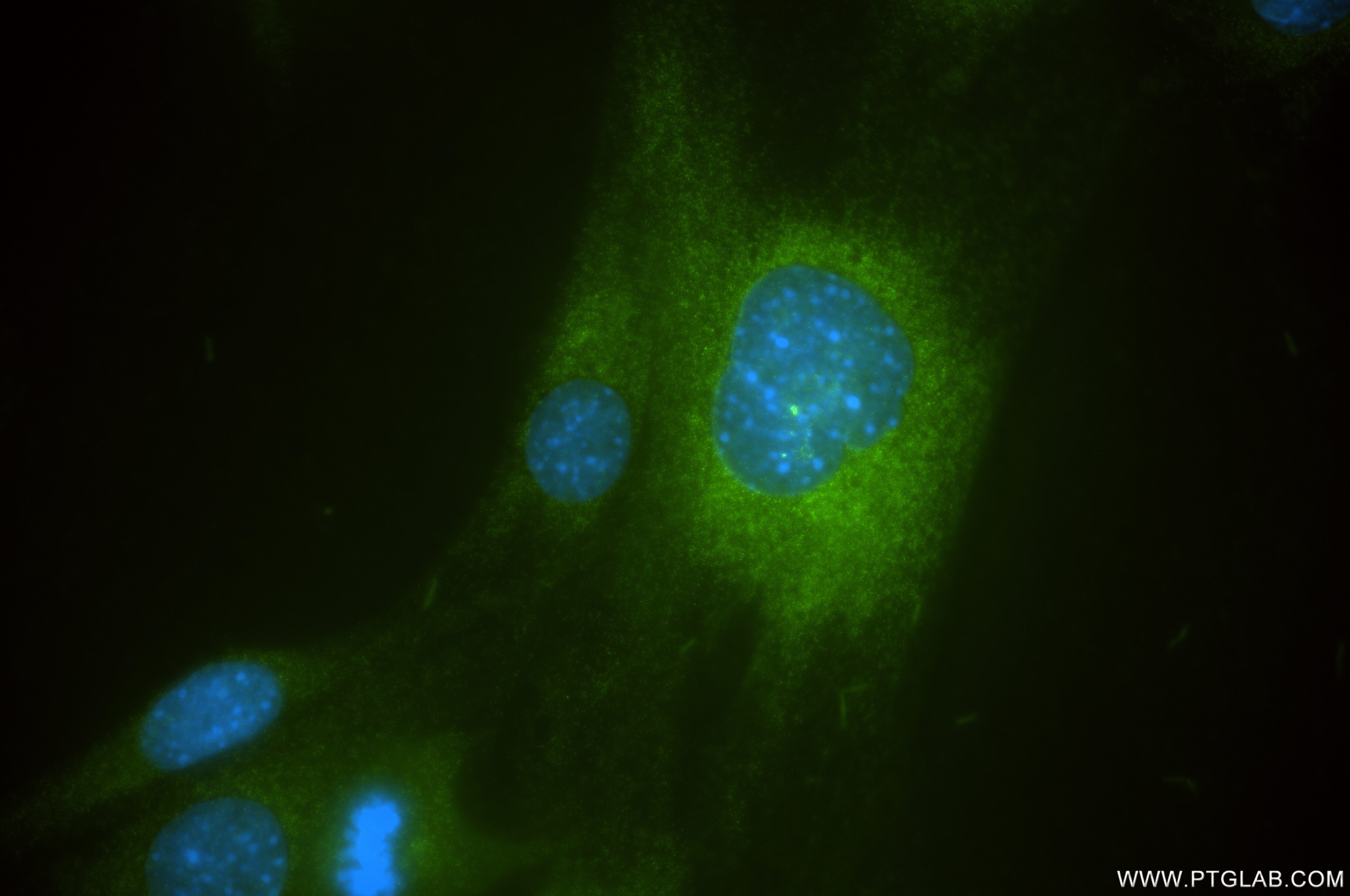
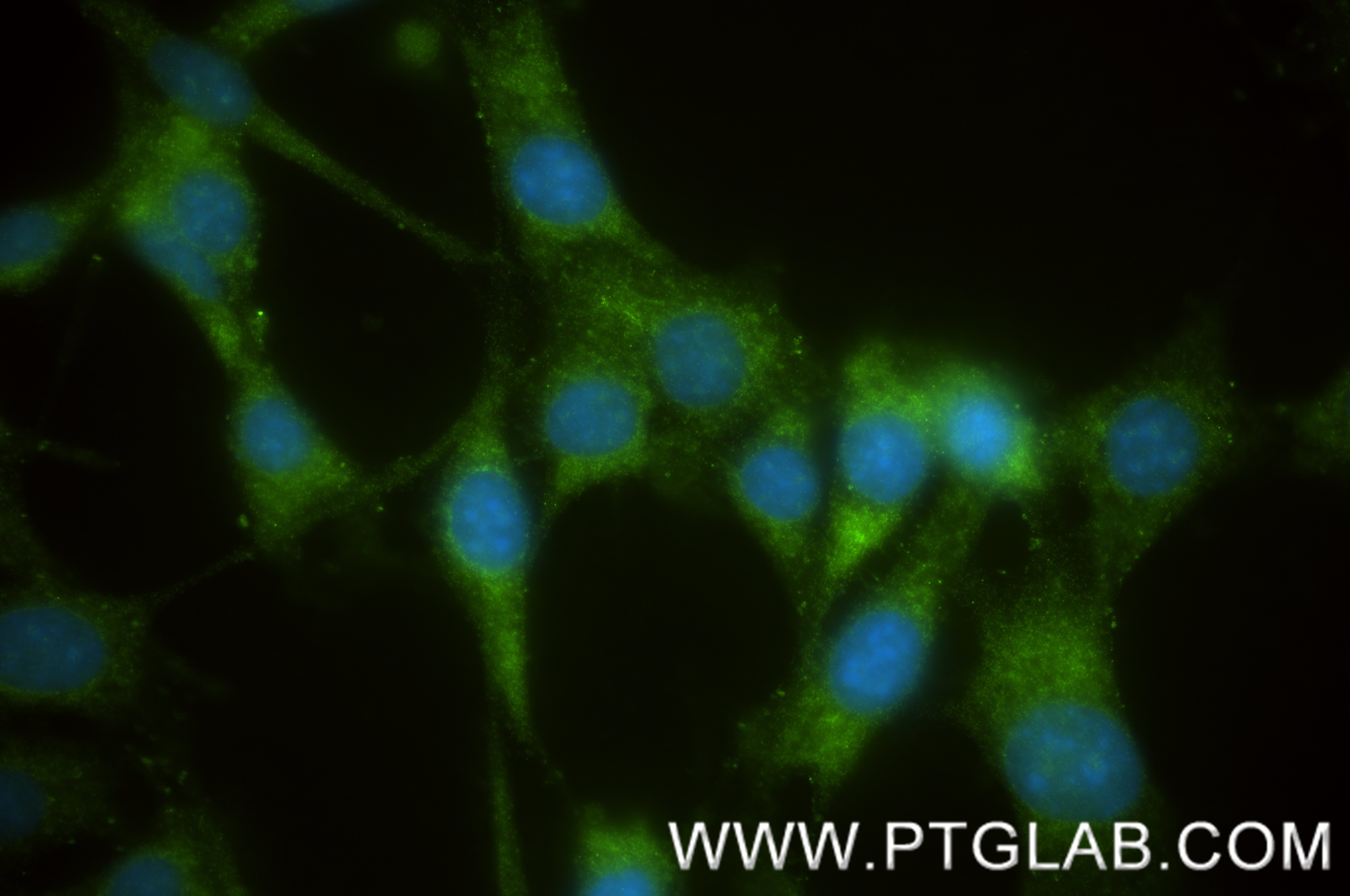
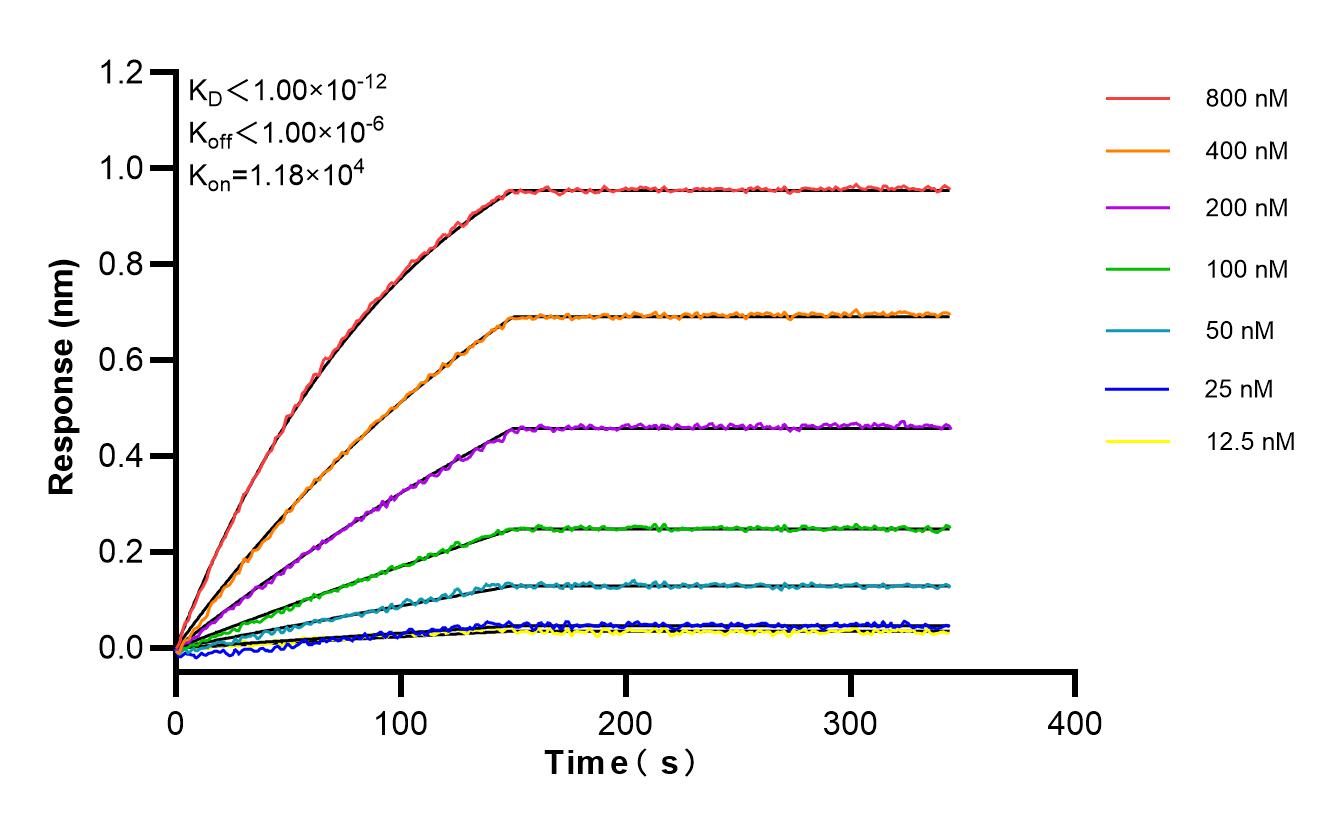
Product Information
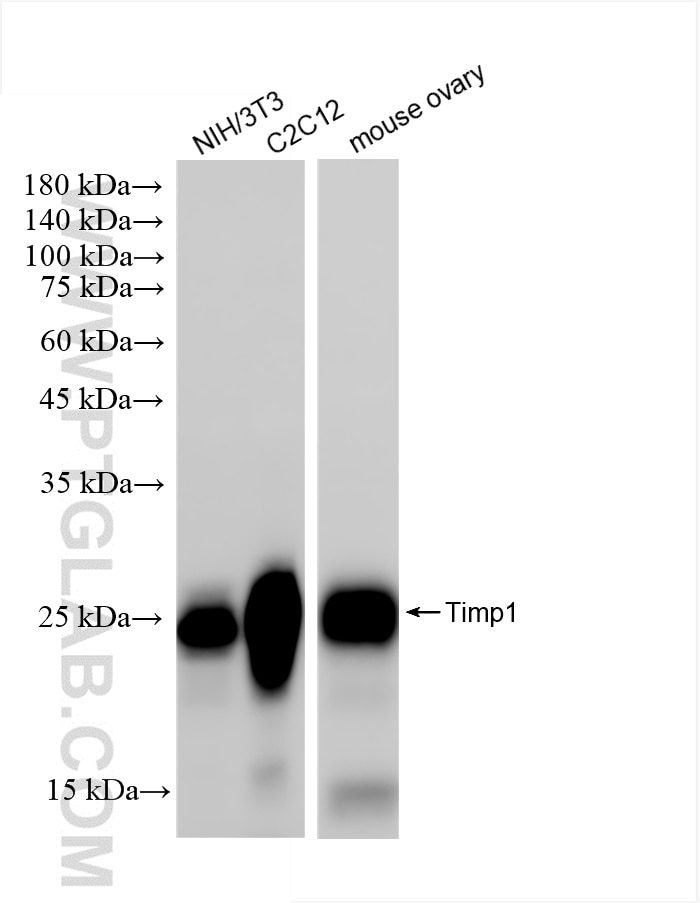
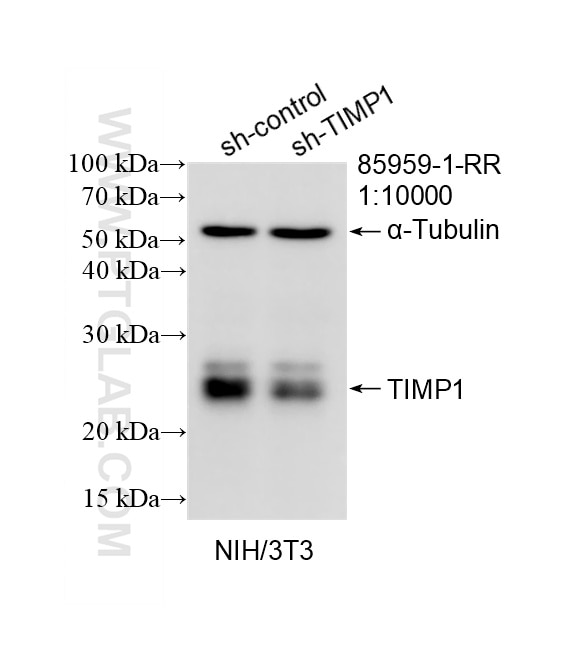
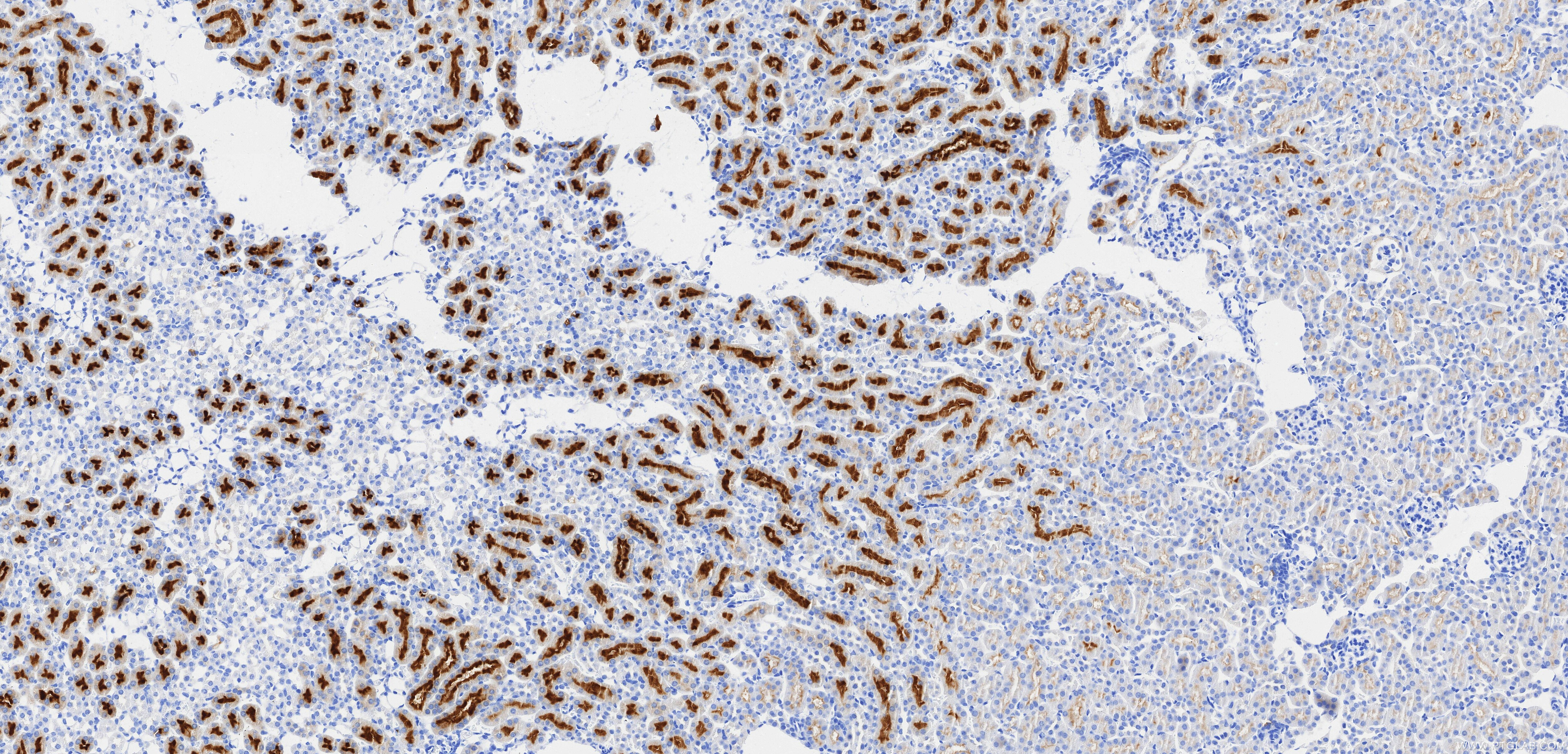
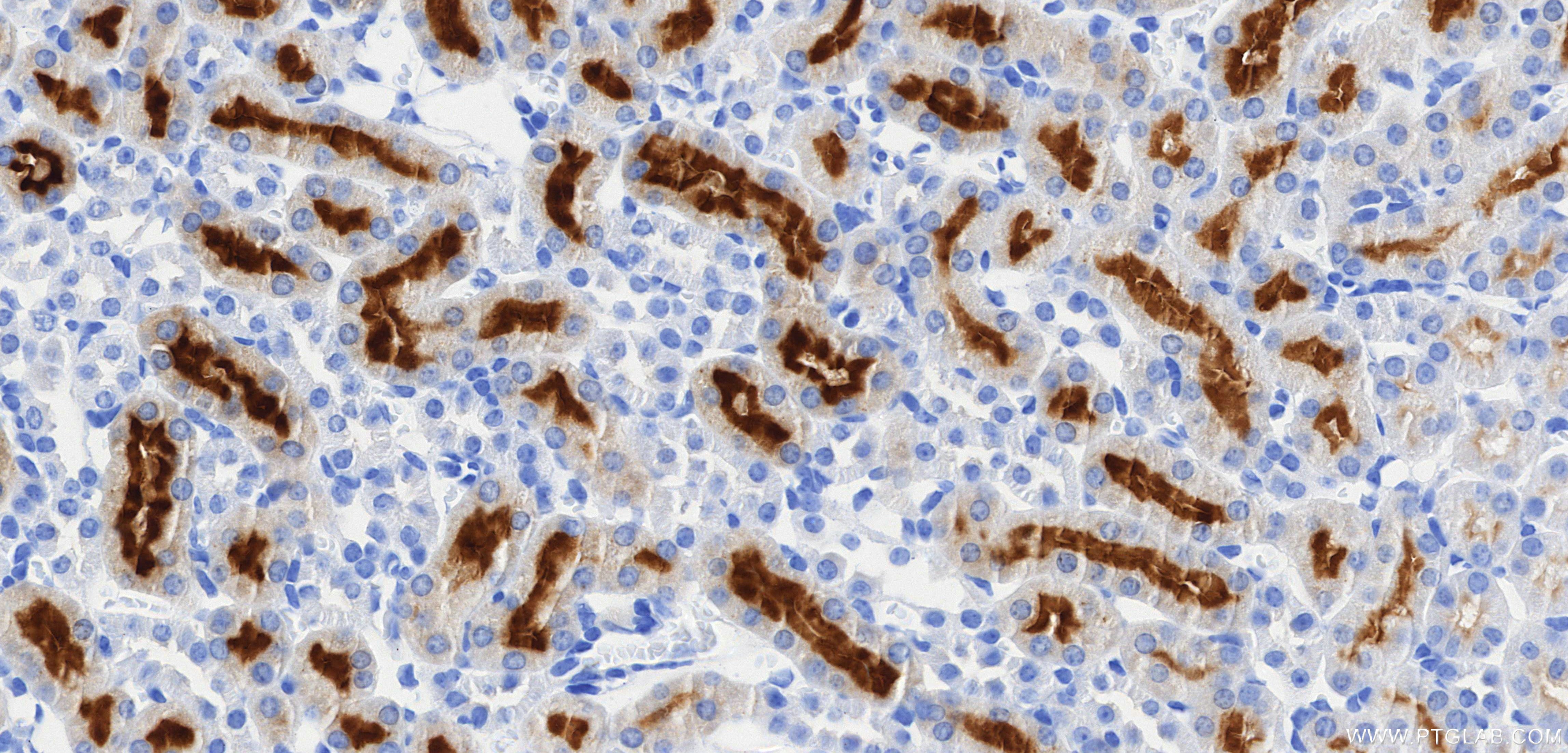
85959-1-PBS targets TIMP1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Eg0630 Product name: Recombinant mouse Timp1 protein Source: mammalian cells-derived, pHZ-KIsec-C-6*HIS Tag: C-6*HIS Domain: 25-205 aa of NM_001044384.1 Sequence: CSCAPPHPQTAFCNSDLVIRAKFMGSPEINETTLYQRYKIKMTKMLKGFKAVGNAADIRYAYTPVMESLCGYAHKSQNRSEEFLITGRLRNGNLHISACSFLVPWRTLSPAQQRAFSKTYSAGCGVCTVFPCLSIPCKLESDTHCLWTDQVLVGSEDYQSRHFACLPRNPGLCTWRSLGAR Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 23KD |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 20-23 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_001044384.1 |
| Gene Symbol | Timp1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 21857 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P12032 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
TIMP1 is a member of the family of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors, which contains four members (TIMP1, TIMP2, TIMP3, and TIMP4). Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) are multifaceted molecules that exhibit properties beyond their classical proteinase inhibitory function. TIMP1 has several MMP-independent functions such as modulation of angiogenesis, promotion of cell proliferation, and inhibition of apoptosis. TIMP1 plays important role in cell cycle regulation and cancer progression. Recently, clinical studies have shown that the aberrant expression of TIMP1 is associated with an unfavorable prognosis in a series of tumors, such as gastric cancer, papillary thyroid carcinoma, cutaneous melanoma and breast cancer. In pregnancy, TIMP1 plays a regulatory role in the process of implantation, particularly the cytotrophoblast invasion of the uterine endometrium. In pregnancy, TIMP1 plays a regulatory role in the process of implantation, particularly the cytotrophoblast invasion of the uterine endometrium.