Tested Applications
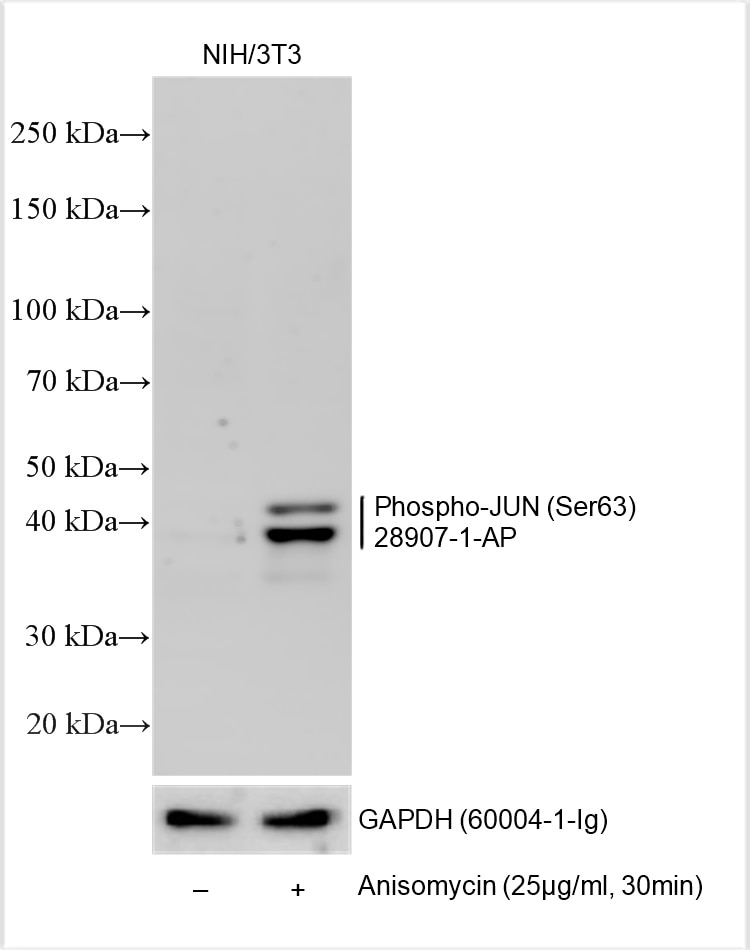
| Positive WB detected in | Anisomycin treated NIH/3T3 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
28907-1-AP targets Phospho-JUN (Ser63) in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Peptide Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | jun oncogene |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 331 aa, 36 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 40-45 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC068522 |
| Gene Symbol | JUN |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3725 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P05412 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
JUN, the most extensively studied protein of the activator protein-1 (AP-1) complex, is involved in numerous cell activities, such as proliferation, apoptosis, survival, tumorigenesis and tissue morphogenesis (PMID: 22180088). JUN is a transcription factor that recognizes and binds to the enhancer heptamer motif 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3'. It promotes activity of NR5A1 when phosphorylated by HIPK3 leading to increased steroidogenic gene expression upon cAMP signaling pathway stimulation. JUN is a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor that acts as homo- or heterodimer, binding to DNA and regulating gene transcription (PMID: 9732876).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Phospho-JUN (Ser63) antibody 28907-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |