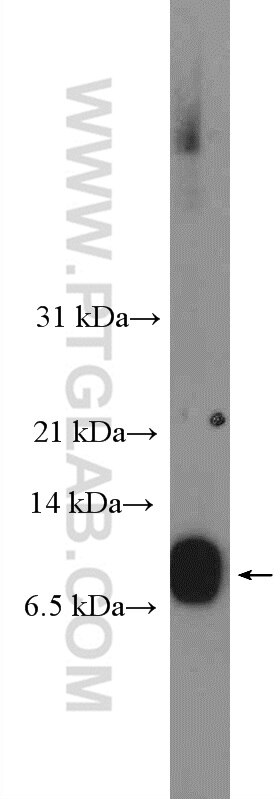
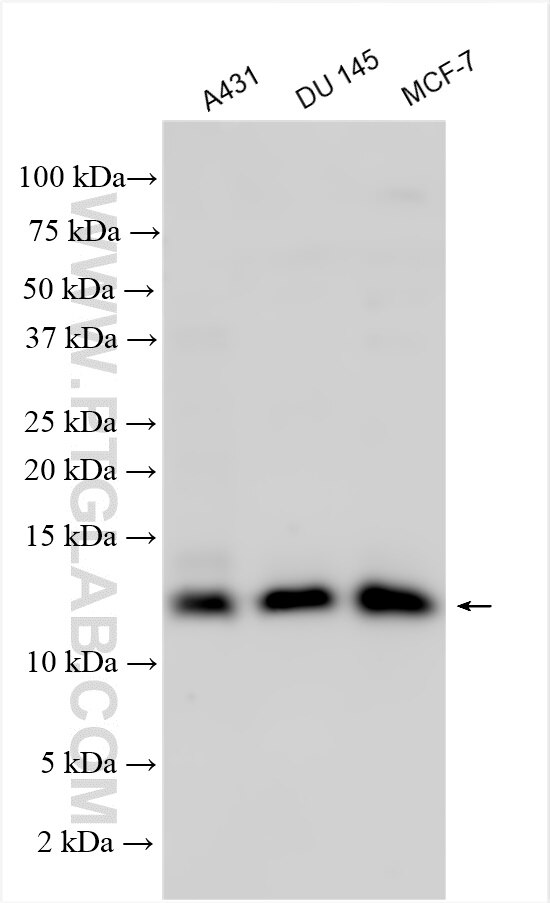
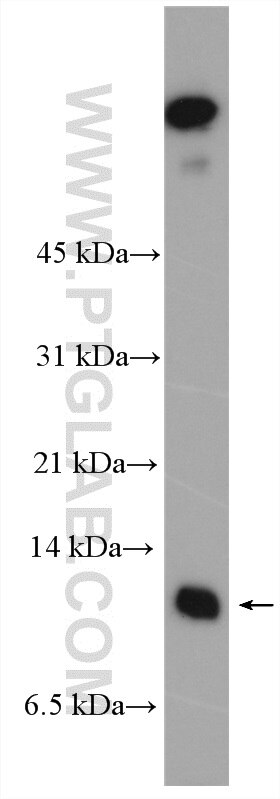
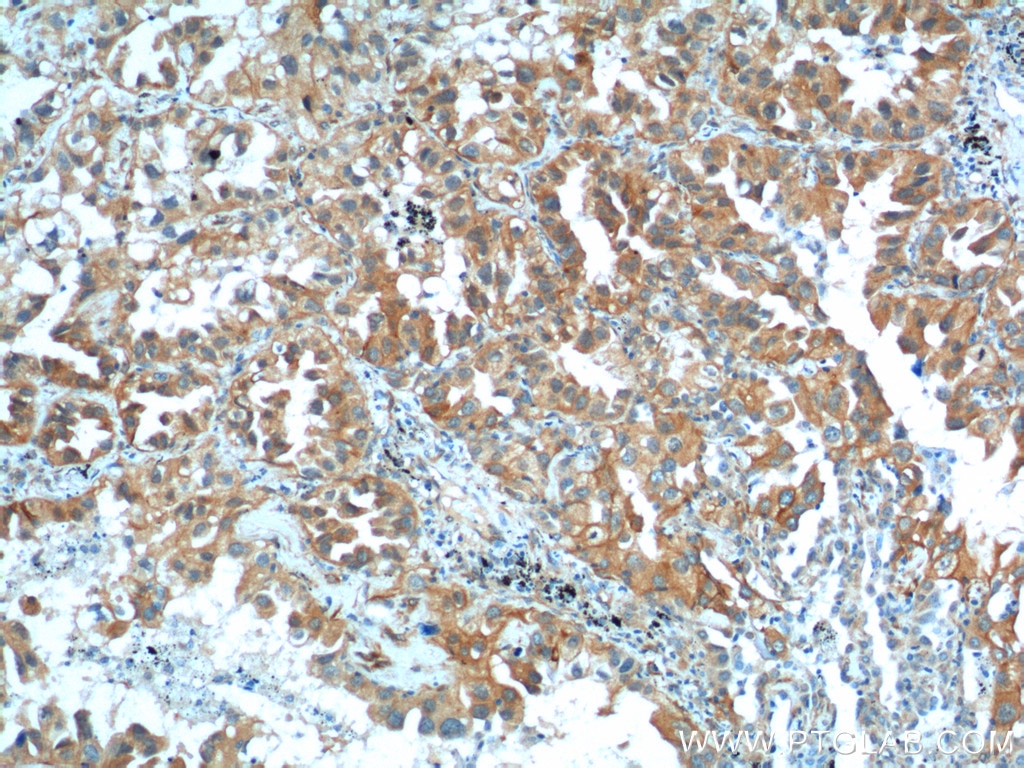
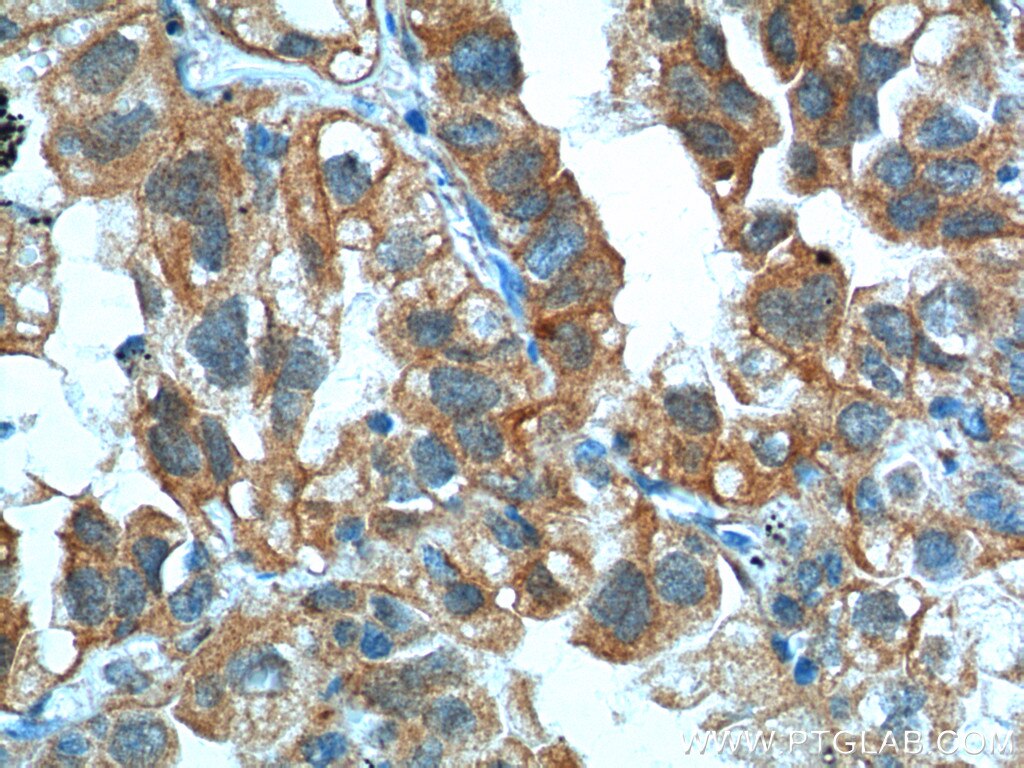
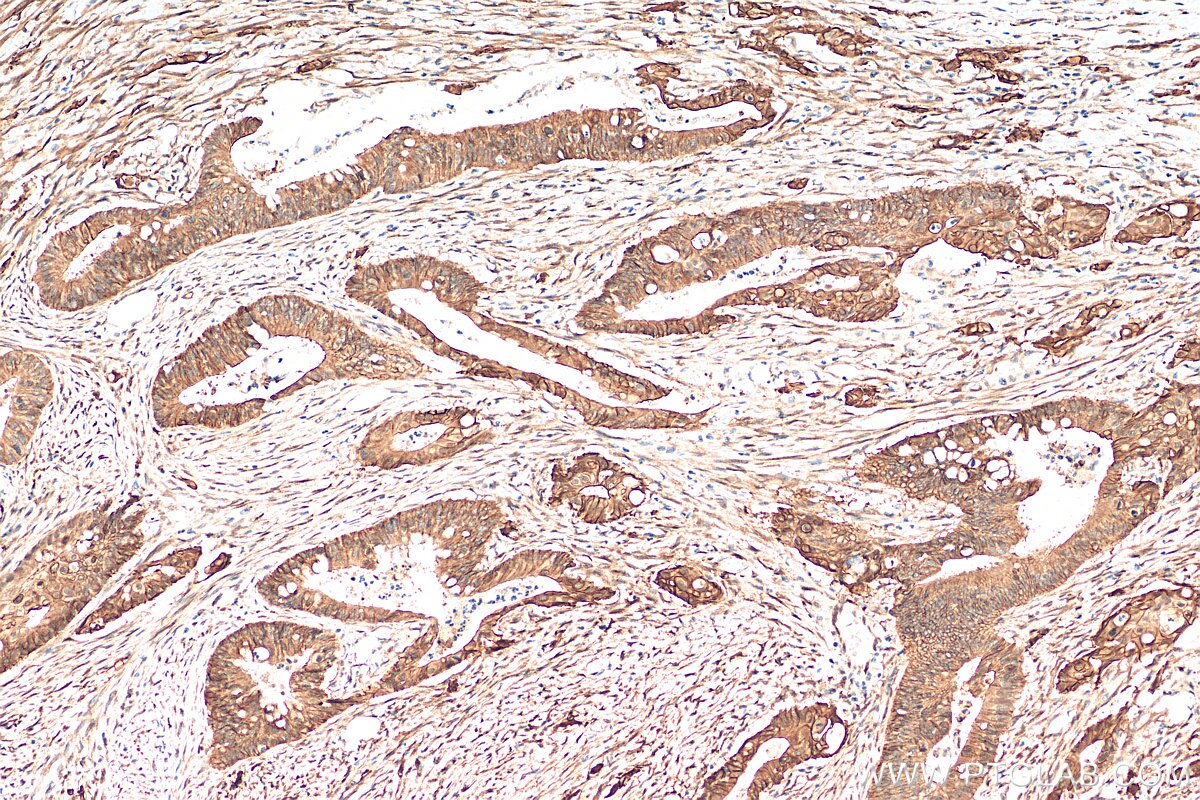
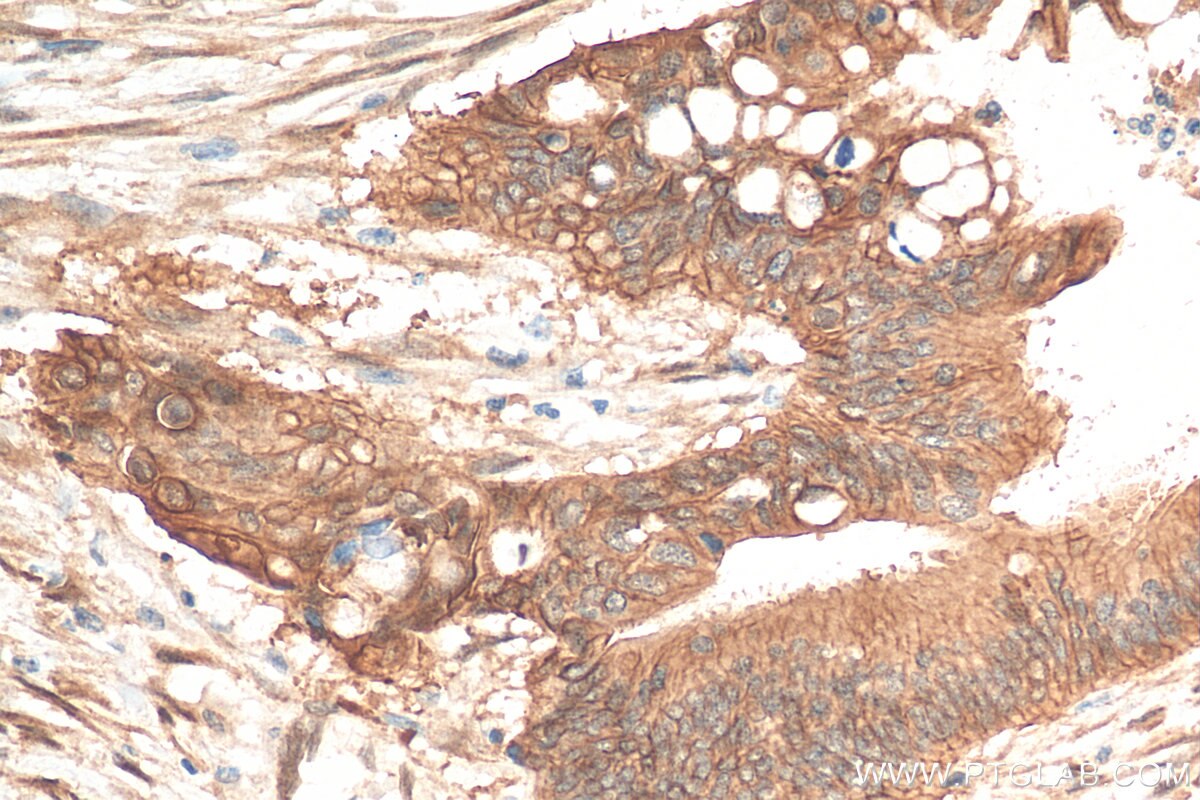
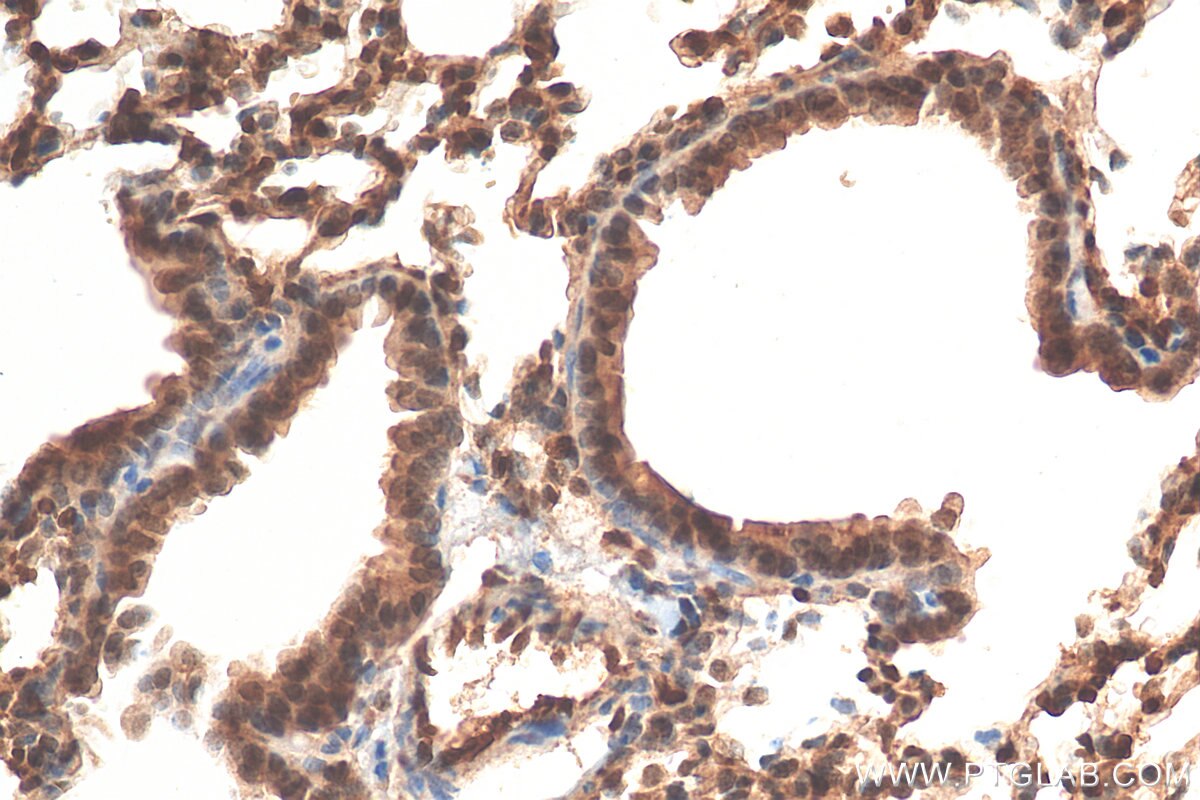
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | A431 cells, DU 145 cells, MCF-7 cells |
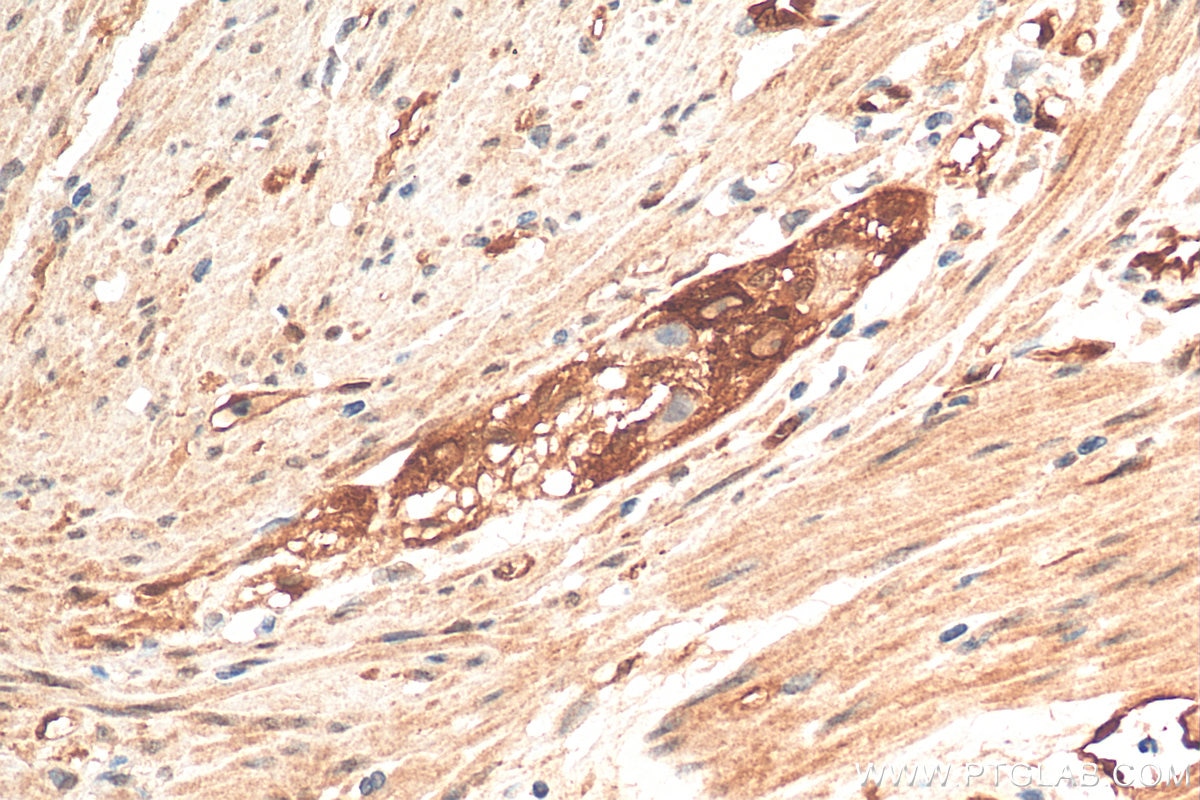
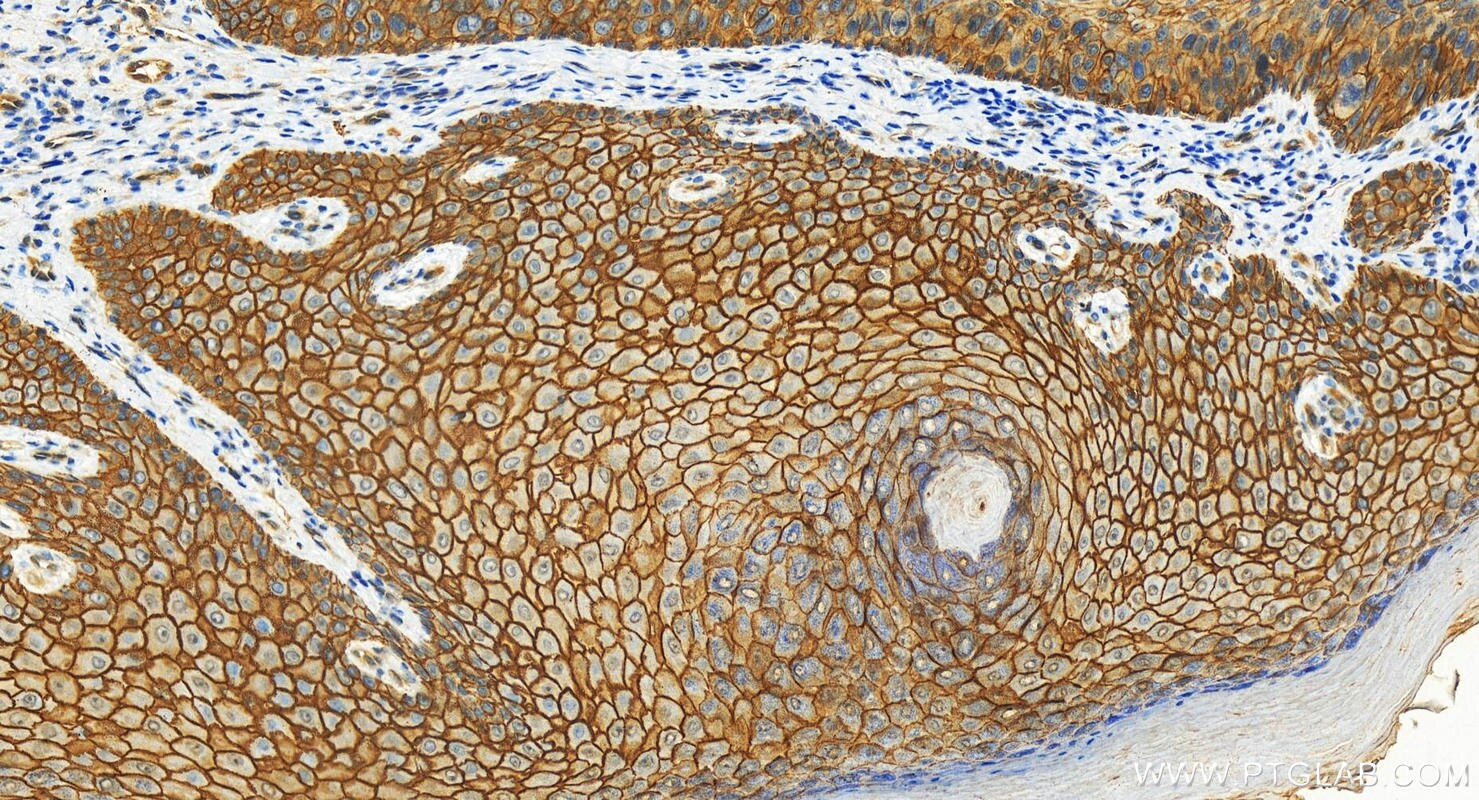
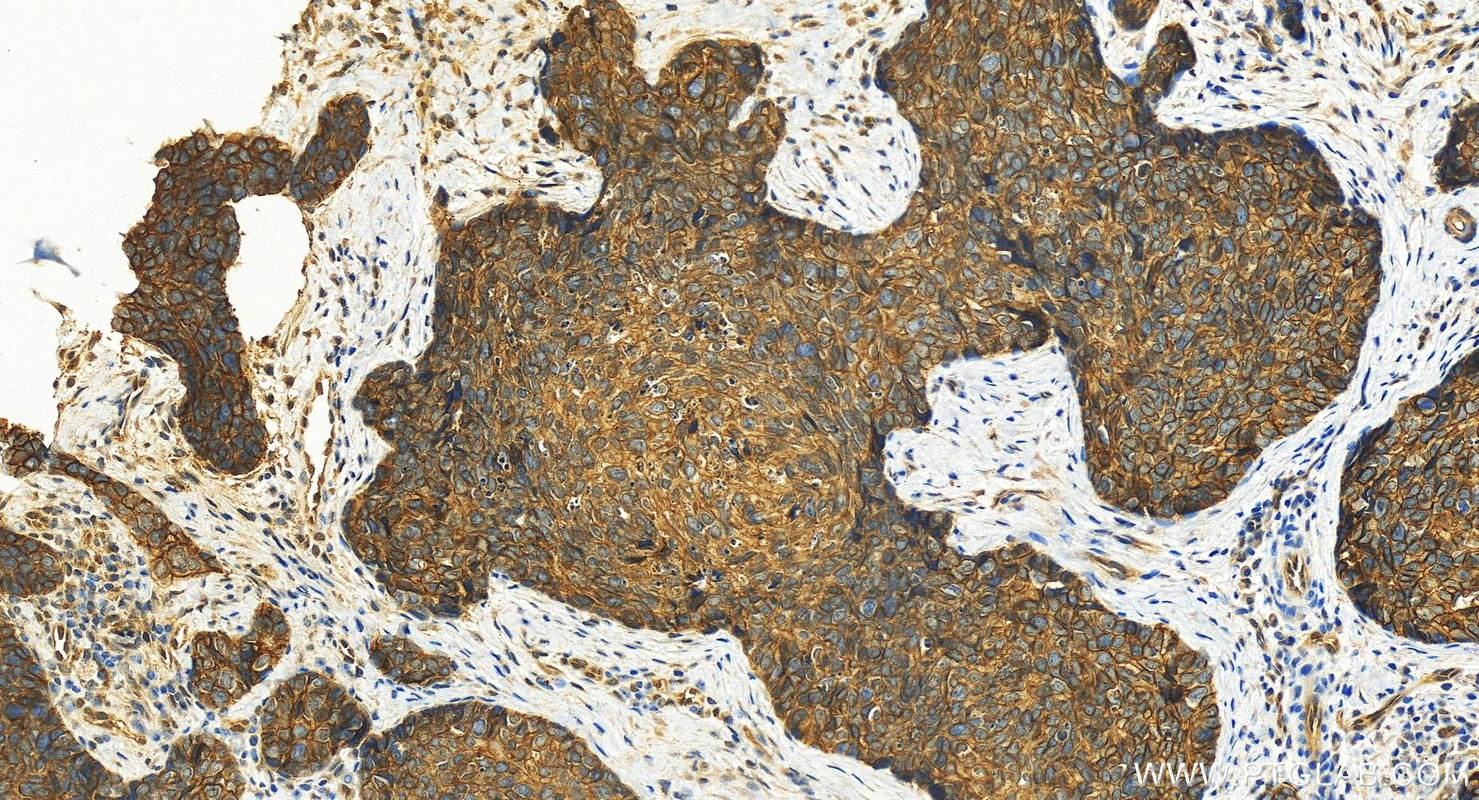
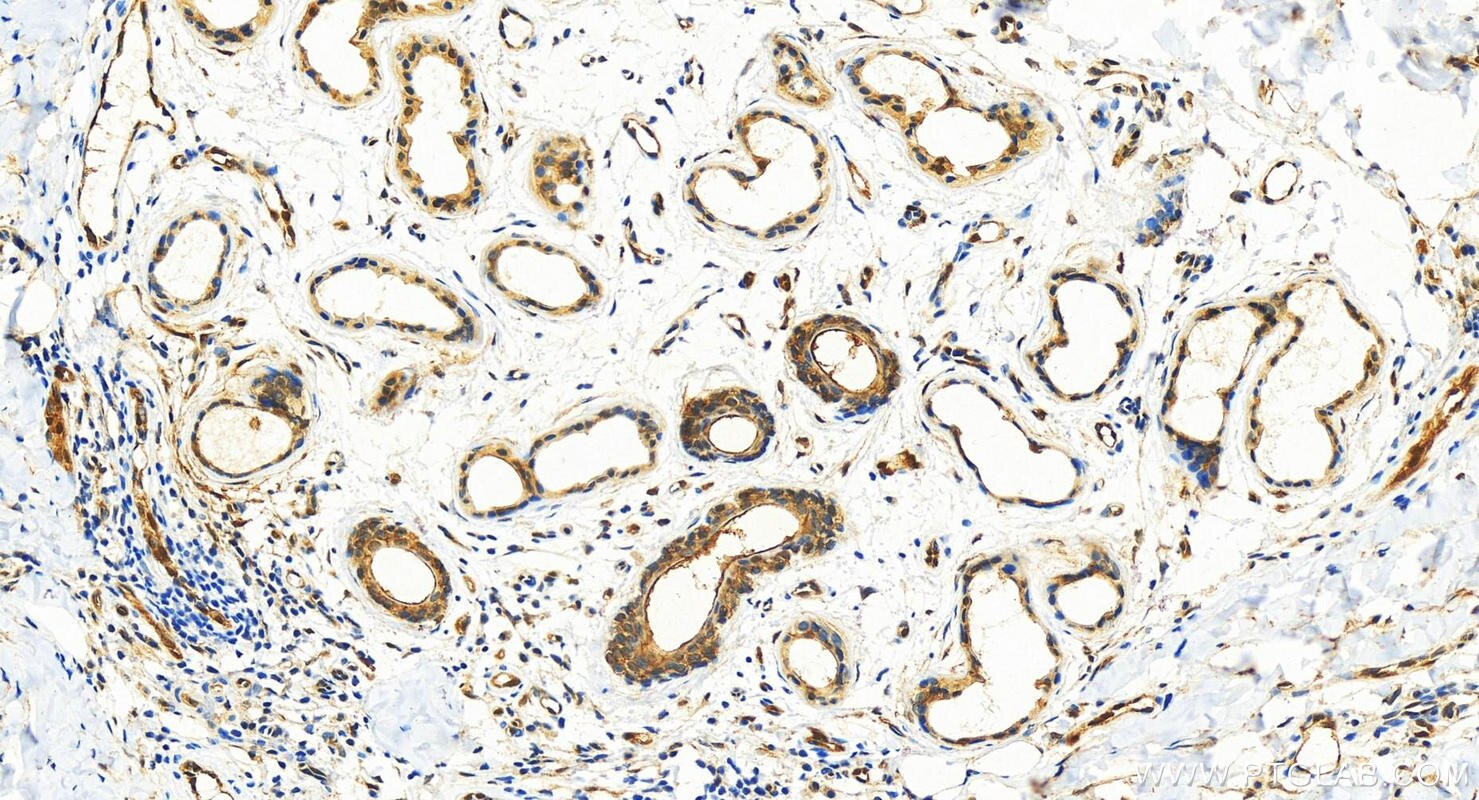
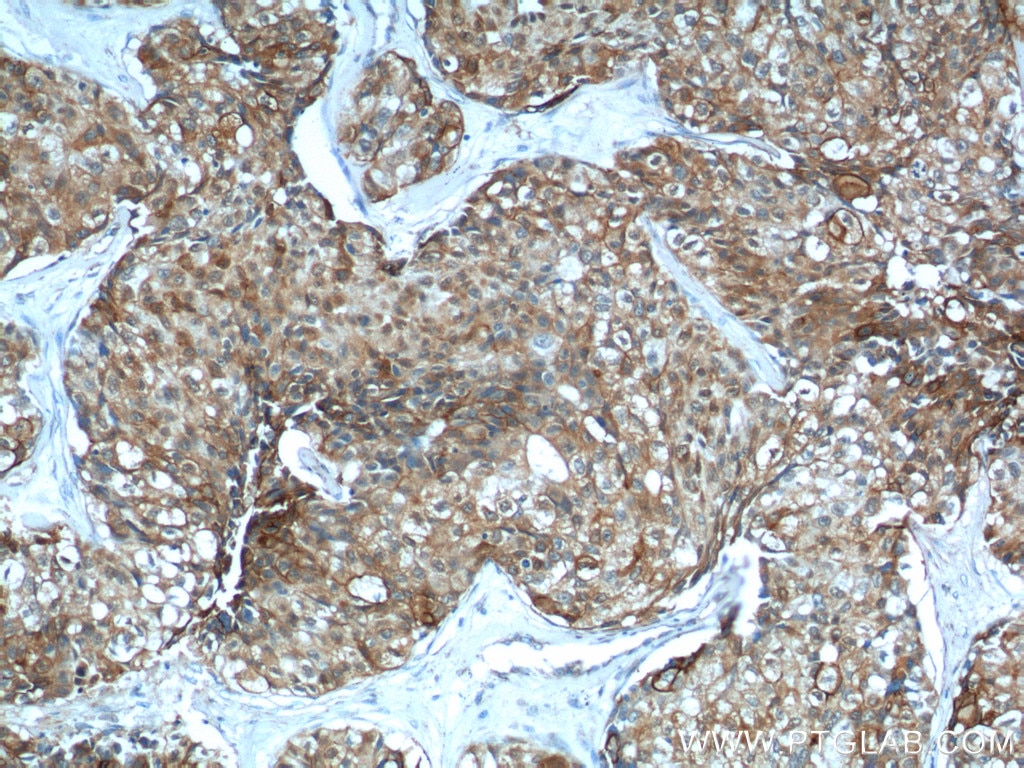
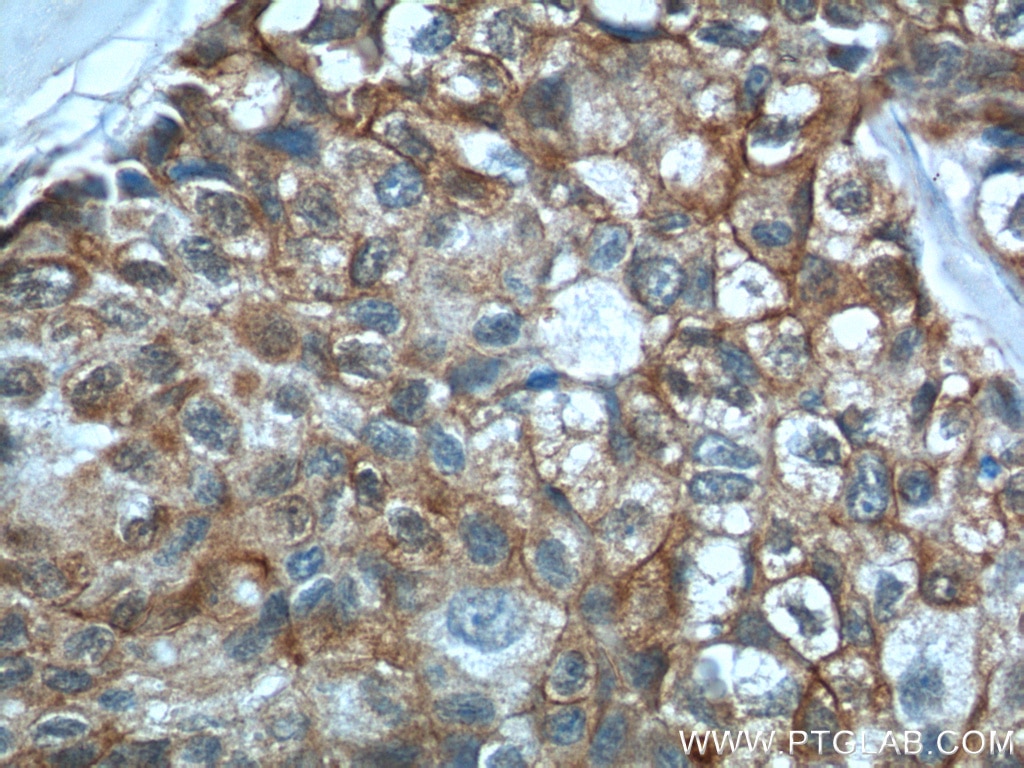
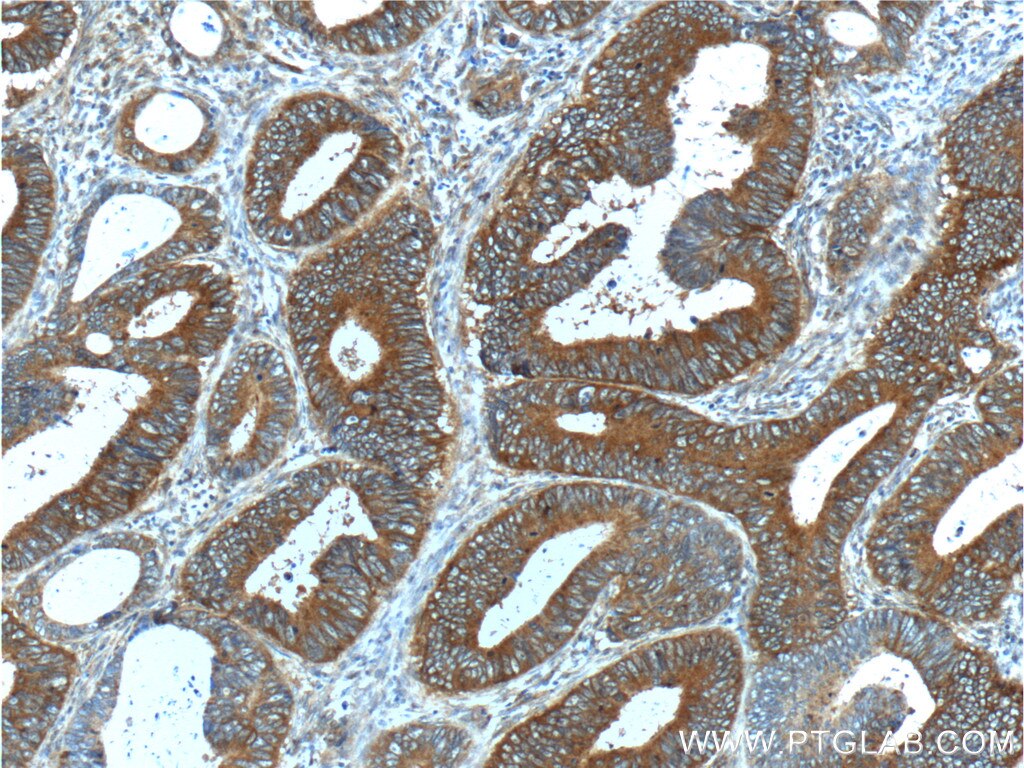
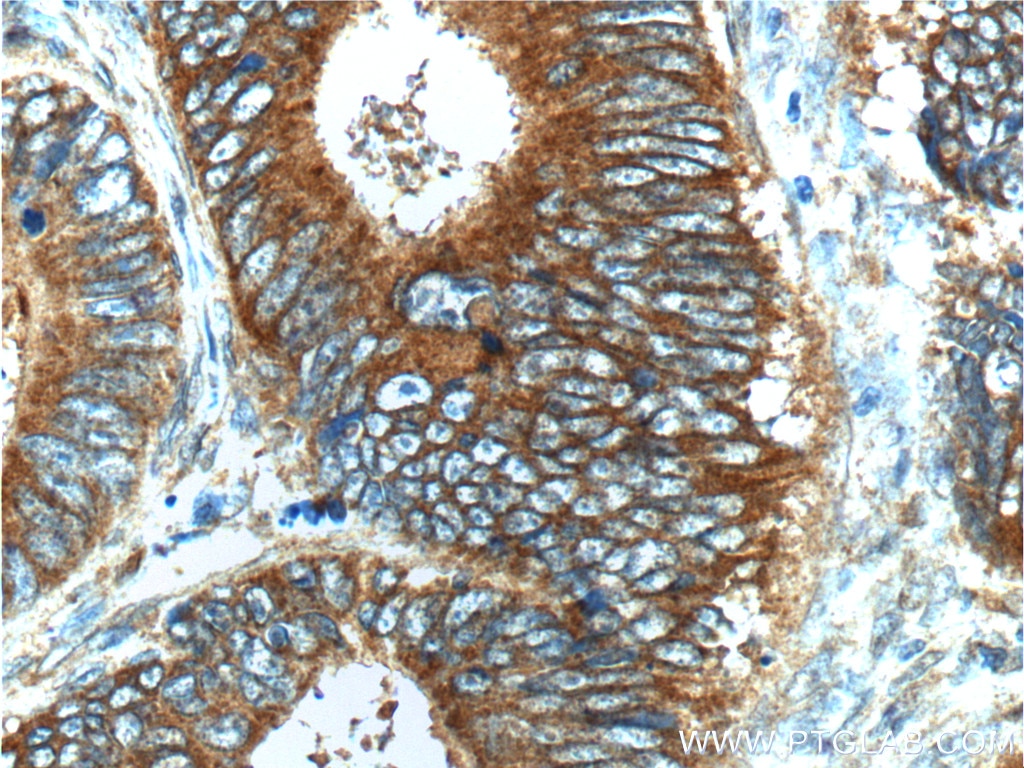
| Positive IHC detected in | human lung cancer tissue, human bowen disease, human colon cancer tissue, mouse lung tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | MCF-7 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 5 publications below |
| WB | See 12 publications below |
| IHC | See 8 publications below |
| IF | See 5 publications below |
| IP | See 2 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
11456-1-AP targets S100A16 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, CoIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag2023 Product name: Recombinant human S100A16 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-103 aa of BC019099 Sequence: MSDCYTELEKAVIVLVENFYKYVSKYSLVKNKISKSSFREMLQKELNHMLSDTGNRKAADKLIQNLDANHDGRISFDEYWTLIGGITGPIAKLIHEQEQQSSS Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | S100 calcium binding protein A16 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 103 aa, 12 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 9-12 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC019099 |
| Gene Symbol | S100A16 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 140576 |
| RRID | AB_2269940 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q96FQ6 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
S100A16 is a member of the S100 protein family. S100A16 is expressed in a variety of human tissues. S100A16 expression is especially high in tissues rich in epithelial cells. Functionally, S100A16 has been linked to several aspects of tumorigenesis, for example, cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT).Accordingly, S100A16 has been suggested to have both tumour-promoting and suppressive roles in human cancers. S100A16-mediated cellular functions are suggested to be mediated by the regulation of various signaling pathways/proteins including EMT-related proteins E-cadherin and Vimentin, PI3K-AKT, p53, MMP1-1, MMP-2, MMP-9, JNK/p38, etc. (PMID: 37509106).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for S100A16 antibody 11456-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for S100A16 antibody 11456-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for S100A16 antibody 11456-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Int J Biol Sci S100 Calcium Binding Protein A16 Promotes Cell Proliferation by triggering LATS1 ubiquitin degradation mediated by CUL4A ligase to inhibit Hippo pathway in Glioma development
| ||
Cell Mol Life Sci S100A16 promotes acute kidney injury by activating HRD1-induced ubiquitination and degradation of GSK3β and CK1α.
| ||
FASEB J Brain microvascular endothelial cell exosome-mediated S100A16 up-regulation confers small-cell lung cancer cell survival in brain. | ||
Front Cell Dev Biol Calcium Binding Protein S100A16 Expedites Proliferation, Invasion and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Process in Gastric Cancer
| ||
Biomolecules ADAMTS19 Suppresses Cell Migration and Invasion by Targeting S100A16 via the NF-κB Pathway in Human Gastric Cancer. | ||
PLoS One S100A14 Interacts with S100A16 and Regulates Its Expression in Human Cancer Cells. |