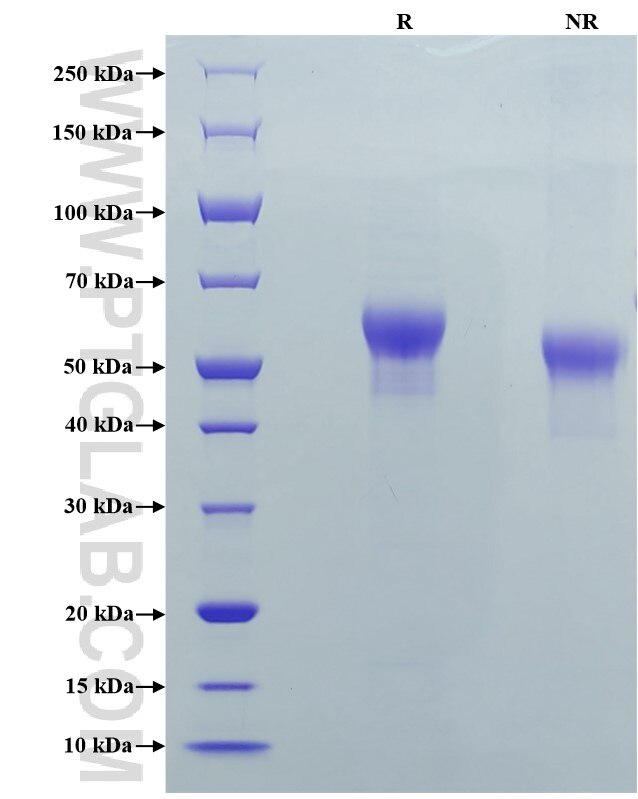
Recombinant Mouse CD126/IL-6R alpha protein (His Tag)
Species
Mouse
Purity
>95 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
His Tag
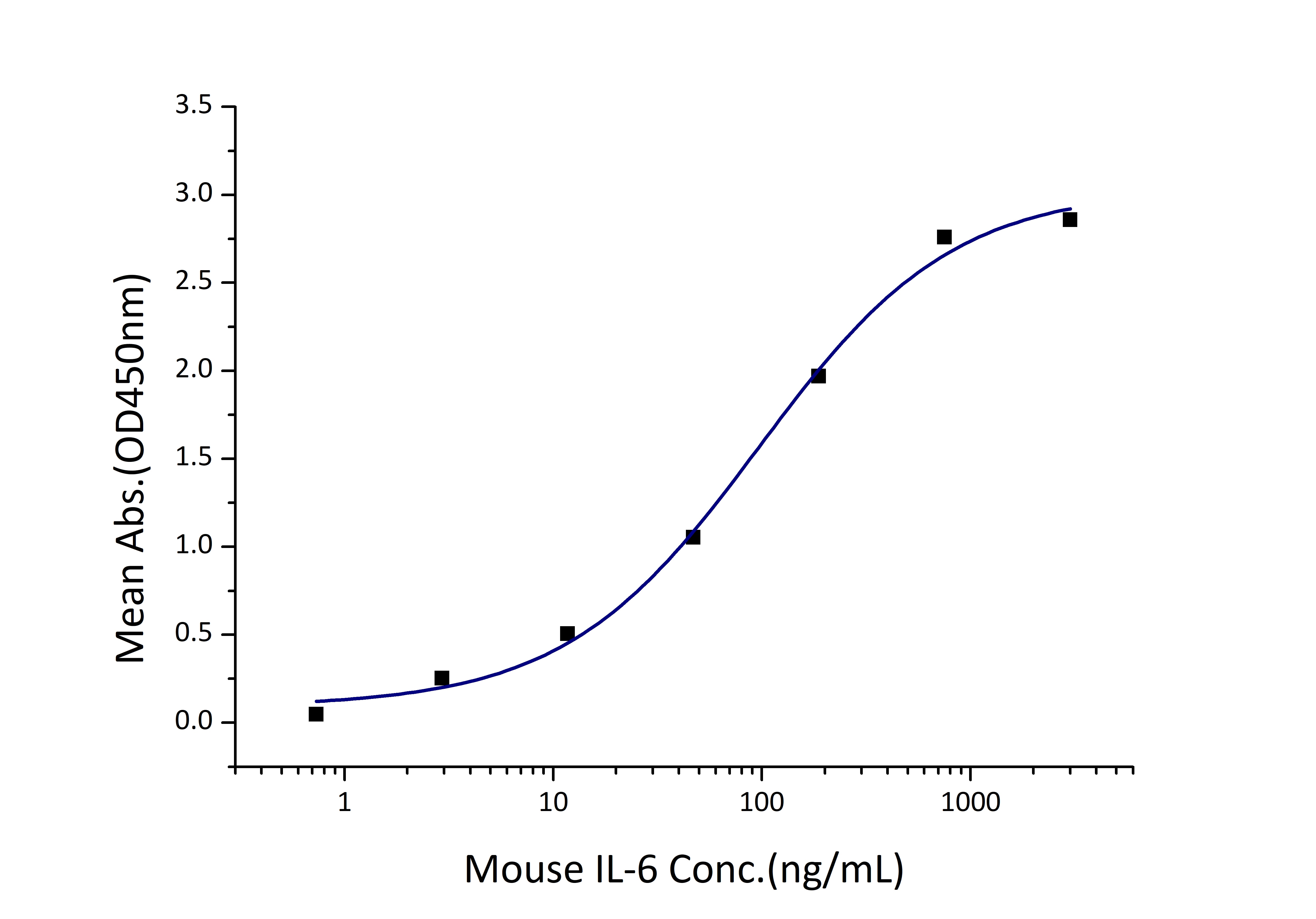
Activity
EC50: 50-200 ng/mL
Cat no : Eg0664
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >95 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Immobilized Mouse IL-6R alpha (His tag) at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Mouse IL-6 (Myc tag, His tag) with a linear range of 50-200 ng/mL. |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Mouse IL-6R alpha protein Leu20-Glu357 (Accession# P22272) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 16194 |
| Accession | P22272 |
| PredictedSize | 38.8 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 52-65 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a pleiotropic cytokine produced by a variety of cells during infection, trauma, and immunological challenge. IL-6 acts via a receptor complex consisting of two distinct membrane-bound glycoproteins, an 80-kDa IL-6-binding subunit (IL-6R alpha, CD126, gp80) and a 130-kDa signal-transducing element (gp130, CD130). After binding of IL-6 to membrane-bound IL-6R alpha, the complex of IL-6 and IL-6R alpha associates with gp130, thus activating the receptor. Expression of gp130 is found in almost all organs while expression of IL-6R alpha is predominantly confined to hepatocytes and leukocyte subpopulations (monocytes, neutrophils, T cells, and B cells). Soluble form of IL-6R alpha has been found in human serum and urine.
References:
1. D Novick. (1989) J Exp Med. 170(4):1409-14. 2. M Honda. (1992) J Immunol. 148(7):2175-80. 3. H Tilg, et al. (1994) Blood. 83(1):113-8. 4. P C Heinrich. (1998) Biochem J. 334(2):297-314. 5. S A Jones. (2001) FASEB J. 15(1):43-58.