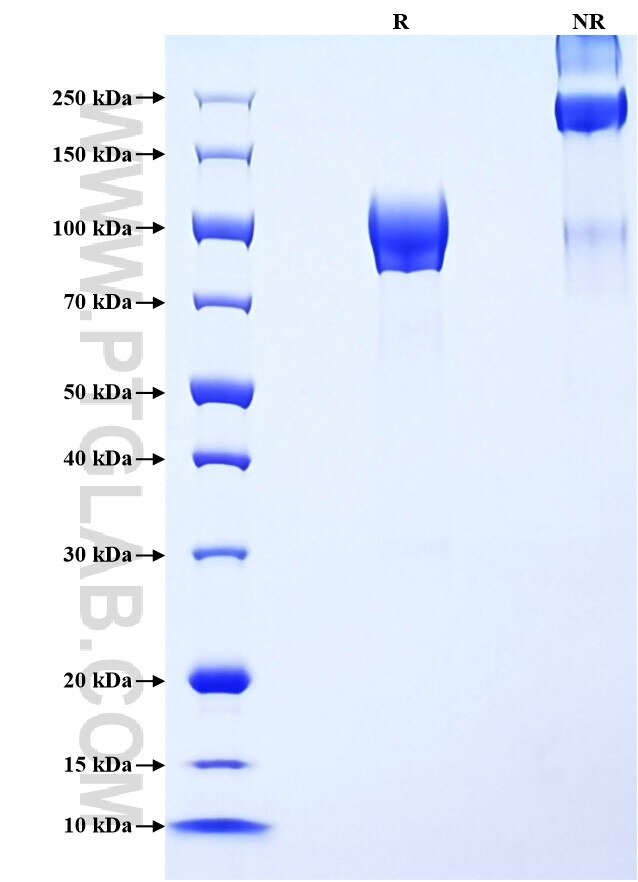
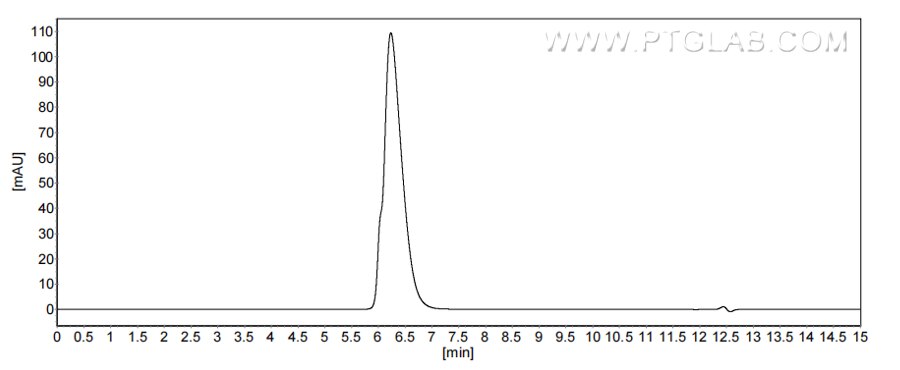
Recombinant Human CD6 protein (rFc Tag)(HPLC verified)
Species
Human
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
>90%, SEC-HPLC
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg2079
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE >90%, SEC-HPLC |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human CD6 protein His18-Glu398 (Accession# P30203-1) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 923 |
| Accession | P30203-1 |
| PredictedSize | 66.9 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 80-120 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
CD6 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein of 105-130 kDa that belongs to the scavenger receptor cysteine-rich superfamily. It is composed of an extracellular region, which consists of three tandem SRCR domains, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail devoid of intrinsic catalytic activity but harboring several phosphorylatable residues suitable for intracellular signal transduction. CD6 is expressed by T cells, medullary thymocytes, a subset of B cells and NK cells, and in some cells of the brain. CD6 plays a role in lymphocyte activation, proliferation, and survival processes via interaction with its endogenous ligands.
References:
1. Vanesa Gabriela Martínez, et al. (2011) Pharmacol Rev. 63(4):967-1000. 2. Lucía Aragón-Serrano, et al. (2023) Int J Mol Sci. 24(24):17510. 3. Lizette Bonet, et al. (2013) FEBS Lett. 587(14):2205-13. 4. A Aruffo, et al. (1991) J Exp Med. 174(4):949-52. 5. Monika Braun, et al. (2011) J Innate Immun. 3(4):420-34.