Recombinant Mouse PSAP/Prosaposin protein (rFc Tag)
Species
Mouse
Purity
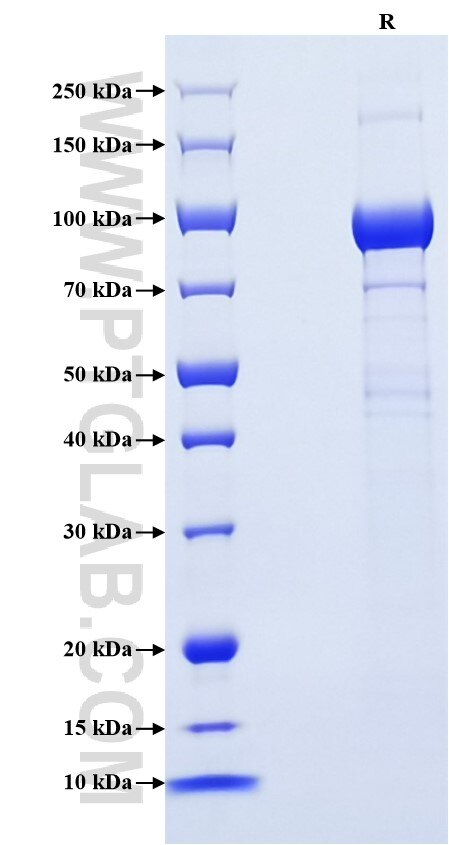
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg3155
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Mouse PSAP protein Ser17-Asn557 (Accession# Q61207) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 19156 |
| Accession | Q61207 |
| PredictedSize | 85.8 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 90-100 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Psap (Prosaposin) is a highly conserved glycoprotein that is involved in the metabolism of various sphingolipids within the cell and can be secreted into plasma, breast milk, or cerebrospinal fluid.Prosaposin proteins are proteolytically cleaved to produce four different polypeptides called saposin A, B, C, or D, which are required for the hydrolysis of certain sphingolipids by lysosomal hydrolases. required for the hydrolysis of certain sphingolipids by lysosomal hydrolases, and whose mutation results in lysosomal hydrolase deficiency and subsequent lysosomal storage disease. (PMID: 33197249) PSAP overexpression is associated with poor prognosis and promotes tumorigenesis and cancer stem cell proliferation in subcutaneous and in situ models of glioma. In patients with mesenchymal glioblastoma, PSAP is a marker of poor prognosis, as its high expression has been found to shorten patients' overall survival.
References:
1.Lin ZH, et al. Brain. 2021;144(1):e3. 2. Wen Z, et al. Pathol Res Pract. 2022;238:154027. 3. Pankaj Sharma et al. Science. 2024; 383,190-200.