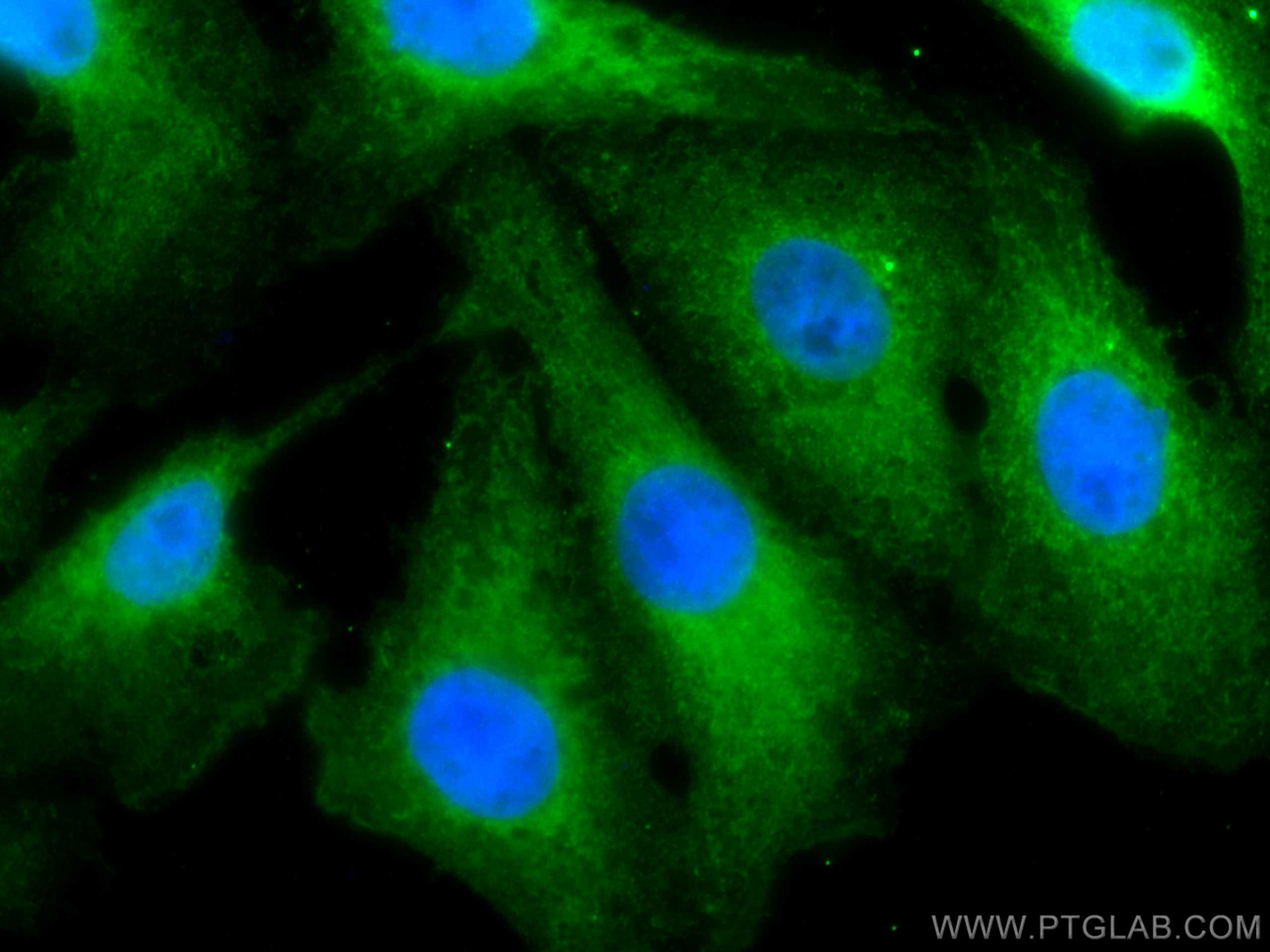
Tested Applications
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | SKOV-3 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
CL488-67753 targets VASH2 in IF/ICC applications and shows reactivity with Human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag29985 Product name: Recombinant human VASH2 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1-156 aa of BC028194 Sequence: METAKEMTRESLPIKCLEAVILGIYLTNGQPSIERFPISFKTYFSGNYFHHVVLGIYCNGRYGSLGMSRRAELMDKPLTFRTLSDLIFDFEDSYKKYLHTVKKVKIGLYVPHEPHSFQPIEWKQLVLNVSKMLRADIRKELEKYARDMRMKGLCSH Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | vasohibin 2 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 355 aa, 40 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 34 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC028194 |
| Gene Symbol | VASH2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 79805 |
| RRID | AB_2919537 |
| Conjugate | CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 493 nm / 522 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q86V25 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
VASH2, also named as vasohibin 2, is an important pro-angiogenesis factor in solid tumor. It has been reported that VASH2 is expressed in mononuclear cells mobilized from bone marrow to promote angiogenesis. VASH2 also plays a key role in axon formation. VASH2 is localized as a nuclear type(with 311 amino acid residues) and cytoplasmic type (with 355 amino acid residues and low abundance). Cytoplasmic VASH2 is associated with carcinoma angiogenesis, while nuclear VASH2 may be associated with cell proliferation. 67753-1-Ig antibody recognizes both the nuclear and cytoplasmic isoforms. (PMID:23615928; 19204325; 31235911; 26177649)
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL Plus 488 VASH2 antibody CL488-67753 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |