Recombinant Mouse CD117/c-kit protein (His Tag)
Species
Mouse
Purity
>95 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
His Tag
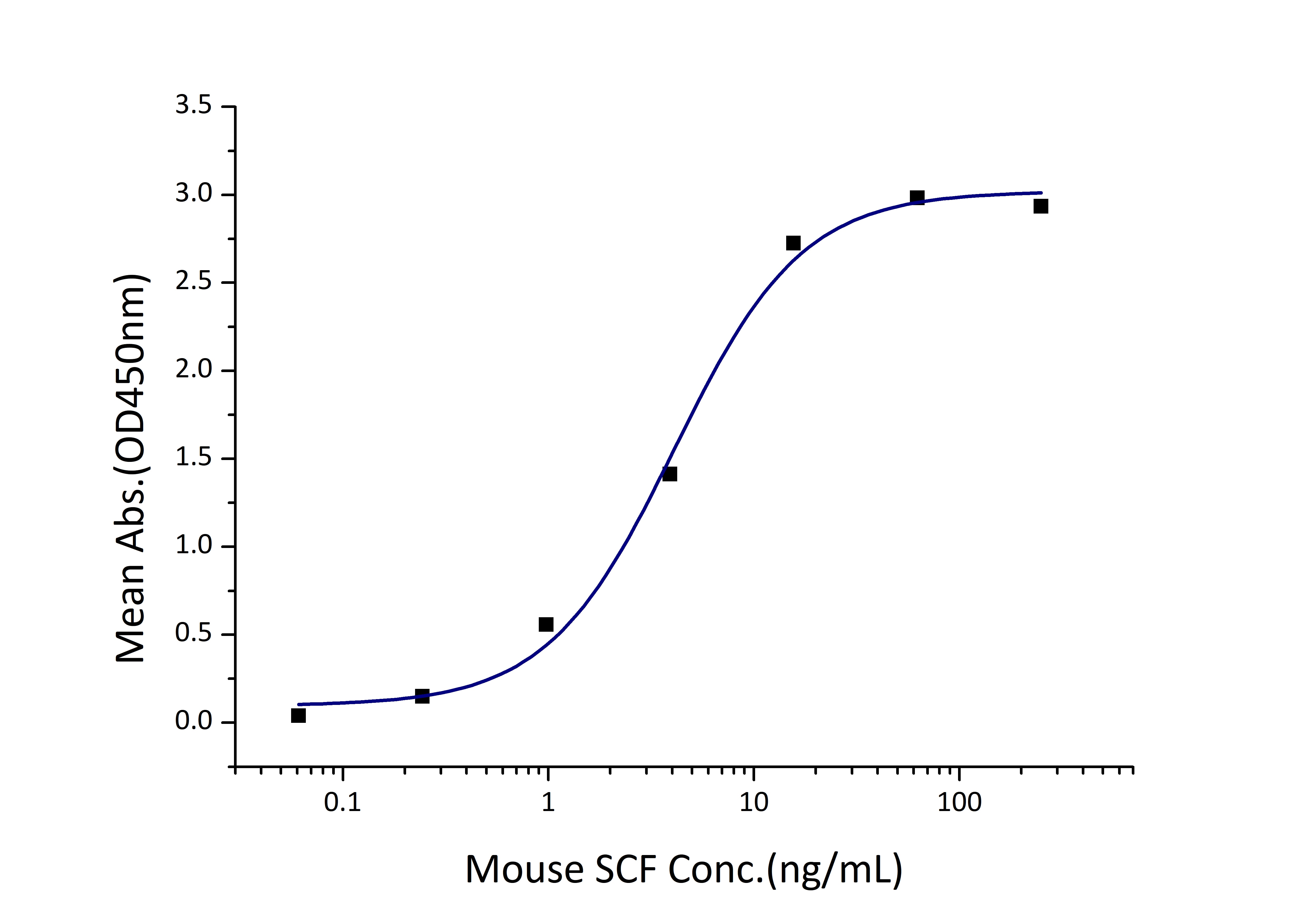
Activity
EC50: 2-8 ng/mL
Cat no : Eg0883
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >95 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Immobilized Mouse CD117 (His tag) at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Mouse SCF (His tag) with a linear range of 2-8 ng/mL. |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Mouse CD117 protein Ser25-Pro527 (Accession# P05532-1) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 16590 |
| Accession | P05532-1 |
| PredictedSize | 56.8 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 65-85 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
CD117, also known as c-Kit and SCFR, is a transmembrane protein with tyrosine kinase activity encoded by the oncogene c-kit. It is a member of the type III receptor tyrosine kinase family, which also includes CSF-1R, PDGFRβ, PDGFRα, and FLT3. CD117 is expressed on hematopoietic stem cells and progenitor cells, mast cells, and is also found in a wide range of non-haemopoietic cell types (including melanocytes, germ cells, astrocytes, renal tubules, breast glandular epithelial cells, sweat glands, and interstitial cells of Cajal). CD117 plays an important role in early haemopoiesis. It is also involved in pigmentation, fertility, gut movement, and some aspects of the nervous system.
References:
1.Y Yarden, et al. (1987) EMBO J. 6(11):3341-51. 2.L K Ashman (1999) Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 31(10):1037-51. 3.Johan Lennartsson (2012) Physiol Rev. 92(4):1619-49. 4.Brittni M Foster, et al. (2018) Biomedicines. 6(1):31.