Recombinant Human CD155/PVR protein (His Tag)
Species
Human
Purity
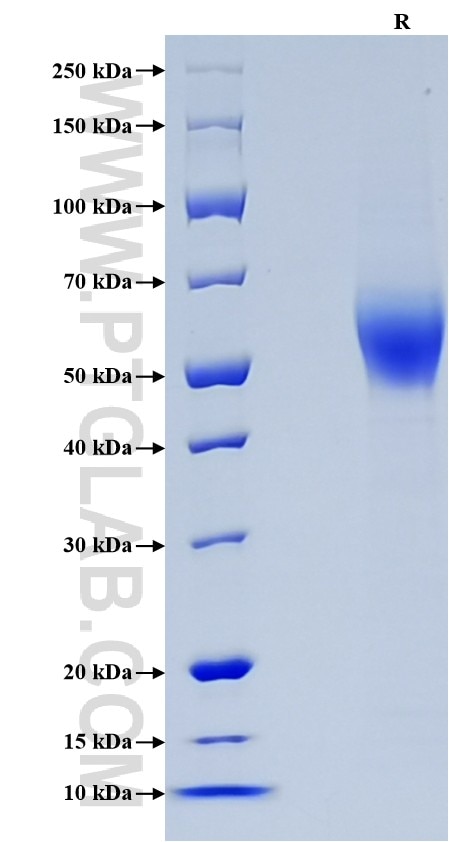
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
His Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg0971
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human CD155 protein Trp21-Asn343 (Accession# NP_006496) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 5817 |
| Accession | NP_006496 |
| PredictedSize | 36.2 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 48-68 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
CD155, also known as PVR, is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein in the immunoglobulin superfamily. It contains three extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains, D1-D3, of which D1 is recognized by the virus. Mature human CD155 consists of a 323 amino acid extracellular domain with one N-terminal V-type and two C2-type Ig-like domains, a 24 amino acid transmembrane segment, and a 50 amino acid cytoplasmic tail. CD155 is thought to play a role in adhesion by interaction with the ECM component vitronectin as well as a role in NK killing of tumor cells. CD155 binds to two receptors of NK cells, CD96 and CD226, and accumulates at cell-cell contact sites, leading to the formation of mature immune synapses between NK cells and target cells. CD155 serves as the entry receptor for poliovirus and thereby mediates human susceptibility to poliovirus infection.
References:
1.Zhang, Ping et al. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America vol. 105,47 (2008): 18284-9. 2.Paolini, Rossella, and Rosa Molfetta. International journal of molecular sciences vol. 24,16 (2023): 12958. 3.Lupo, Kyle B, and Sandro Matosevic. Journal of hematology & oncology vol. 13,1 (2020): 76. 4.Solecki, David J et al. The Journal of biological chemistry vol. 277,28 (2002): 25697-702.