- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
CD206 Monoklonaler Antikörper
CD206 Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF-P, IP, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG2a
Getestete Reaktivität
human
Anwendung
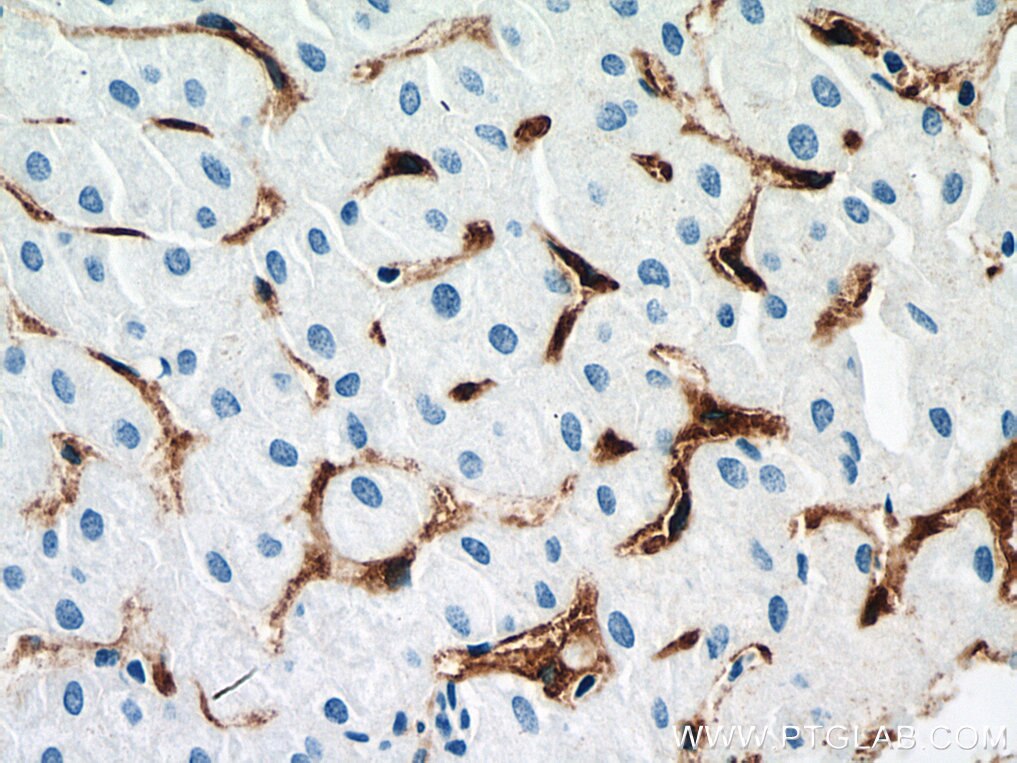
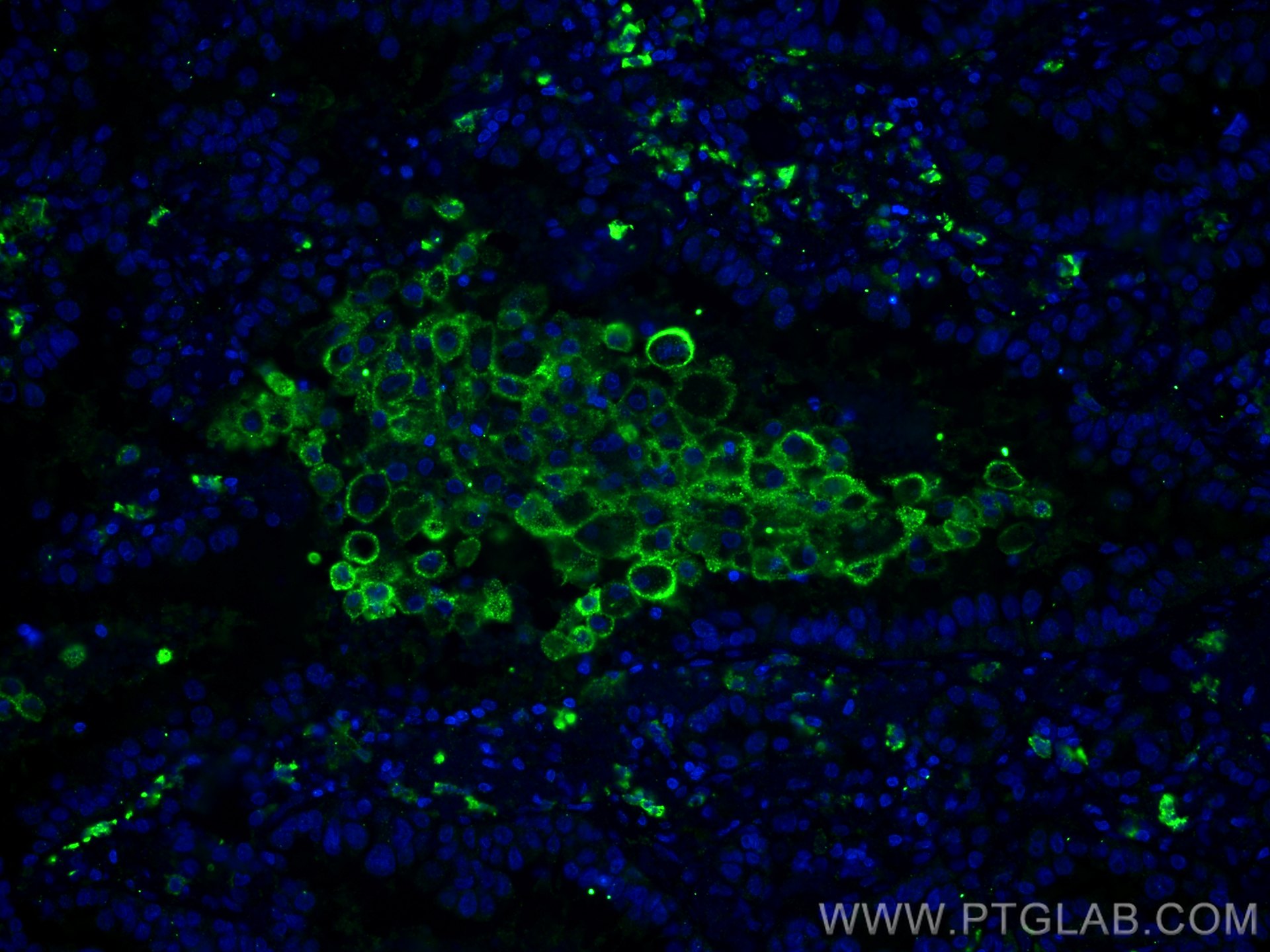
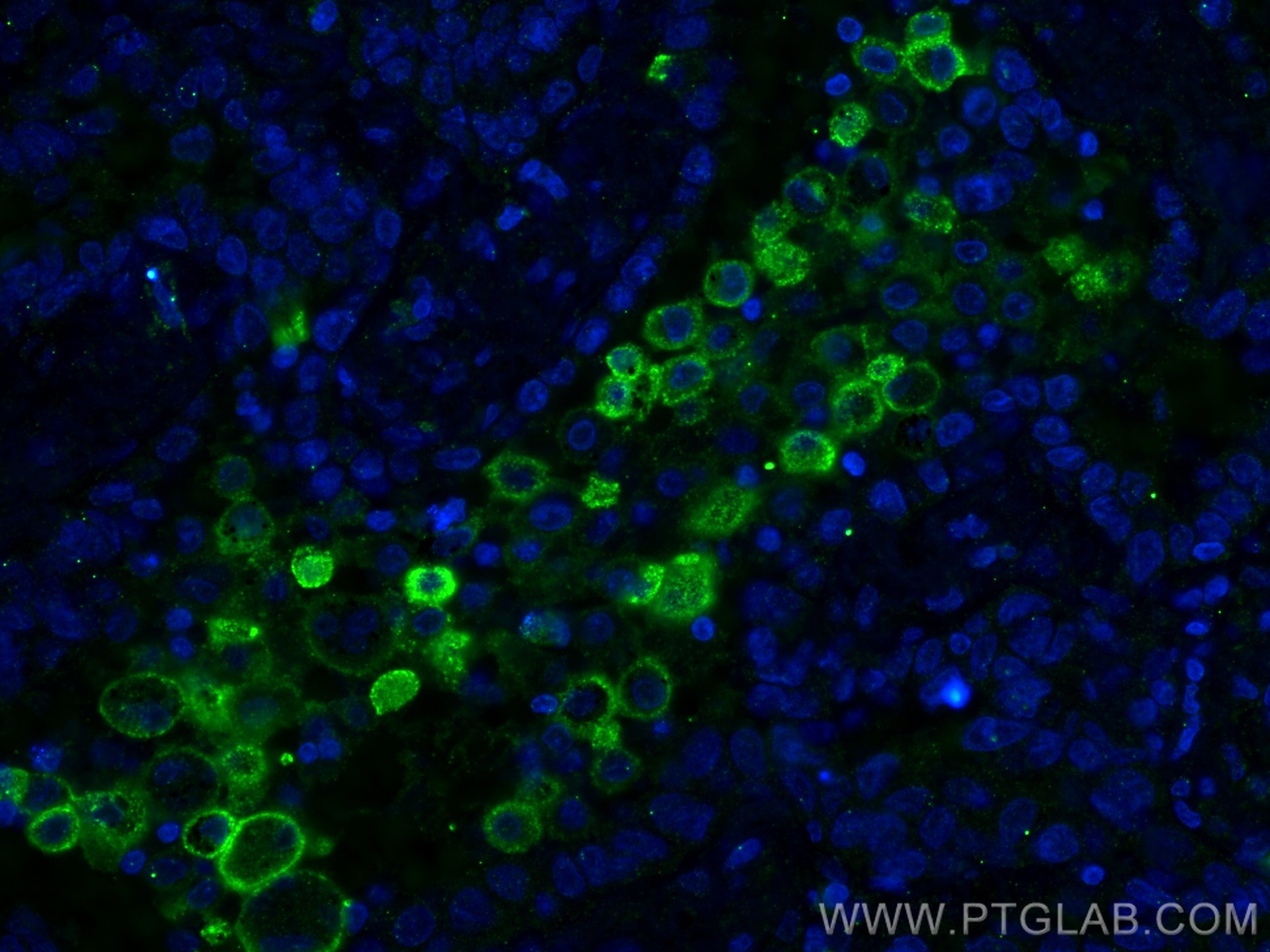
WB, IHC, IF-P, IP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
2A6A10
Kat-Nr. : 60143-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
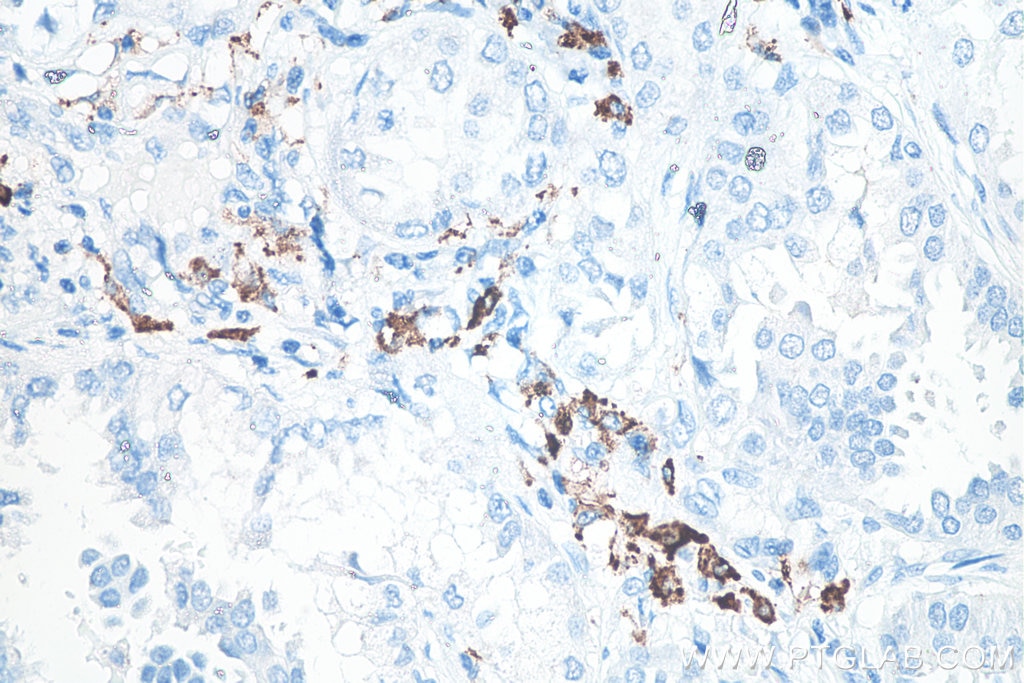
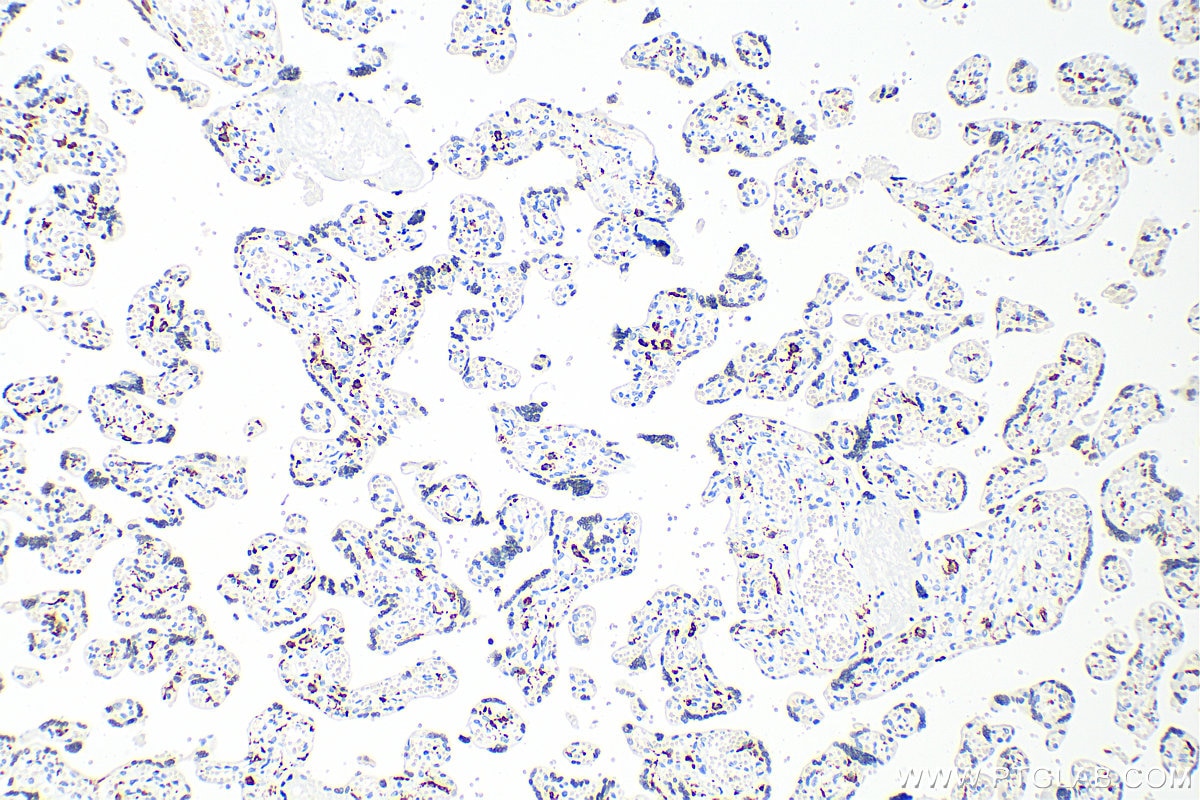
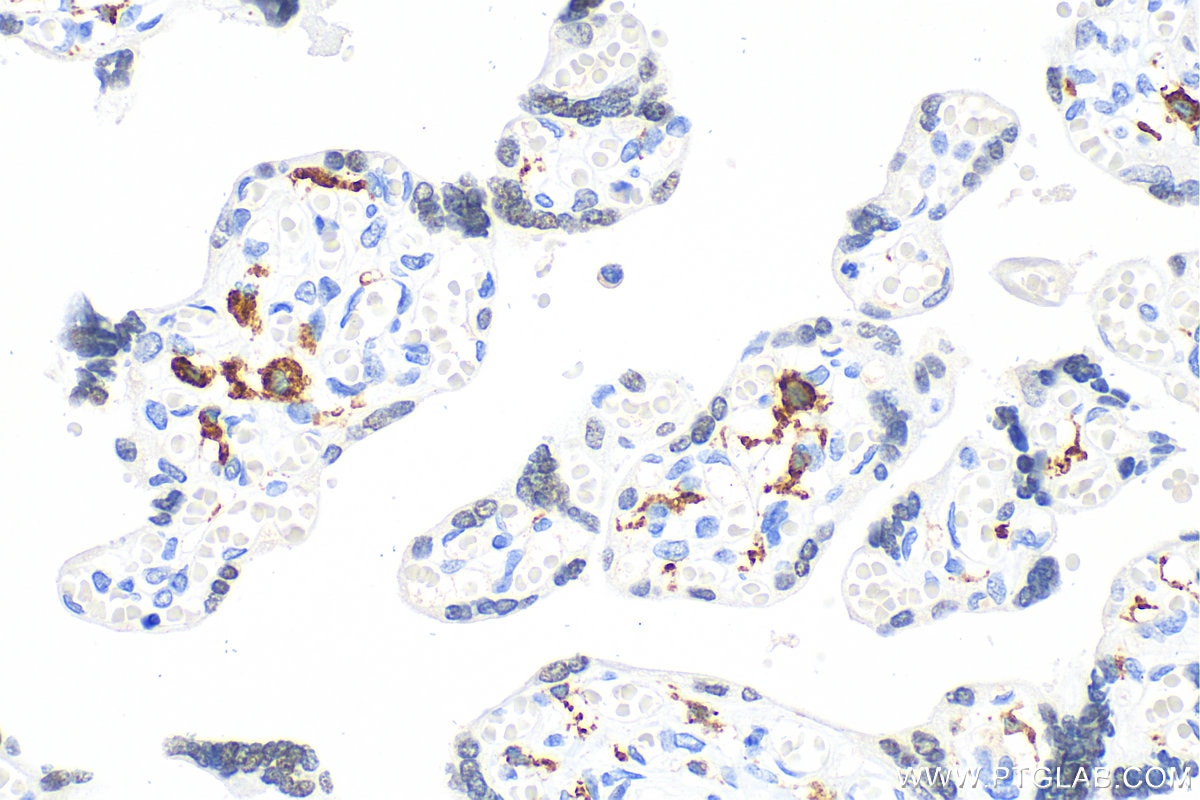
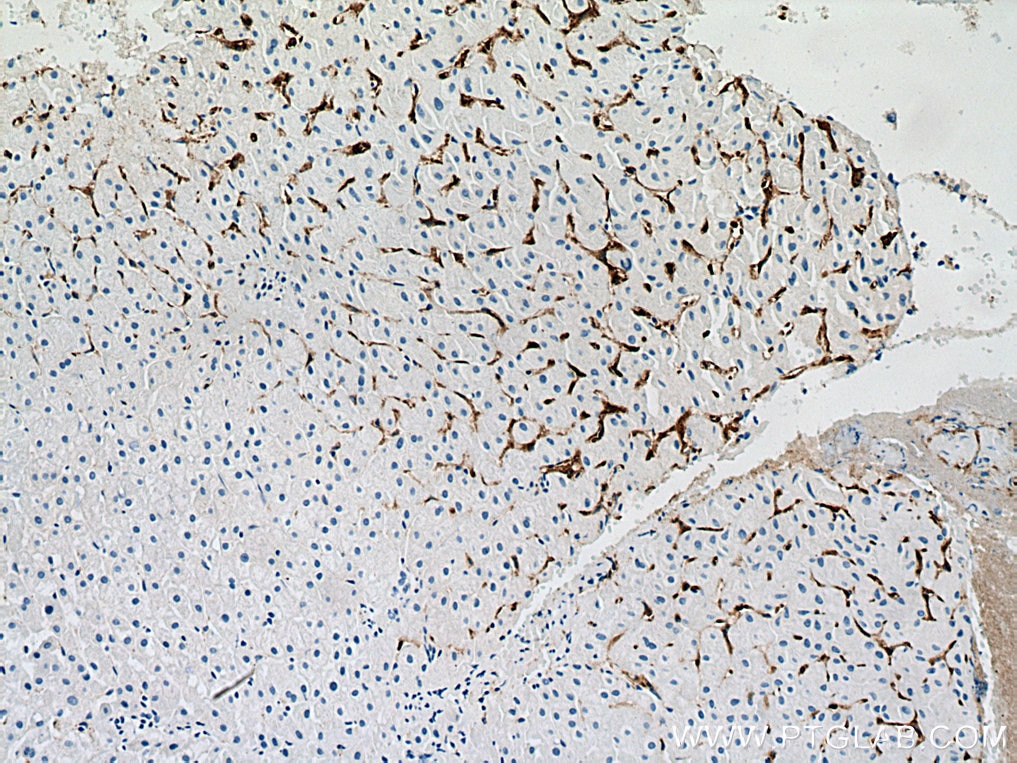
60143-1-PBS bindet in WB, IHC, IF-P, IP, ELISA CD206 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG2a |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Peptid |
| Vollständiger Name | mannose receptor, C type 1 |
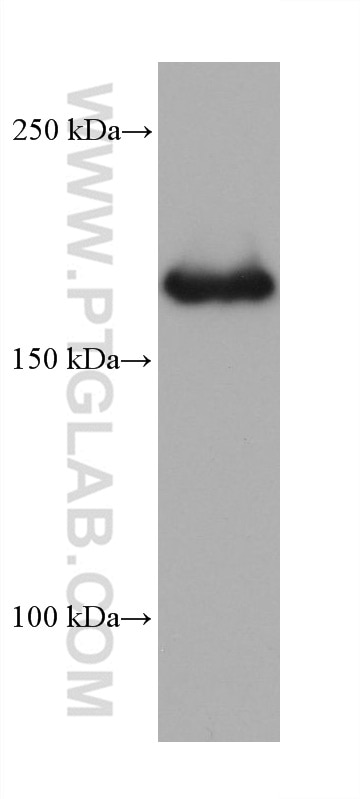
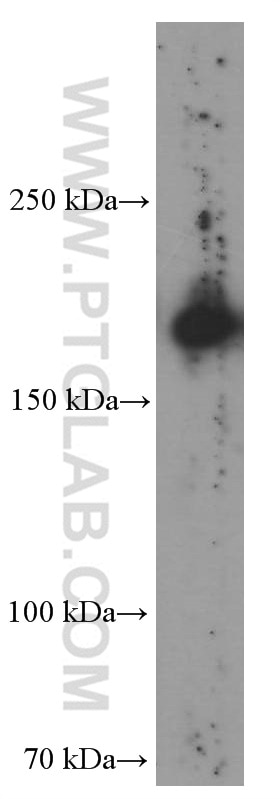
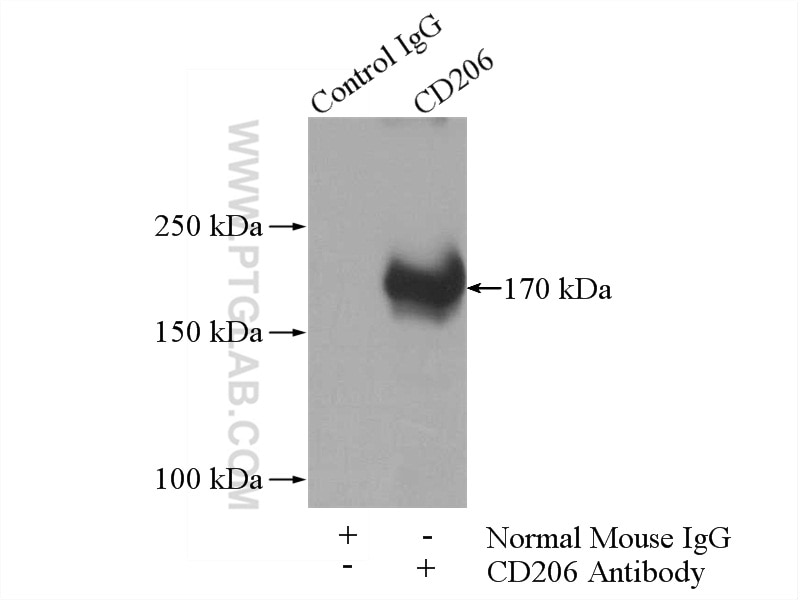
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 166 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 170 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | NM_002438 |
| Gene symbol | CD206 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4360 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-A-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Background
CD206 (macrophage mannose receptor 1) is a lectin-type endocytic receptor expressed on selected macrophages, dendritic cells, and non-vascular endothelium and plays a role in antigen processing and presentation, phagocytosis, and intracellular signaling.
1. What is the molecular weight of CD206?
The molecular size of full-length CD206 is 170-180 kDa, depending on the exact tissue-specific glycosylation pattern (PMID: 19427834). Additionally, CD206 can be cleaved off and a soluble form (sMR) lacking the tail, with a slightly lower molecular weight, can be released to the cell medium (PMID: 9722572).
2. What is the subcellular localization of CD206?
CD206 is a type I membrane protein composed of a large extracellular multidomain, a transmembrane domain, and a short cytoplasmic tail. It is present at the plasma membrane and in endosomes, as CD206 undergoes constant recycling between the plasma membrane and endosomal compartment.
3. Is CD206 post-translationally modified?
CD206 undergoes quite extensive post-translational modifications, predominantly N-linked glycosylation that affects ligand binding recognition and affinity (PMID: 22966131).
4. Can CD206 marker be used as a marker of M2 macrophages?
The activation of macrophages with various stimuli leads to their polarization into classical (M1) or alternatively activated (M2) subtypes spectrums and both subtypes differ in their regulatory and effector functions (PMID: 24669294). Pathogens and IFN-γ promote M1 polarization, while IL-4 released during parasite infections and allergen response promotes M2 polarization. Classically, the markers of M2 macrophages include CD206, as well as arginase-1 (ARG1; https://www.ptglab.com/products/ARG1-Antibody-16001-1-AP.htm), CD163 (https://www.ptglab.com/products/CD163-Antibody-16646-1-AP.htm), and thrombospondin 1 (TSP1/ THBS1; https://www.ptglab.com/products/TSP1-Antibody-18304-1-AP.htm).
5. How can you polarize macrophages into M2 direction?
One of the most commonly used methods is stimulation by the addition of IL-4 cytokine. We recommend using our animal-free human IL-4 (https://www.ptglab.com/products/recombinant-human-il-4.htm).