Tested Applications
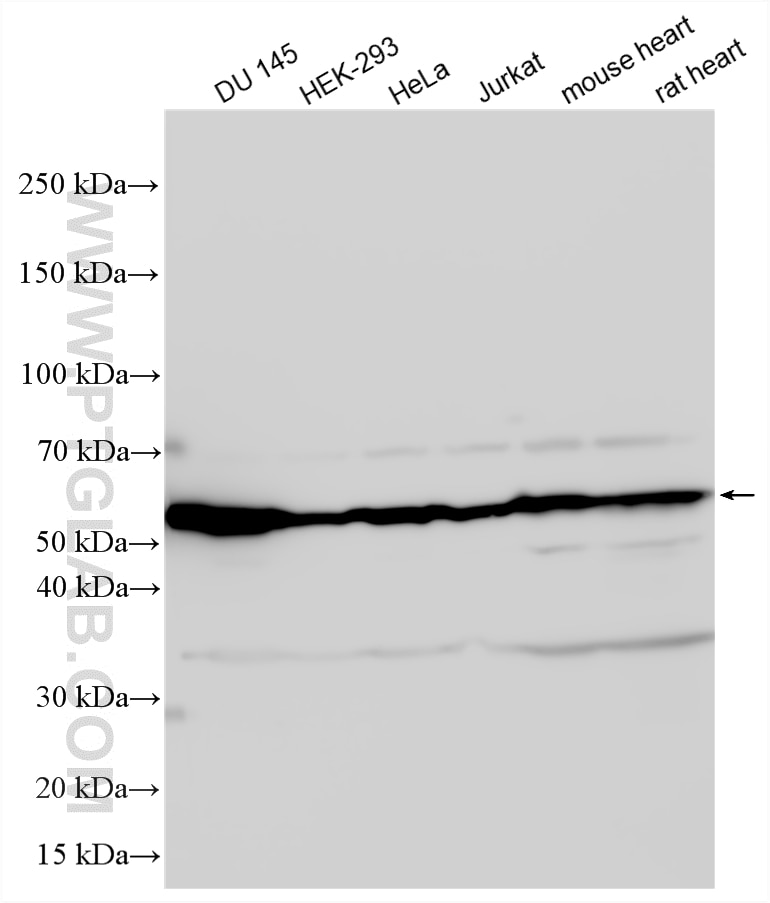
| Positive WB detected in | DU 145 cells, A549 cells, HEK-293 cells, mouse heart tissue, HeLa cells, Jurkat cells, rat heart tissue |
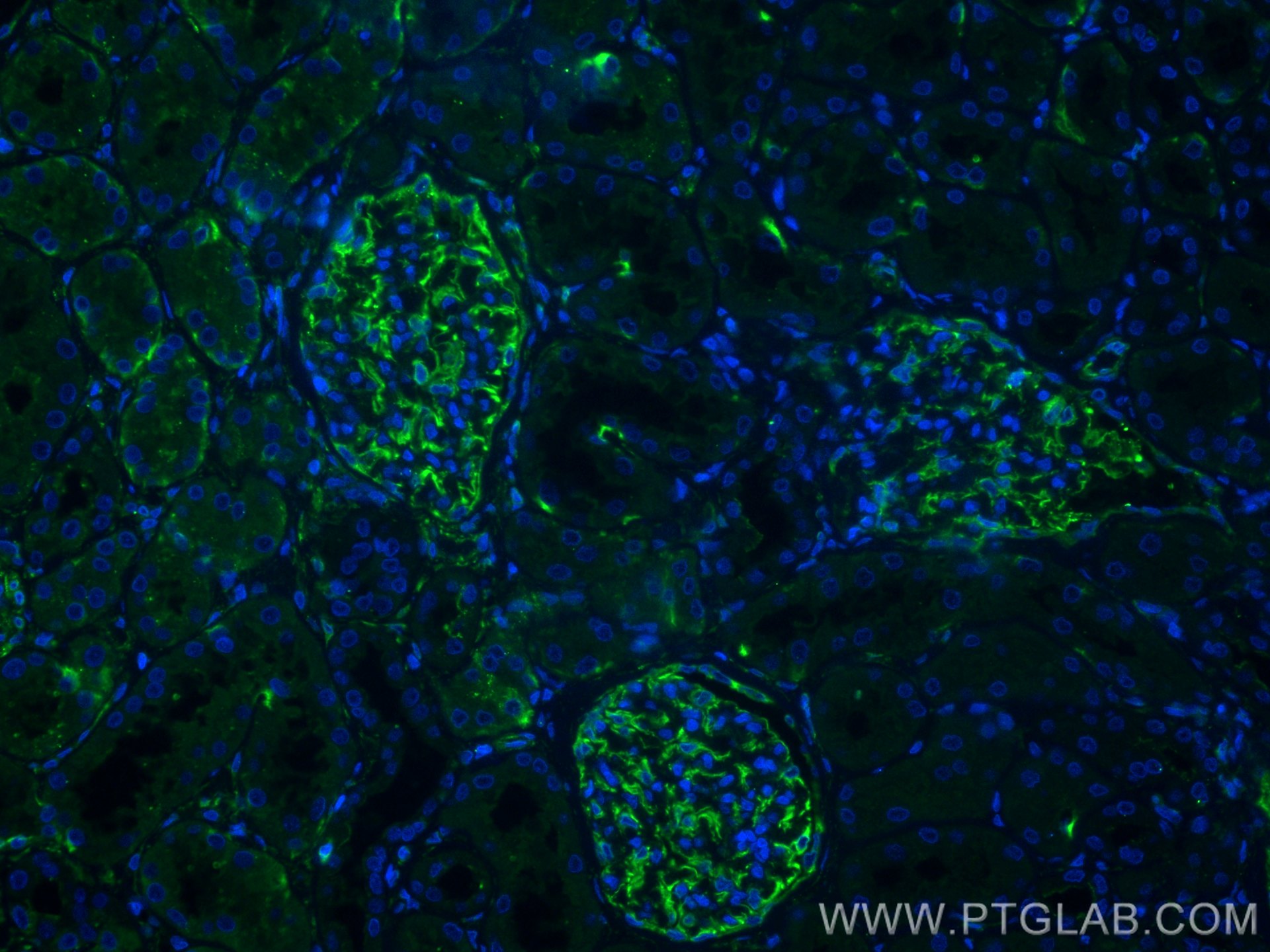
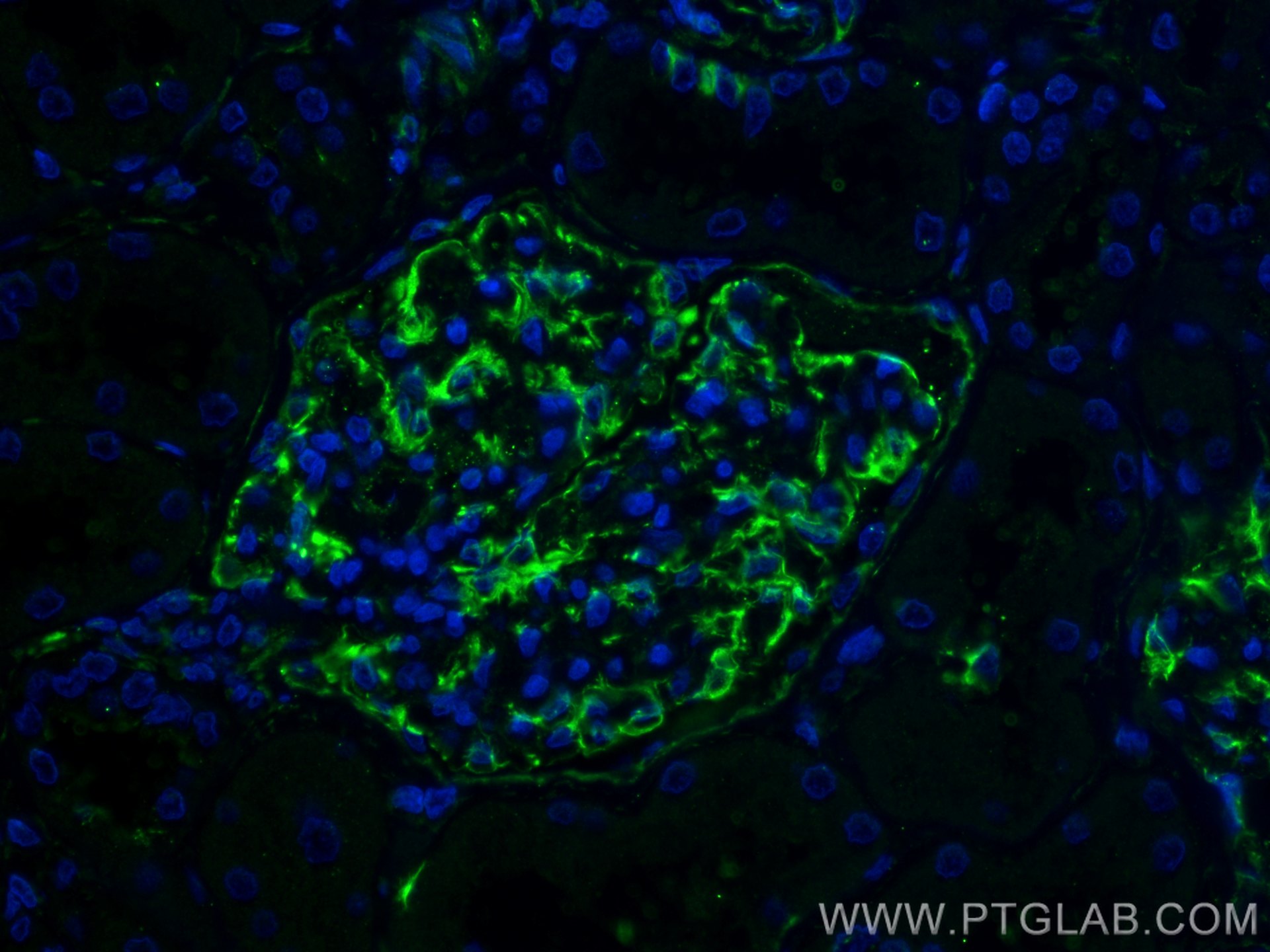
| Positive IF-P detected in | human kidney tissue |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:8000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 20 publications below |
| IHC | See 4 publications below |
| IF | See 9 publications below |
Product Information
22031-1-AP targets Vimentin in WB, IHC, IF-P, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag16898 Product name: Recombinant human Vimentin protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-86 aa of BC000163 Sequence: MSTRSVSSSSYRRMFGGPGTASRPSSSRSYVTTSTRTYSLGSALRPSTSRSLYASSPGGVYATRSSAVRLRSSVPGVRLLQDSVDF Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | vimentin |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 466 aa, 54 kDa |
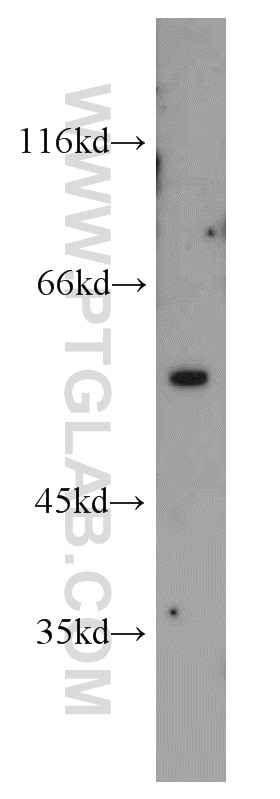
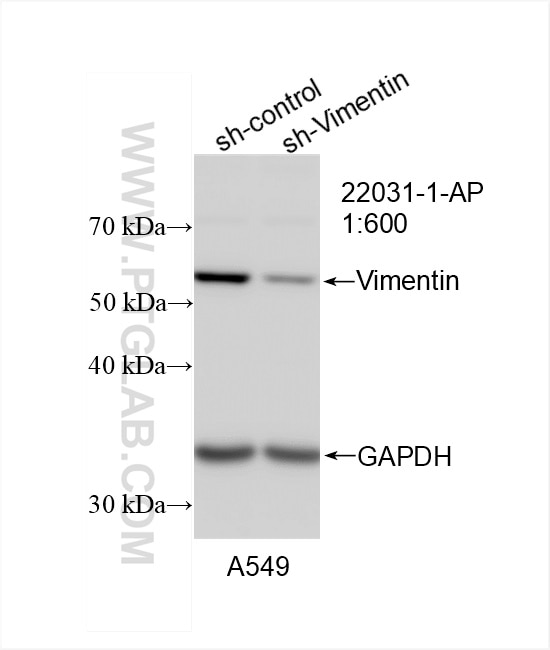
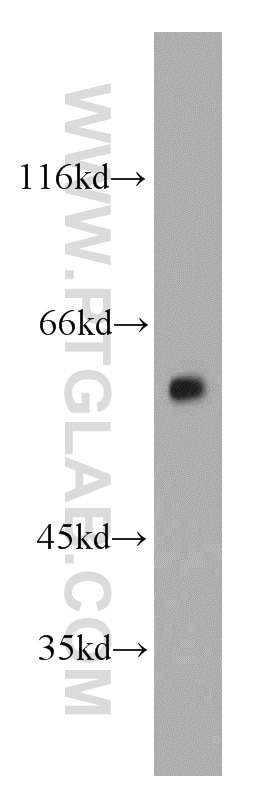
| Observed Molecular Weight | 57 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC000163 |
| Gene Symbol | VIM |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7431 |
| ENSEMBL Gene ID | ENSG00000026025 |
| RRID | AB_11182825 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P08670 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Vimentin, also named as VIM, belongs to the intermediate filament family. Vimentin is class-III intermediate filaments found in various non-epithelial cells, especially mesenchymal cells. Vimentin is important for stabilizing the architecture of the cytoplasm. Monocyte-derived macrophages secrete vimentin into the extracellular space in vitro. Secretion of vimentin was enhanced by the proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFA; 191160) and inhibited by the antiinflammatory cytokine IL10 (124092), suggesting that vimentin is involved in the immune response. Vimentin has specialized functions that contribute to specific dynamic cellular processes. As a phosphoprotein, 55-60 kDa of vimentin proteins can be observed due to the different phosphorylation level. Isoforms of vimentin (49 kDa and 60 kDa) had also been reported. (PMID: 8640945, 22728585).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for Vimentin antibody 22031-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for Vimentin antibody 22031-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Death Dis ZNF652 exerts a tumor suppressor role in lung cancer by transcriptionally downregulating cyclin D3 | ||
J Transl Med Single-cell and spatial transcriptome profiling reveal CTHRC1+ fibroblasts promote EMT through WNT5A signaling in colorectal cancer | ||
Cell Signal N-glycosylation stabilized TNFAIP6 promotes ovarian cancer metastasis by activating the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway | ||
Tissue Eng Part C Methods Pretreatment with Inflammatory Factors Altered the Secretome of Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells | ||
Clin Respir J SIRT3 Inhibits Cell Proliferation of Nonsmall Cell Lung Carcinoma by Inducing ROS Production | ||
Mol Neurobiol The Ile35 Residue of the ALS-Associated Mutant SOD1 Plays a Crucial Role in the Intracellular Aggregation of the Molecule |