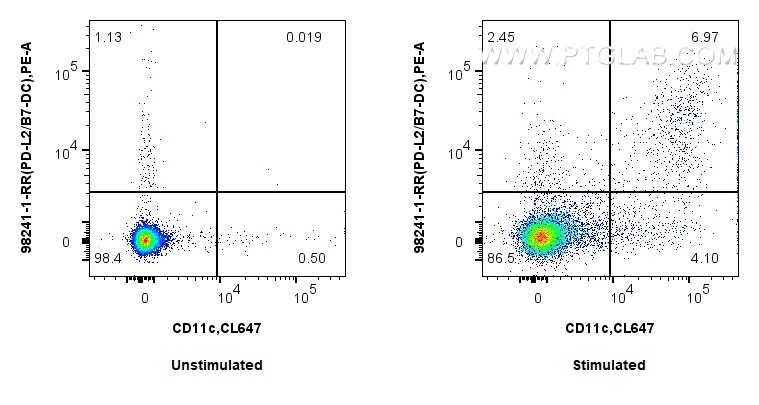
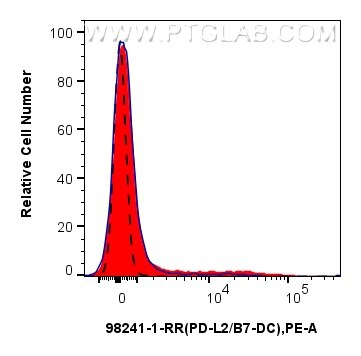
Tested Applications
| Positive FC detected in | GM-CSF treated mouse splenocytes |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry (FC) | FC : 0.25 ug per 10^6 cells in 100 μl suspension |
| This reagent has been tested for flow cytometric analysis. It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
98241-1-RR targets PD-L2/CD273 in FC applications and shows reactivity with mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 28kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_021396.2 |
| Gene Symbol | Pdcd1lg2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 58205 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purfication |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9WUL5 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at 2 - 8°C. Stable for one year after shipment. |
Background Information
Programmed cell death ligand 2 (PD-L2, also known as CD273, or B7-DC), is one of the B7 family molecules which are type I transmembrane proteins belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. PD-L2 was identified both by its homology to PD-L1 and by analysis of genes differentially expressed in libraries generated from dendritic cells (DC) and activated macrophages (PMID: 14515254). PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1, a costimulatory molecule that plays an inhibitory role in regulating T cell activation in the periphery.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for PD-L2/CD273 antibody 98241-1-RR | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |