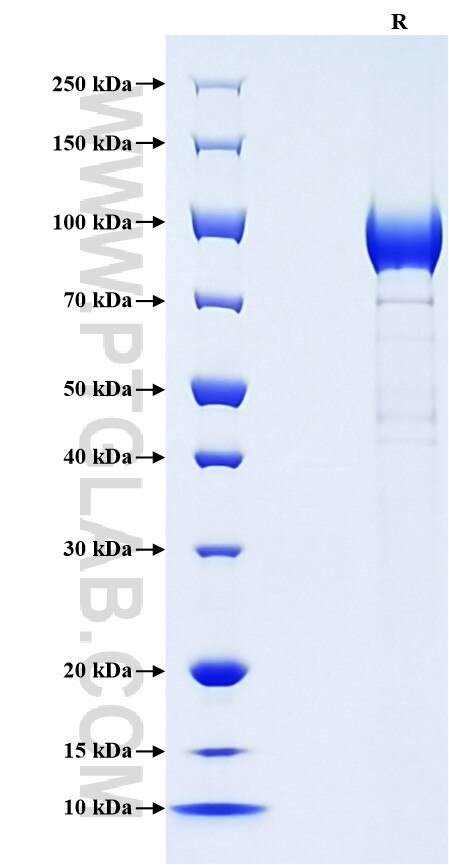
Recombinant Mouse LCAT protein (rFc Tag)
Species
Mouse
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg2756
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Mouse LCAT protein Phe25-Glu438 (Accession# P16301) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 16816 |
| Accession | P16301 |
| PredictedSize | 73.3 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 80-110 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Lecithin-cholesterolacyltransferase (LCAT) is an enzyme that acts as a catalyst in plasma, is synthesized by the liver and released into the bloodstream, and exists either free or bound to lipoproteins. The main function of LCAT is to transfer unsaturated fatty acids at the C2 position of HDL lecithin to free cholesterol to generate hemolytic lecithin and cholesteryl esters. The main function of LCAT is to transfer unsaturated fatty acids from the C2 site of HDL lecithin to free cholesterol, resulting in the production of hemolysed lecithin and cholesteryl esters, which are catalyzed by LCAT in almost 70-80% of plasma cholesterol.Reduced or complete lack of normal function of LCAT leads to two autosomal recessive disorders, familial LCAT deficiency and fish-eye disease, respectively. (PMID: 35121343)
References:
1. Yang K, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;147:112677. 2. Lin X, et al. J Adv Res. 2024;63:187-194. 3. Leal-Gonzalez R, et al. Obstet Med. 2021;14(3):193-196. 4. Mehta R, et al. Lipids Health Dis. 2021;20(1):70.