Tested Applications
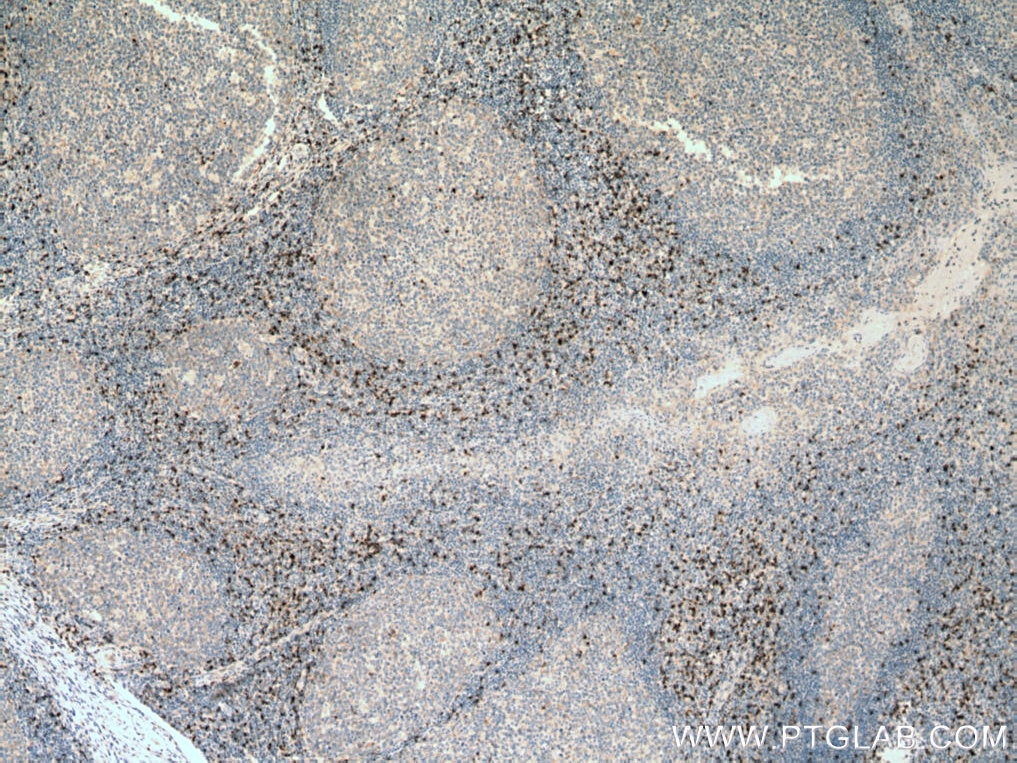
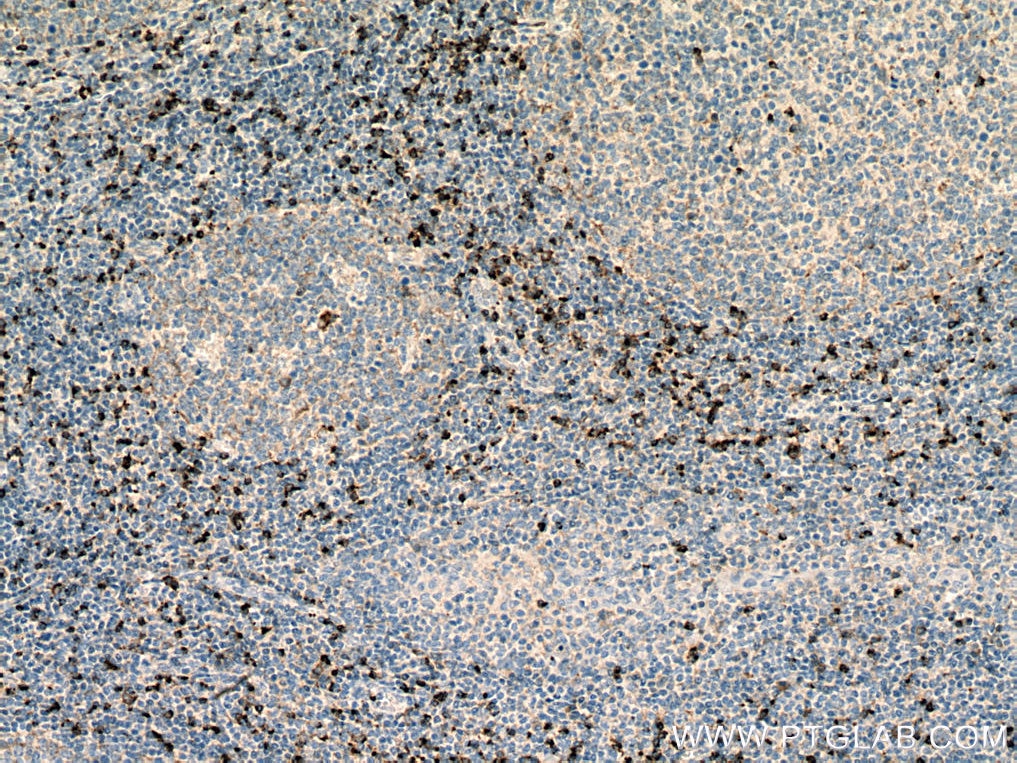
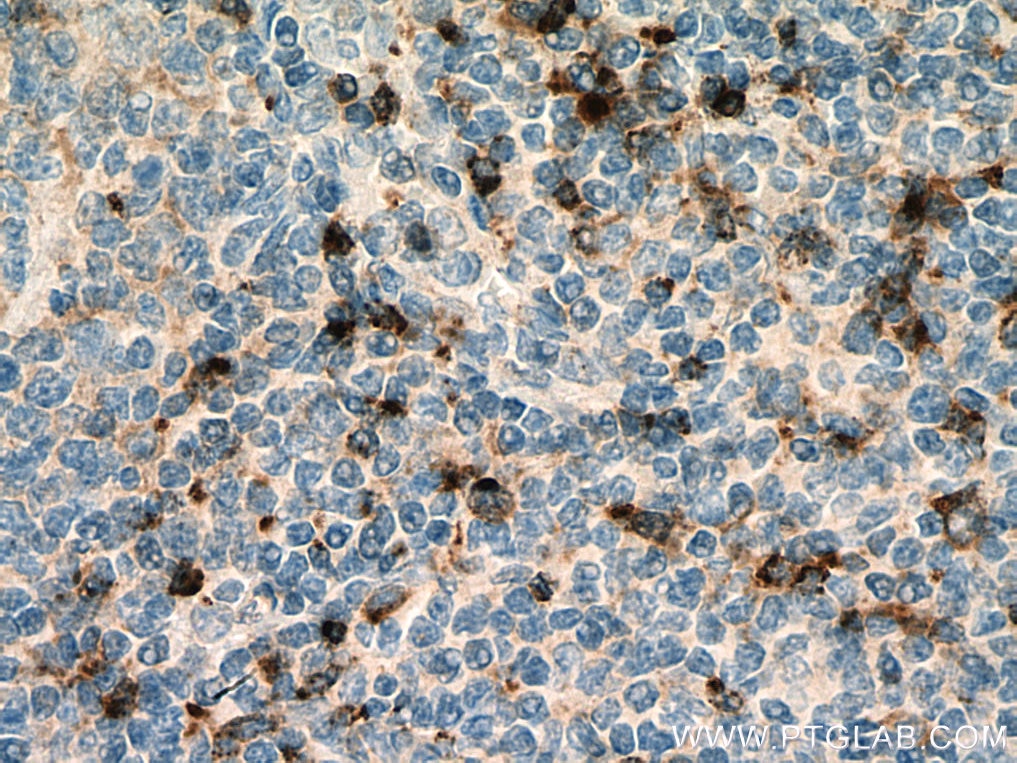
| Positive IHC detected in | human tonsillitis tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
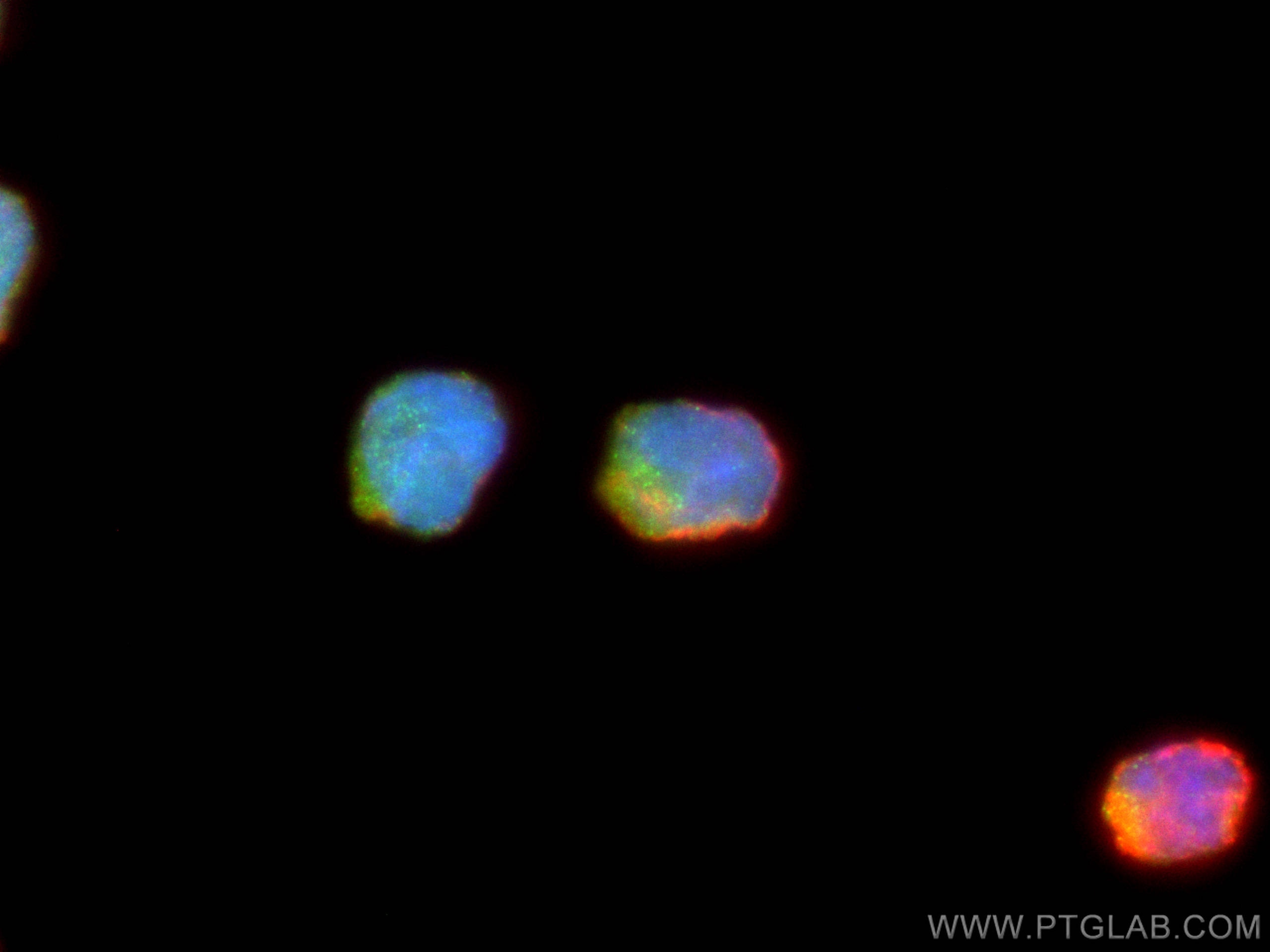
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | NK-92 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:250-1:1000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
27894-1-AP targets Granzyme K in IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag27281 Product name: Recombinant human GZMK protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 85-215 aa of BC035802 Sequence: HSLSKNEASKQTLEIKKFIPFSRVTSDPQSNDIMLVKLQTAAKLNKHVKMLHIRSKTSLRSGTKCKVTGWGATDPDSLRPSDTLREVTVTVLSRKLCNSQSYYNGDPFITKDMVCAGDAKGQKDSCKGDSG Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | granzyme K (granzyme 3; NK tryptase II) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 29 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC035802 |
| Gene Symbol | GZMK |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3003 |
| RRID | AB_2881008 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P49863 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Granzymes are a family of serine proteases stored in granules inside cytotoxic cells of the immune system. There are five human granzymes (granzyme A (GrA), GrB, GrH, GrK and GrM) currently identified, whereas mice have ten known granzymes (GrA-G, GrK, GrM and GrN) (PMID:14499263). Human GrK was first discovered in 1988 after purification from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. GrK is expressed by cytotoxic T lymphocytes, natural killer T cells (NKT), γδ T cells and CD56bright+ NK cells.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for Granzyme K antibody 27894-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Granzyme K antibody 27894-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |