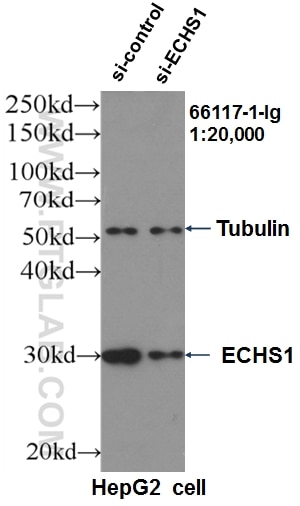
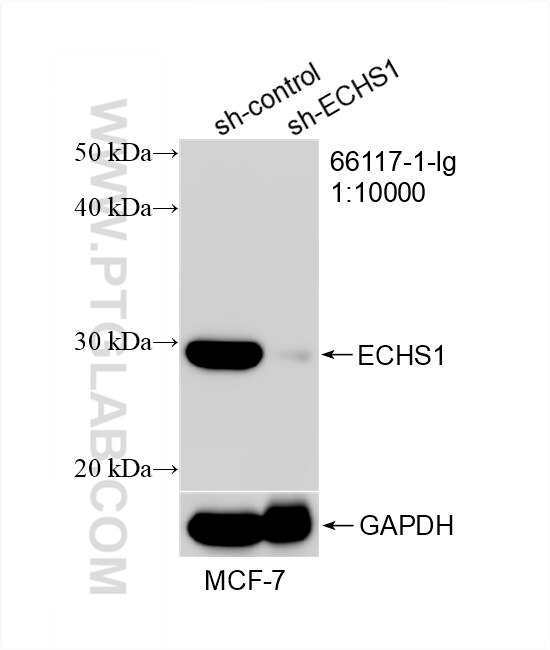
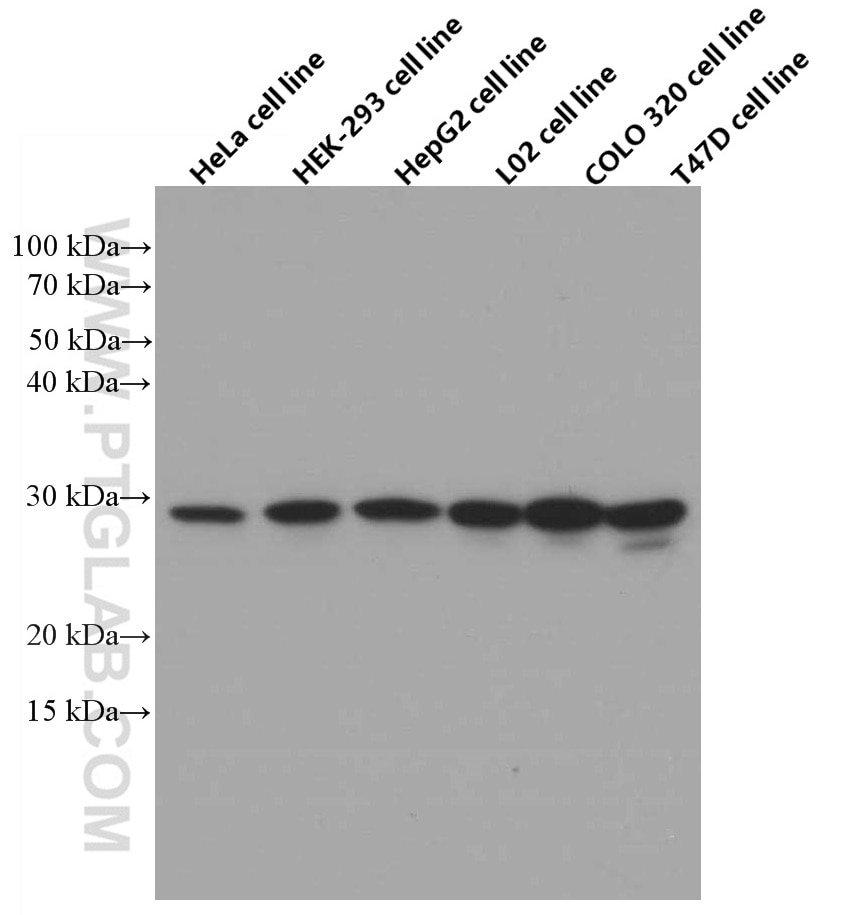
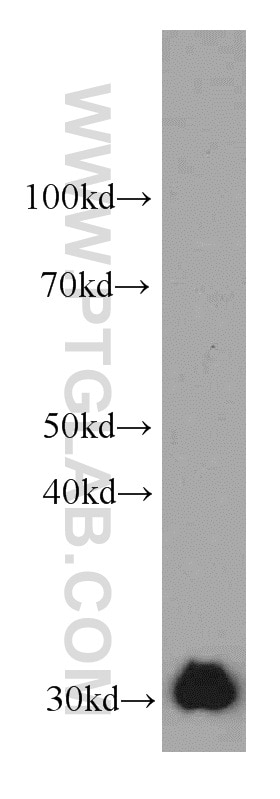
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | HeLa cells, HepG2 cells, human testis tissue, MCF-7 cells, PC-3 cells, HEK-293 cells, L02 cells, COLO 320 cells, T47D cells |
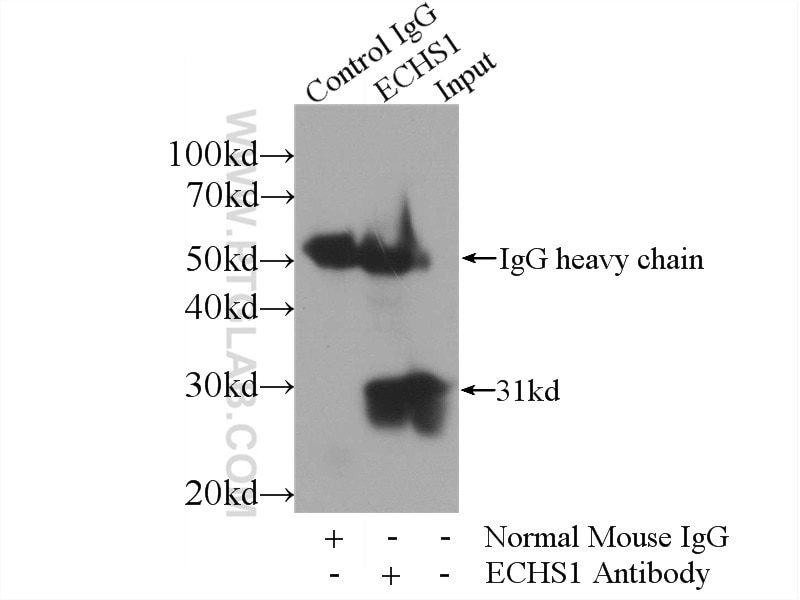
| Positive IP detected in | HepG2 cells |
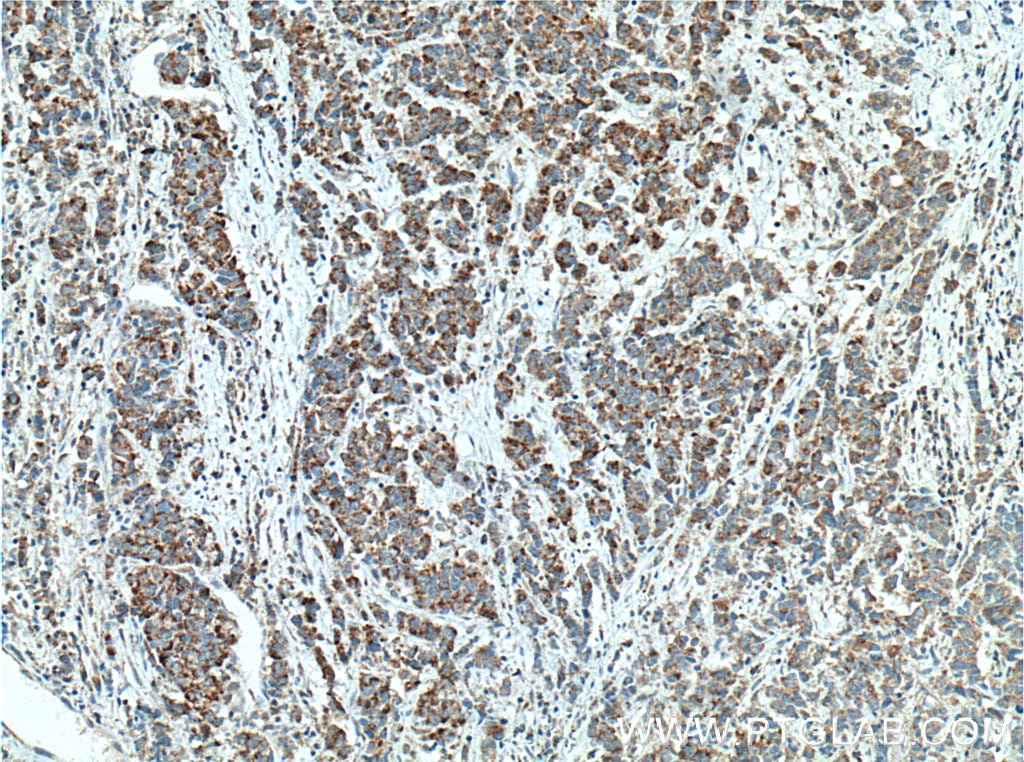
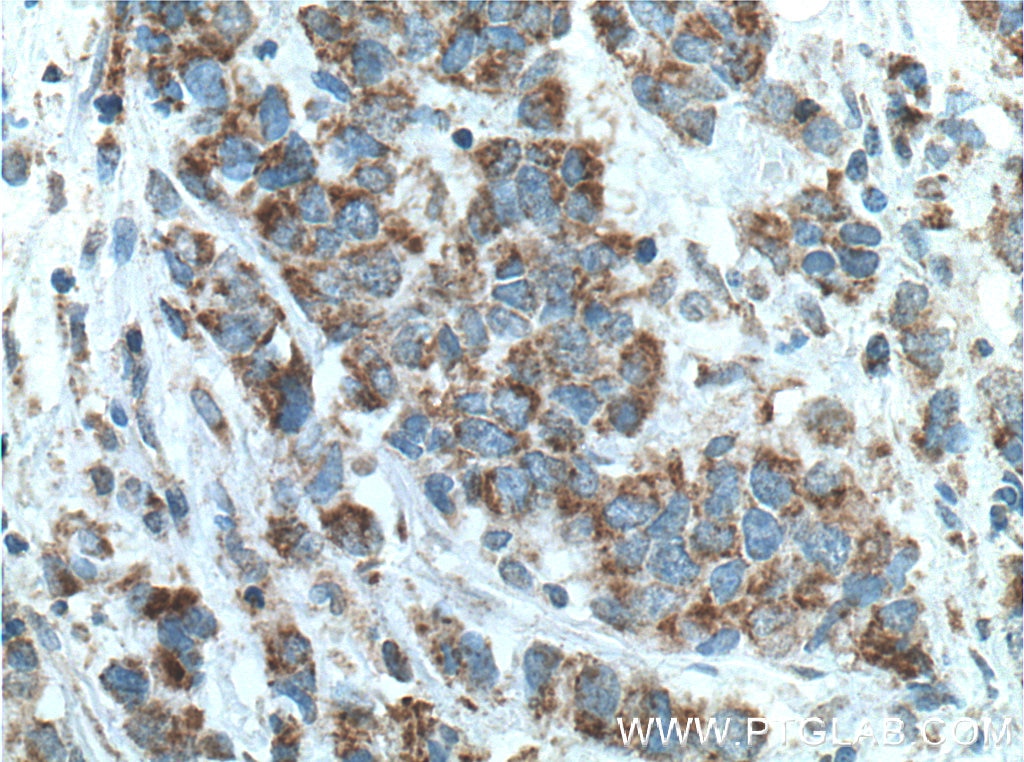
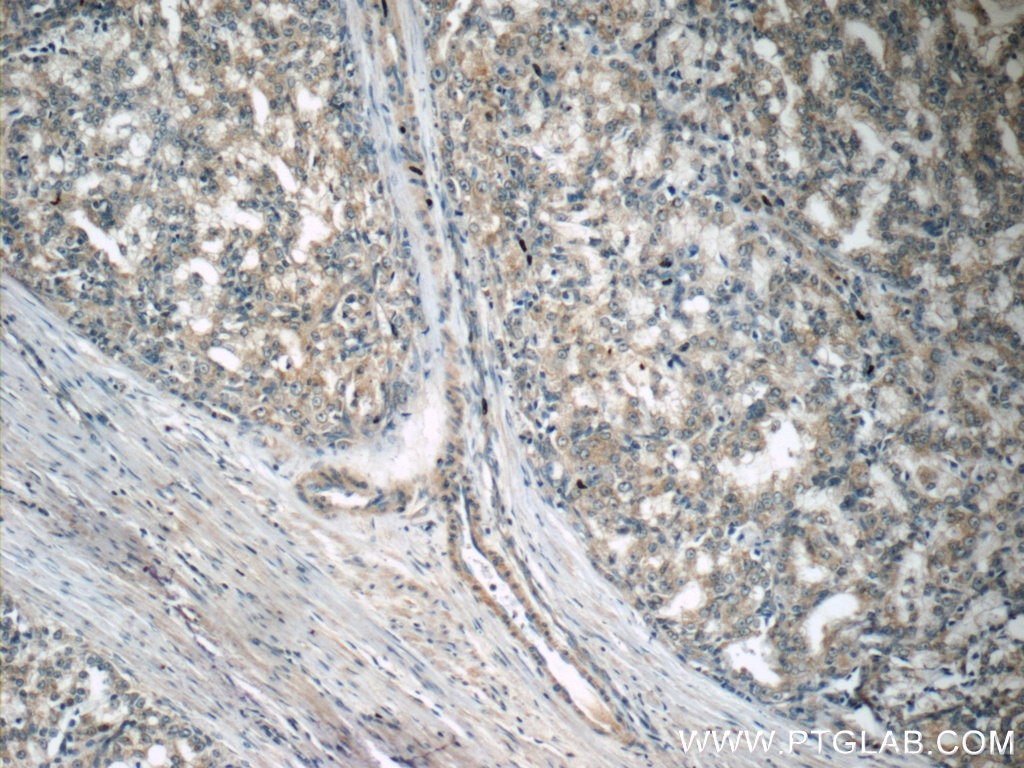
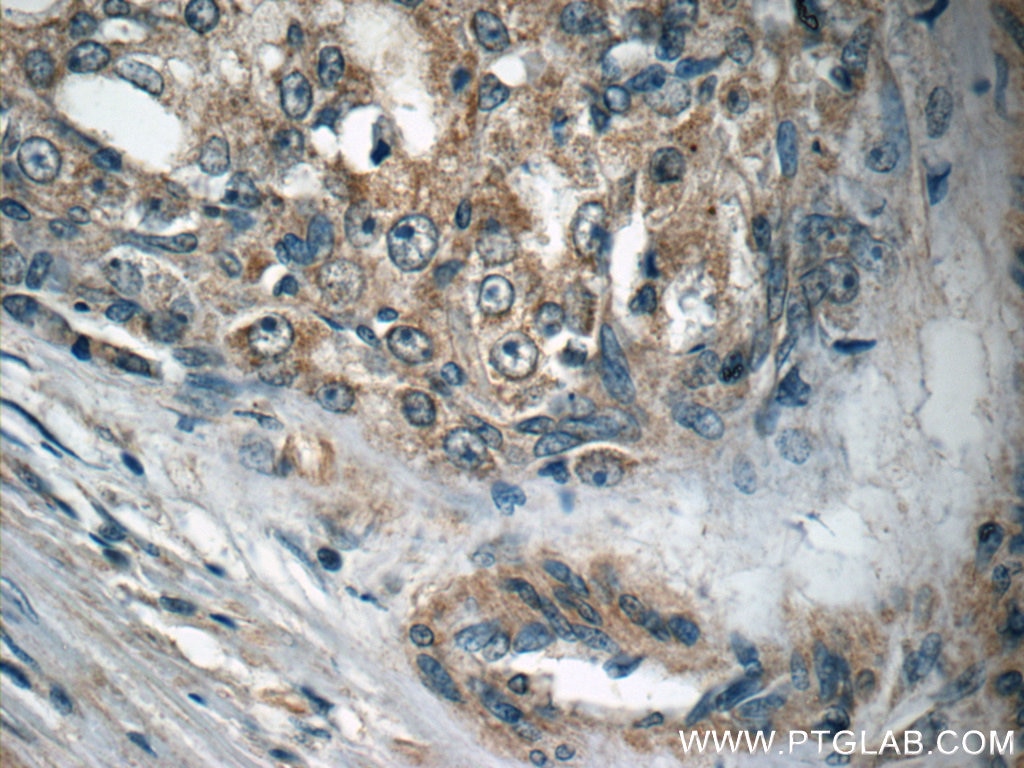
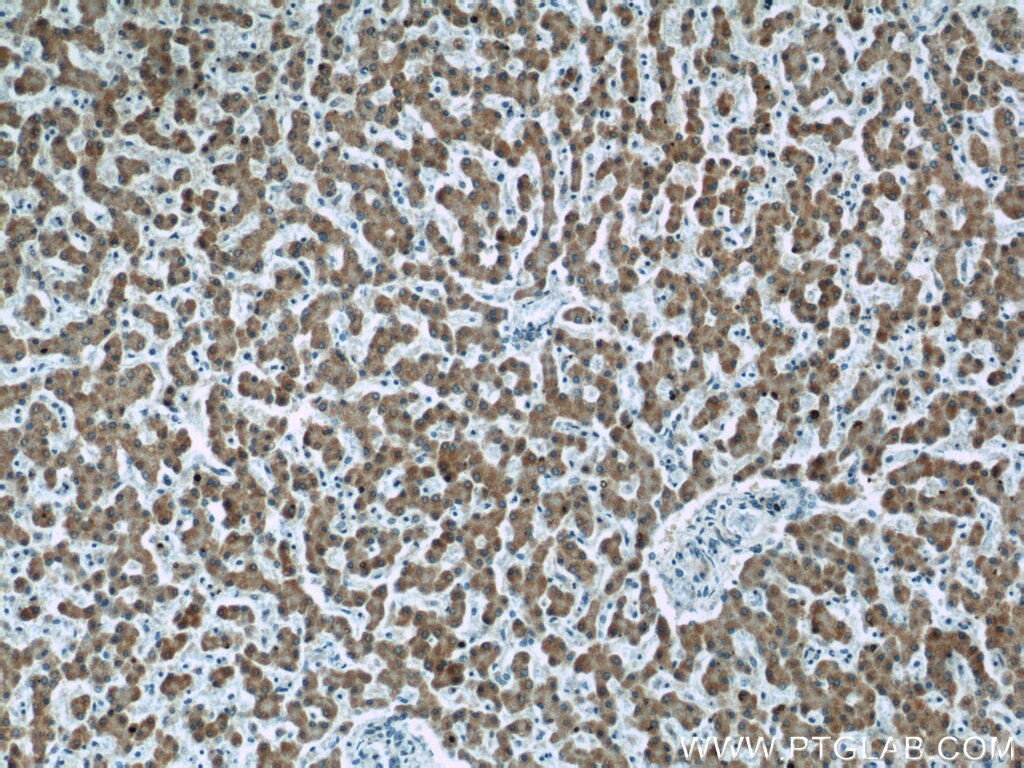
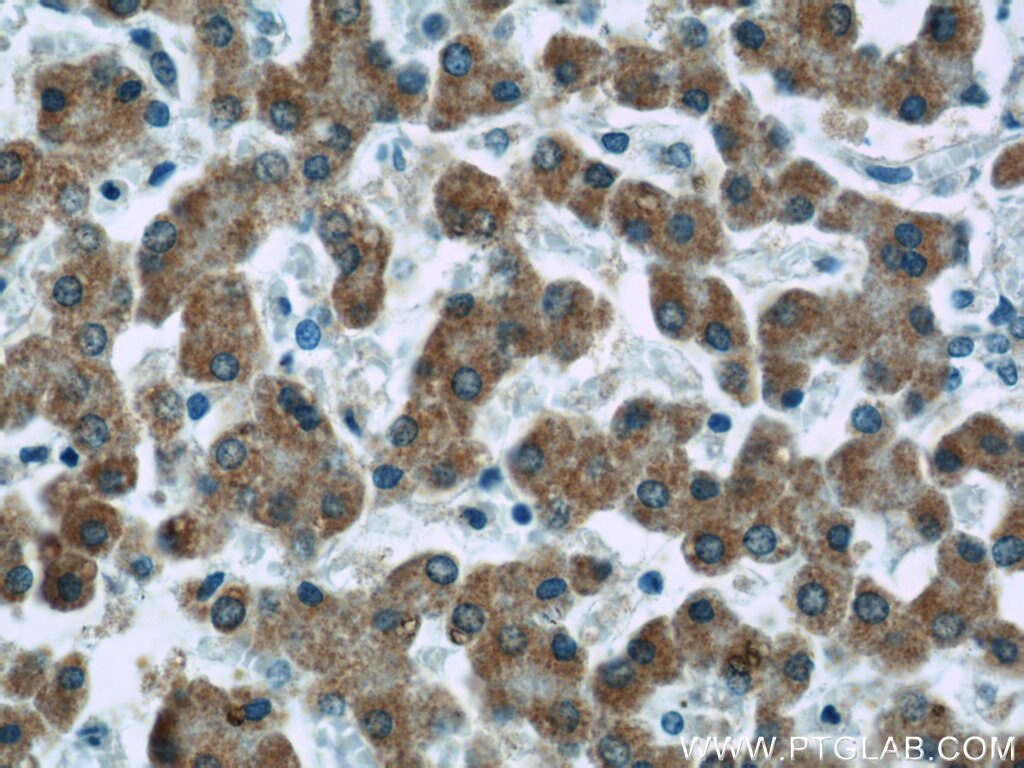
| Positive IHC detected in | human prostate cancer tissue, human liver tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
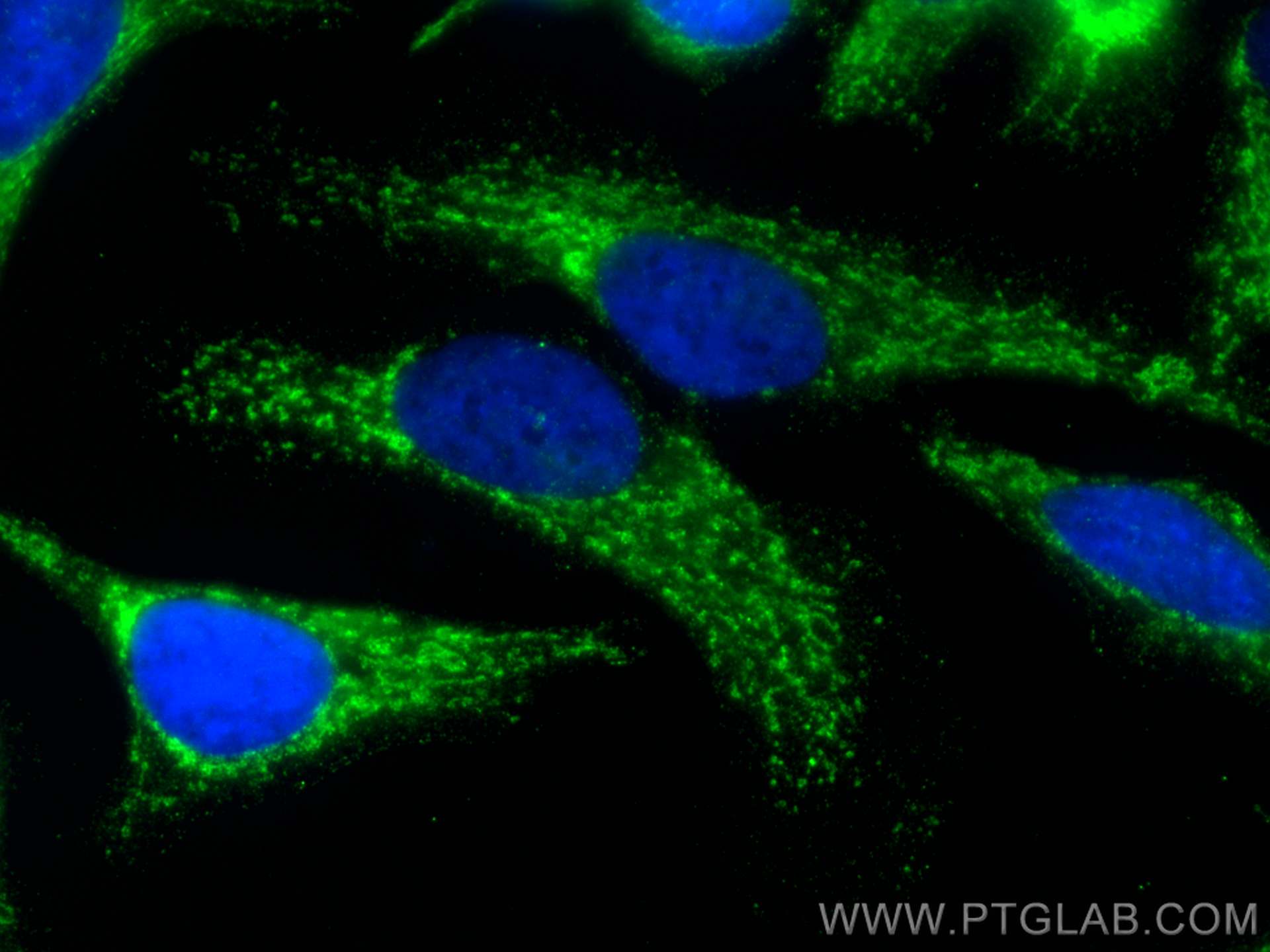
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HeLa cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:20000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:1000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:400-1:1600 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 2 publications below |
| WB | See 6 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
66117-1-Ig targets ECHS1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag16775 Product name: Recombinant human ECHS1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1-290 aa of BC008906 Sequence: MAALRVLLSCVRGPLRPPVRCPAWRPFASGANFEYIIAEKRGKNNTVGLIQLNRPKALNALCDGLIDELNQALKIFEEDPAVGAIVLTGGDKAFAAGADIKEMQNLSFQDCYSSKFLKHWDHLTQVKKPVIAAVNGYAFGGGCELAMMCDIIYAGEKAQFAQPEILIGTIPGAGGTQRLTRAVGKSLAMEMVLTGDRISAQDAKQAGLVSKICPVETLVEEAIQCAEKIASNSKIVVAMAKESVNAAFEMTLTEGSKLEKKLFYSTFATDDRKEGMTAFVEKRKANFKDQ Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | enoyl Coenzyme A hydratase, short chain, 1, mitochondrial |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 31 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 31 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC008906 |
| Gene Symbol | ECHS1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1892 |
| RRID | AB_2881516 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P30084 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Enoyl-coenzyme A hydratase (ECHS1) is a mitochondrial protein which catalyzes the hydration of 2-trans-enoyl-coenzyme A intermediates to L-3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A, playing key role in metabolism of fatty acids in mitochondria. ECHS1 is highly expressed in muscle, liver and fibroblasts. Altered expression of ECHS1 has been considered as a characteristic feature of mitochondria dysfunction. (23275097, 23235493)
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for ECHS1 antibody 66117-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for ECHS1 antibody 66117-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for ECHS1 antibody 66117-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for ECHS1 antibody 66117-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Proteomics Up-regulation of fatty acid oxidation in the ligament as a contributing factor of ankylosing spondylitis: A comparative proteomic study. | ||
Ann Clin Transl Neurol Deficiency of ECHS1 causes mitochondrial encephalopathy with cardiac involvement. | ||
FEBS Open Bio The role of SAMM50 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: from genetics to mechanisms. | ||
Cell Death Dis ECHS1, an interacting protein of LASP1, induces sphingolipid-metabolism imbalance to promote colorectal cancer progression by regulating ceramide glycosylation.
| ||
bioRxiv Valine and Inflammation Drive Epilepsy in a Mouse Model of ECHS1 Deficiency
| ||
J Cancer Knockdown of HOXD13 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Inhibited its Proliferation, Migration, and Influenced Fatty Acid Metabolism |