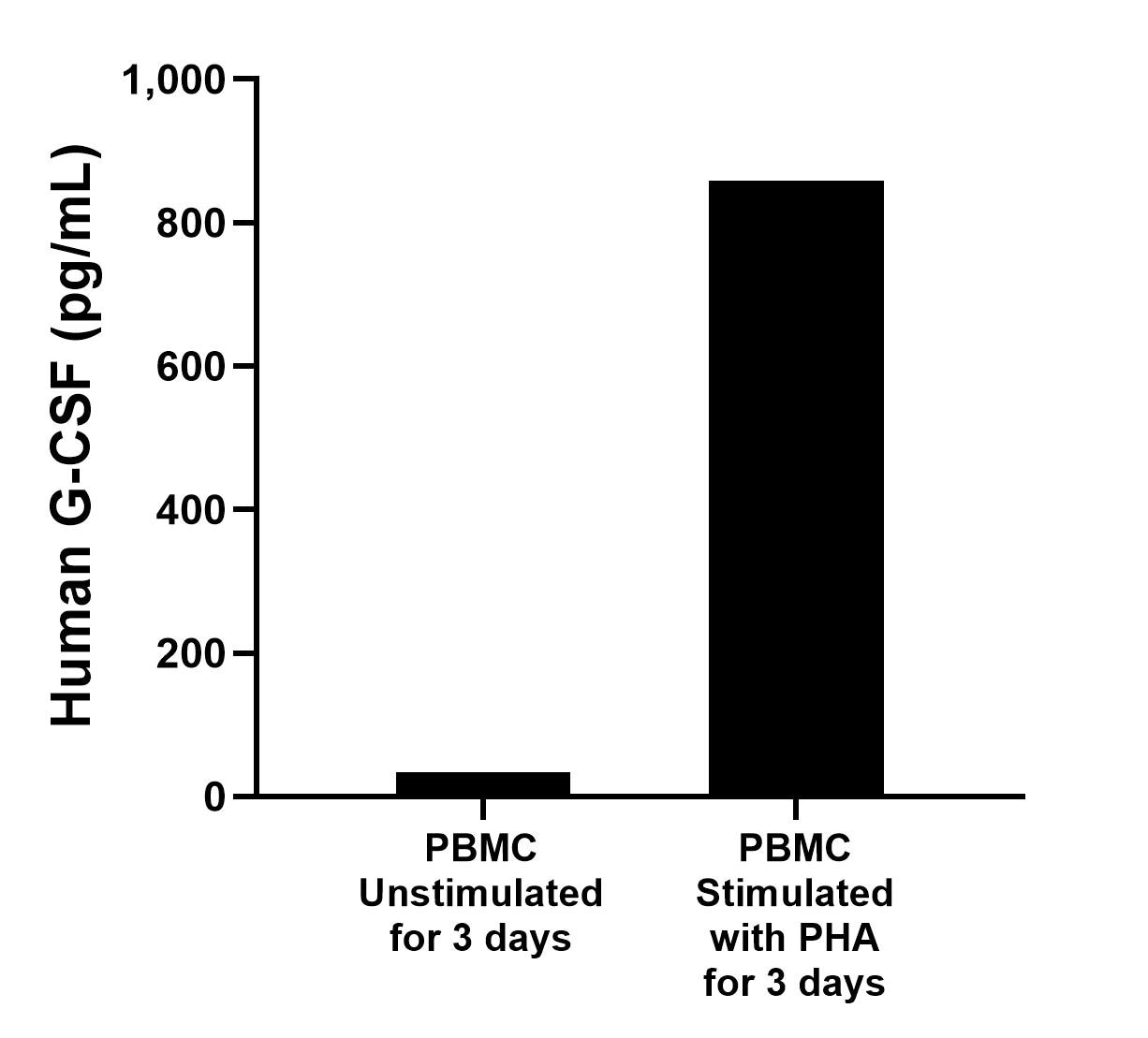
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), also referred to as CSF3, is a protective cytokine with anti-inflammatory effects. G-CSF is important in promoting survival of the granulocytic lineage cells and proliferation and migration of neutrophils as well as trophoblast cells. G-CSF acts by binding to its receptor G-CSFR (also called CSF3R), which after binding with G-CSF activates the canonical Janus kinase (Jak)/signal transducer, activator of transcription (STAT)and Ras/Raf/MAP kinase pathways. G-CSF potently stimulates the proliferation and release of peripheral blood progenitor cells into the bloodstream and is therefore used to treat neutropenia after chemotherapy. Furthermore, G-CSF levels are elevated upon intensive exercise leading to increased neutrophil counts, which are predominantly due to delayed neutrophil apoptosis.