Tested Applications
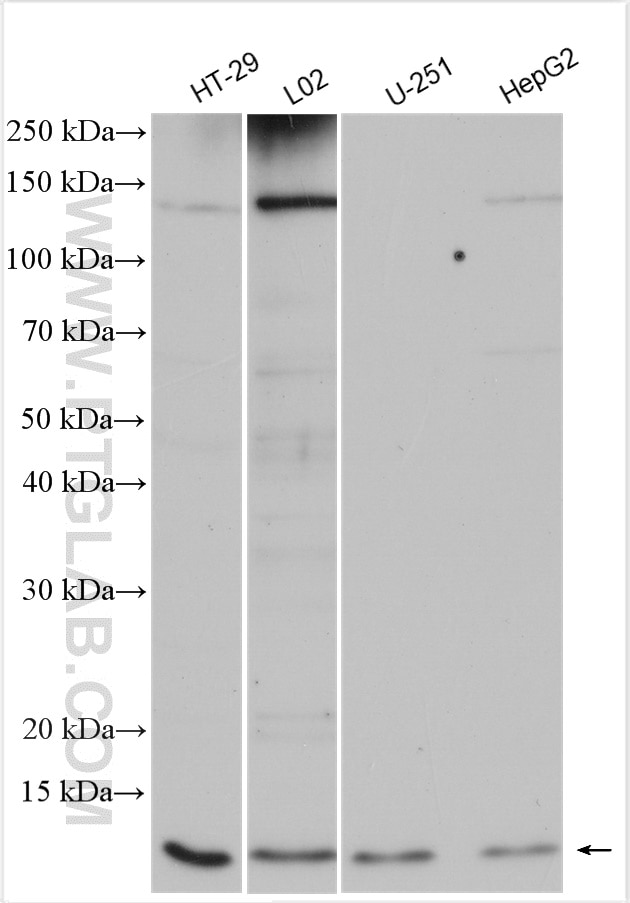
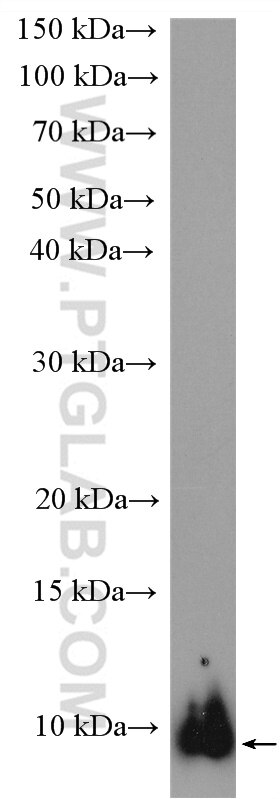
| Positive WB detected in | HT-29 cells, HEK-293 cells, HepG2 cells, mouse liver tissue, mouse lung tissue, L02 cells, U-251 cells |
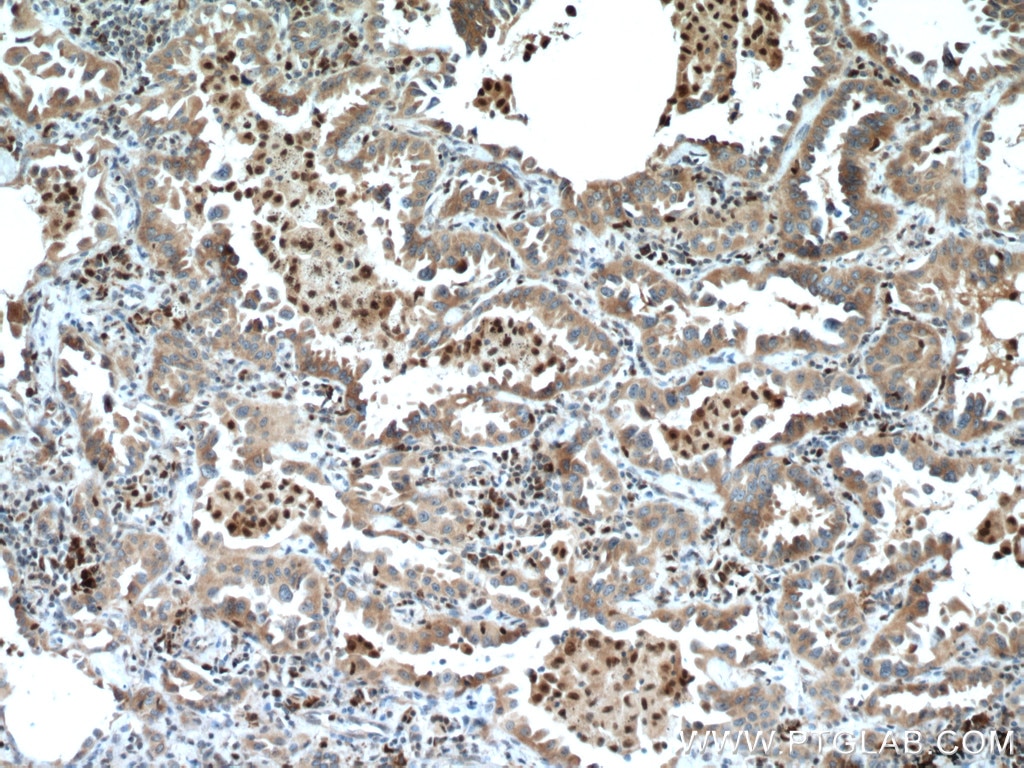
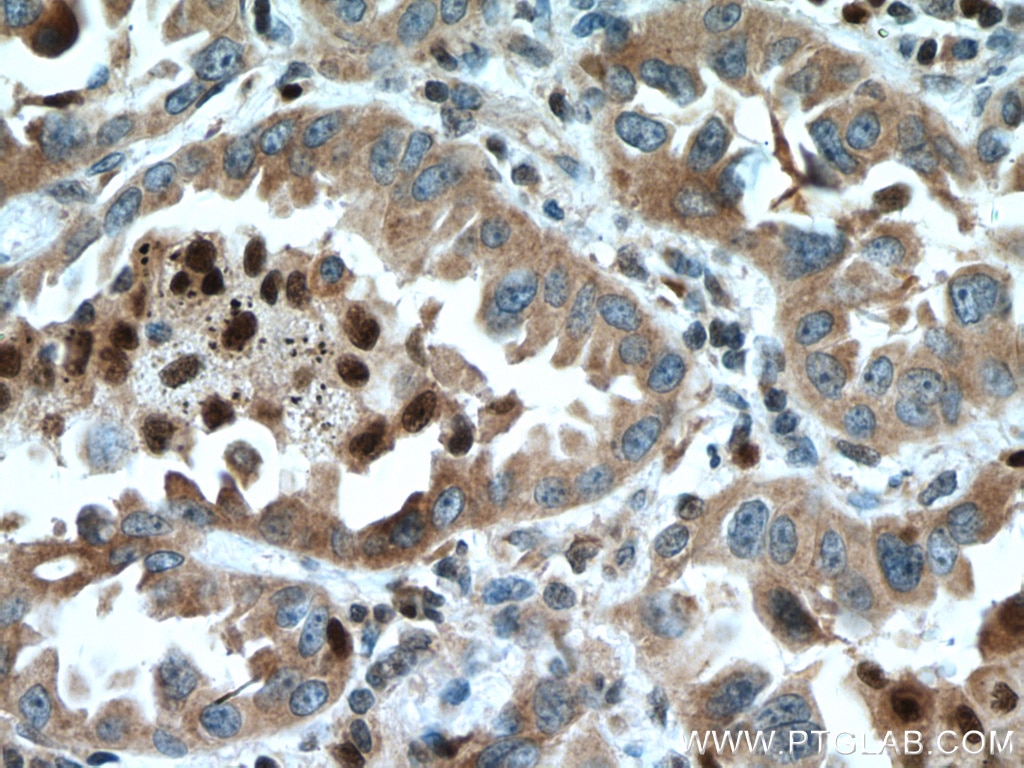
| Positive IHC detected in | human lung cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 5 publications below |
Product Information
15883-1-AP targets UFM1 in WB, IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Cited Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag8667 Product name: Recombinant human UFM1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-85 aa of BC005193 Sequence: MSKVSFKITLTSDPRLPYKVLSVPESTPFTAVLKFAAEEFKVPAATSAIITNDGIGINPAQTAGNVFLKHGSELRIIPRDRVGSC Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | ubiquitin-fold modifier 1 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 85 aa, 9 kDa |
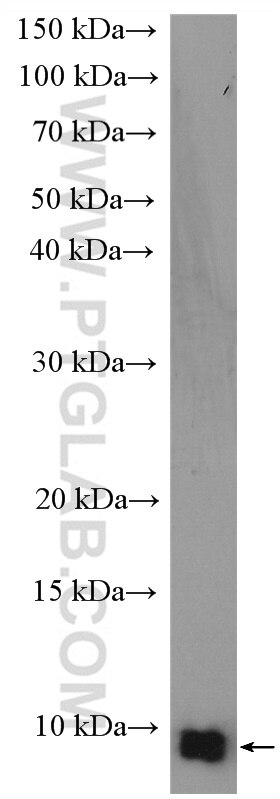
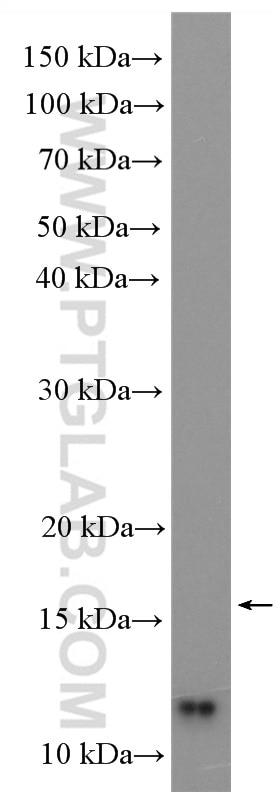
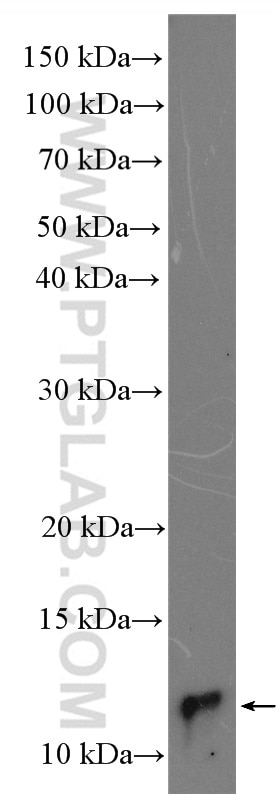
| Observed Molecular Weight | 9-12 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC005193 |
| Gene Symbol | UFM1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 51569 |
| RRID | AB_2878195 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P61960 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
UFM1 (Ubiquitin-fold modifier 1) is a ubiquitin-like protein covalently conjugated with intracellular proteins through UFMylation (modification by UFM1), a process similar to ubiquitylation (PMID: 38141606). UFM1 is conjugated to its target proteins by E1-like activating enzyme UBE1DC1 and E2-like conjugating enzyme UFC1 in a manner analogous to ubiquitylation (PMID: 28234446; 33066455). At the molecular level, UFMylation is an important mediator of the protein function. Dysregulation of the UFM1 system, e.g., the knockout of UFMylation components, disturbs proteome homeostasis and triggers endoplasmic reticulum stress. Such changes are linked to developmental disorders, tumorigenesis, tissue injury, inflammation, and several hereditary neurological syndromes (PMID: 36932998). Western blot images showed that bands larger than 100kd may be proteins modified by UFM1.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for UFM1 antibody 15883-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for UFM1 antibody 15883-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Mol Cell An Epstein-Barr virus protein interaction map reveals NLRP3 inflammasome evasion via MAVS UFMylation | ||
Autophagy VCP/p97 UFMylation stabilizes BECN1 and facilitates the initiation of autophagy | ||
bioRxiv Proximity biotinylation at the host- Shigella interface reveals UFMylation as an antibacterial pathway | ||
Mol Cell Proteomics Quantification Quality Control Emerges as A Crucial Factor to Enhance Single Cell Proteomics Data Analysis |