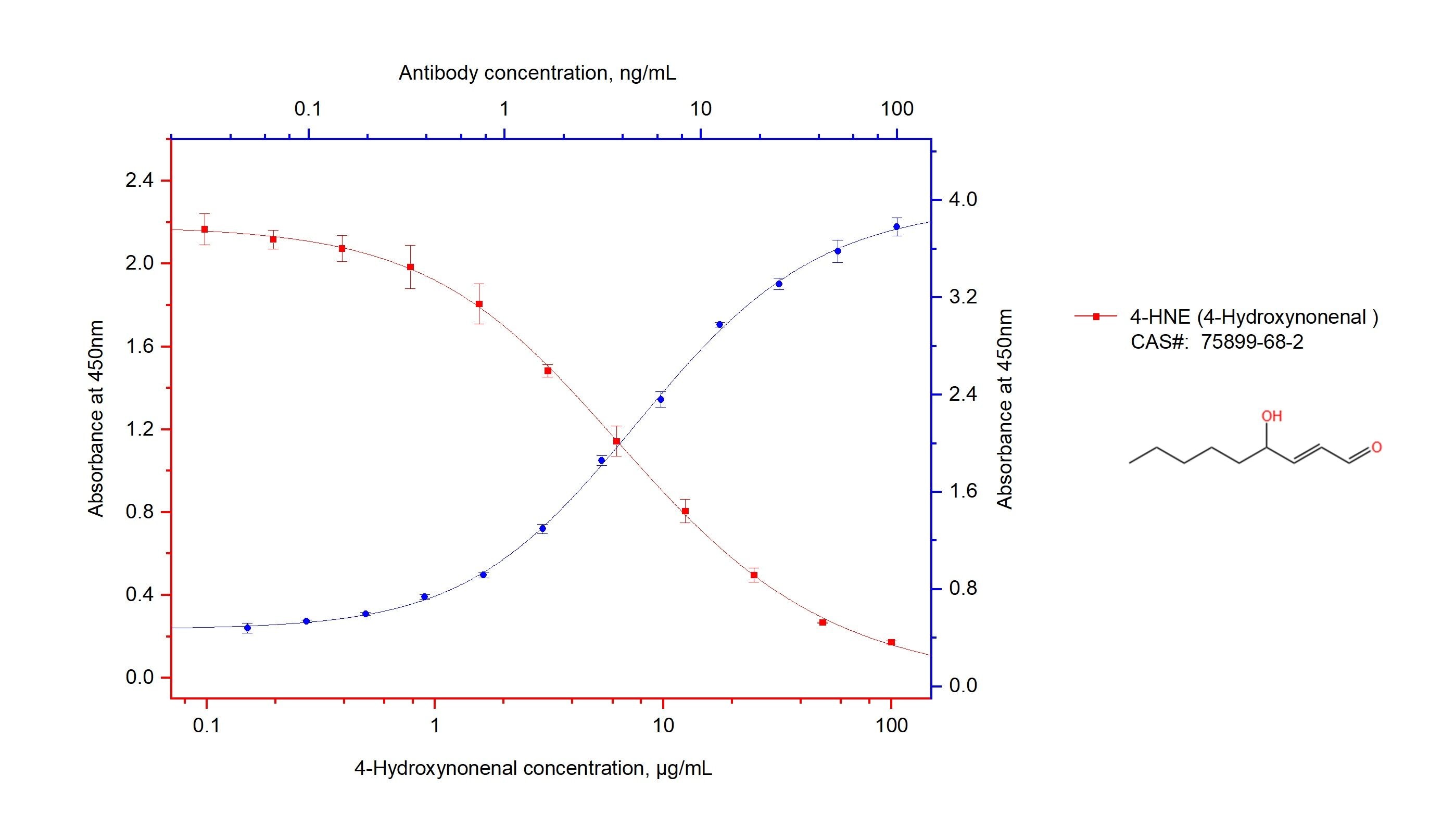
Product Information
68538-1-PBS targets 4-Hydroxynonenal in ELISA, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with 4-hydroxynonenal, chemical compound samples.
| Tested Reactivity | 4-hydroxynonenal, chemical compound |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
PTG Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | 4-Hydroxynonenal |
| Gene Symbol | |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
4-Hydroxynonenal is a uremic toxin. Uremic toxins can be subdivided into three major groups based upon their chemical and physical characteristics: 1) small, water-soluble, non-protein-bound compounds, such as urea; 2) small, lipid-soluble and/or protein-bound compounds, such as the phenols and 3) larger so-called middle-molecules, such as beta2-microglobulin. 4-Hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) is a major aldehydic product of ω-6-unsaturated fatty acid peroxidation. It is considered a lipid peroxidation specific marker. 4-HNE has been found to induce differentiation and inhibit proliferation of HL-60 human leukemic cells. It has also been found to induce murine alveolar macrophage cell death. 4-HNE has been shown to inhibit State 3 respiration, causing a transient cytosolic Ca2+ increase. In addition, it irreversibly inhibits Na+-K+-ATPase activity.