V5-Tag: Properties
V5-Tag: Properties, origin, specifications, antibodies & Nanobodies
V5-tag is a short peptide tag for detection and purification of proteins. The V5-tag can be fused/cloned to a recombinant protein and detected in ELISA, flow cytometry, immunoprecipitation, immunofluorescence, and Western blotting with antibodies and Nanobodies.
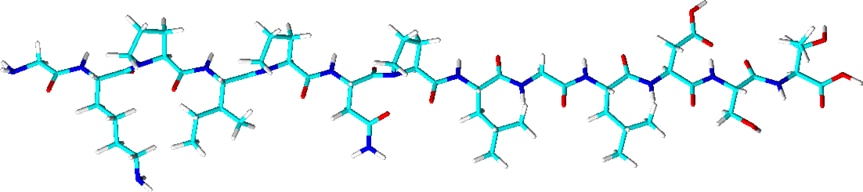
3D structure of V5 tag
Origin
The V5-tag derived from the P and V protein of the simian virus 5 (SV5, a paramyxovirus), amino acid residues 95 to 108 of RNA polymerase alpha subunit. First referenced in Hanke et al, Journal of General Virology 19921.
Properties
The V5-tag contains 14 amino acids (aa) and the sequence is GKPIPNPLLGLDST. There is also a shorter version with 9 aa (IPNPLLGLD) which is rarely used.
Size of V5-tag
Number of amino acids: 14
Molecular weight (MW): 1421.66 Da
Specifications of the V5-tag
Theoretical isoelectric point (pI): 5.84
Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu): 1
Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys): 1
V5 epitope tag sequences
V5-tag amino acid sequence:
GKPIPNPLLGLDST
V5-tag DNA sequence:
GGT AAG CCT ATC CCT AAC CCT CTC CTC GGT CTC GAT TCT ACG
Please note, the mentioned sequence is for mammals and insects. The sequence is not codon optimized for other organisms.
Applications
The most common applications of V5-tagged proteins are ELISA, flow cytometry, immunofluorescence (IF), immunoprecipitation (IP), protein purification, and Western blotting.
V5-tag vs. Flag-tag
Here is a comparison of V5-tag and Flag-tag
|
|
V5-tag |
Flag-tag |
|
Origin |
P and V protein of the simian virus 5 |
artificial design |
|
3D Structure |
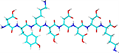 |
|
|
Amino acid sequence |
GKPIPNPLLGLDST |
DYKDDDDK |
|
Number of amino acids |
14 |
8 |
|
Molecular weight (in Da) |
1421.66 |
1012.98 |
|
Theoretical isoelectric point (pI) |
5.84 |
3.97 |
|
Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu) |
1 |
5 |
|
Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys) |
1 |
2 |
V5-tag vs. HA-tag
Here is a comparison of V5-tag and HA-tag
|
|
V5-tag |
HA-tag |
|
Origin |
P and V protein of the simian virus 5 |
Human influenza hemagglutinin (HA)is derived from human influenza virus |
|
3D Structure |
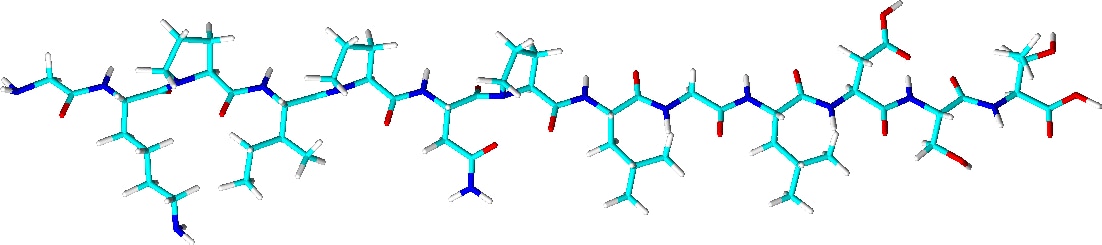 |
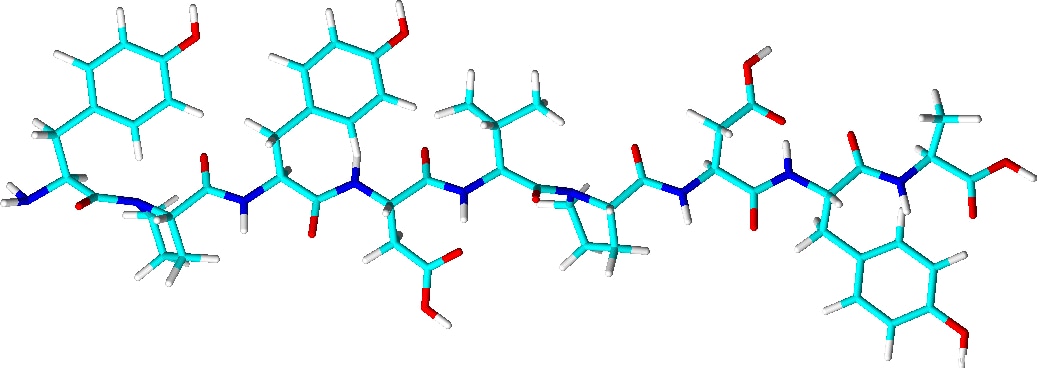 |
|
Amino acid sequence |
GKPIPNPLLGLDST |
YPYDVPDYA |
|
Number of amino acids |
14 |
9 |
|
Molecular weight (in Da) |
1421.66 |
1102.17 |
|
Theoretical isoelectric point (pI) |
5.84 |
3.56 |
|
Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu) |
1 |
2 |
|
Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys) |
1 |
0 |
How to elute V5-tag?
Elution of V5-tagged proteins is normally performed by glycine or citric acid or by competitive elution with V5-peptide (GKPIPNPLLGLDST).
V5-tag plasmids
There are commercially available plasmids for expression with V5-tag for mammalian cells, Drosophila, etc. from ThermoFisher and Merck (Sigma Aldrich).
V5-tag antibodies and Nanobodies
There are different polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies and one Nanobody against V5 commercially available. For immunoprecipitation, ChromoTek V5-Trap®, an anti-V5-tag Nanobody conjugated to beads, is recommended. Nanobodies have a lower background in IP compared to antibodies since. No dissociating heavy and light antibody chains are released from the beads and these chains don't show up on SDS-Page and WB.
You can request a free test sample of the V5-Trap®.
V5-tag beads
ChromoTek offers V5 Nanobodies conjugated to beads for immunoprecipitation and unconjugated V5 Nanobodies/ VHHs:
V5-Trap® Agarose: anti-V5 Nanobody conjugated to agarose beads
V5-Trap® Magnetic Agarose: anti-V5 Nanobody conjugated to magnetic agarose beads
V5-Trap® Magnetic Particles M-270: anti-V5 Nanobody conjugated to magnetic particles
V5 VHH: anti-V5 Nanobody, unconjugated
Reference
- Tomas Hanke, Paul Szawlowski and Richard E. Randall; Construction of solid matrix-antibody-antigen complexes containing simian immunodeficiency virus p27 using tag-specific monoclonal antibody and tag-linked antigen, Journal of General Virology (1992), 73, 653-660
Related Content
How to immunoprecipitate Flag®-tagged proteins
Immunoprecipitation without additional band
How to conduct a Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
Which beads should I use for my immunoprecipitation?
Advantages and limitations of different antibody formats in immunoprecipitation
8 Top Tips For Immunoprecipitation
Learn how to save precious hours on your IP, IF, and western blotting experiments
Support
Request a Free Nano-Trap Sample
Nano-Trap system provides fast, reliable, and effective immunoprecipitation of fusion proteins. More than 3,000 peer-reviewed articles have already been published using ChromoTek's Nano-Traps.