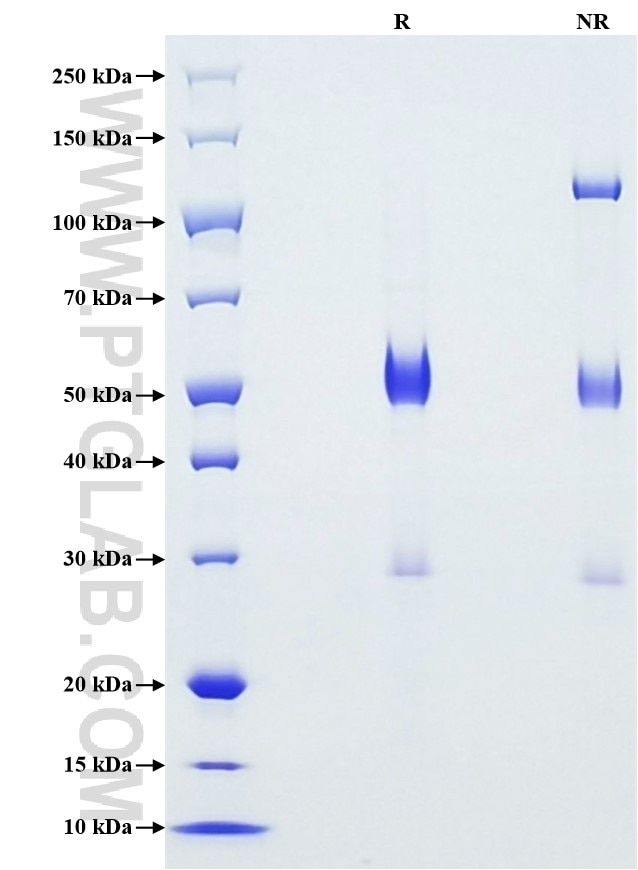
Recombinant Human HSP47/SERPINH1 protein (His Tag)
Species
Human
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
His Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg1201
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human HSP47 protein Ala19-Leu418 (Accession# P50454) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 871 |
| Accession | P50454 |
| PredictedSize | 45.6 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 48-60 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
HSP47/SERPINH1 is also named as Serpin H1, CBP1, CBP2, 47 kDa heat shock protein, Arsenic-transactivated protein 3 (AsTP3) and Collagen-binding protein (Colligin). It belongs to the serpin family. The Serpin Family H Member 1 (SERPINH1) gene encodes a protein called HSP47, which is required for the correct folding and secretion of collagen. SERPINH1 has been implicated in several collagen-related diseases, such as, brittle bone disease, keloid scars, and lung fibrosis. SERPINH1 also correlates with the grade of glioma, and regulates proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma cell lines. SERPINH1 regulates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and modulates gastric cancer (GC) progression. SERPINH1 is aberrantly expressed in cervical cancer, breast cancer, glioblastoma and colorectal cancer. SERPINH1 promotes invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells by regulating the expression of several extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins.
References:
1. Duarte BDP, Bonatto D. (2018) J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 144(12):2319-2328. 2. Tian S, et al. (2020) Aging (Albany NY). 12(4):3574-3593. 3. Zhao D, et al. (2014) J Neurooncol. 118(1):39-47. 4. Zhu J, et al. (2015) Cancer Res. 75(8):1580-91.